Method for testing content of main components in Rhodiola rosea extracts
A determination method and technology of Rhodiola, applied in the directions of measuring device, material separation, analysis of materials, etc., can solve the problems of complex plant sources of Rhodiola, large differences in the composition of Rhodiola, and different cultivars, and achieve quality control. Rigorous, reducing the number of experiments, the effect of clear ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] [Example 1] Preparation of Rhodiola Rosea Extract
[0056] Take 10kg of Rhodiola rosea (Rhodiola rosea content ≥ 1.0%) medicinal material produced in Tibet, decoct it with 8 times the weight of water for 2 hours and take the filtrate for the first time; Filtrate, the two filtrates were combined and concentrated under reduced pressure to 10L to obtain concentrate I. Purify the concentrated solution I with a macroporous resin, the loading ratio is 1g rhodiola medicinal material: 2g resin; then first elute with water, discard the water, then elute with 20% ethanol, collect 20% ethanol for elution liquid. Concentrate the eluate to a density of 1.05-1.10 to obtain Concentrate II. Then the concentrate II was precipitated with 80% ethanol for 24-32 hours to obtain a supernatant, and the precipitate was discarded. Concentrate, dry and pulverize the alcohol precipitation supernatant to obtain the rhodiola rosea extract.
Embodiment 2
[0057] [Example 2] The detection conditions for screening the content of gallic acid, salidroside, tyrosol and p-coumaric acid in the Rhodiola rosea extract.
[0058] Preparation of Rhodiola rosea extract: prepared according to the method described in Example 1, the batch number is 100702.
[0059] Screening of chromatographic conditions
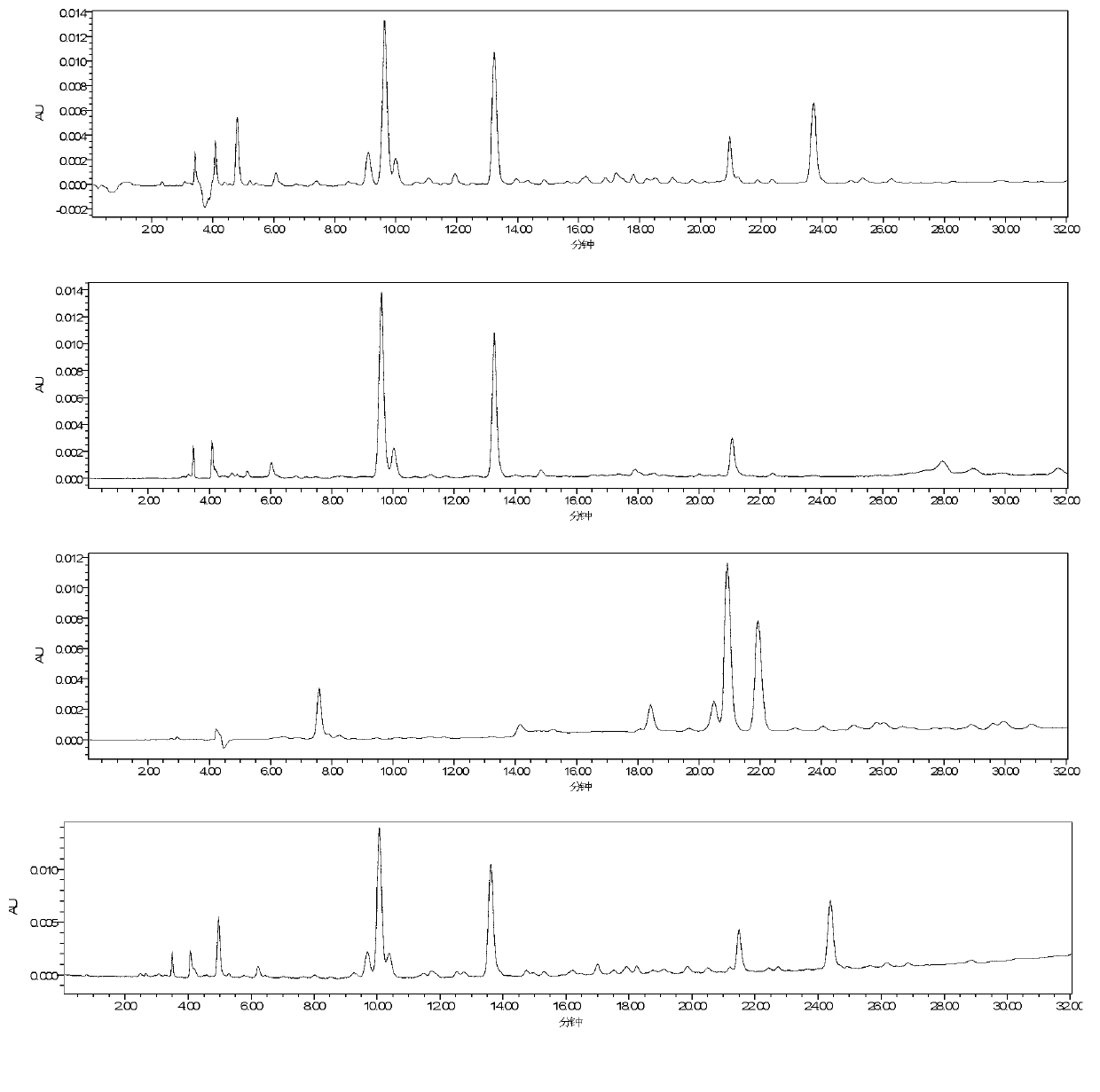
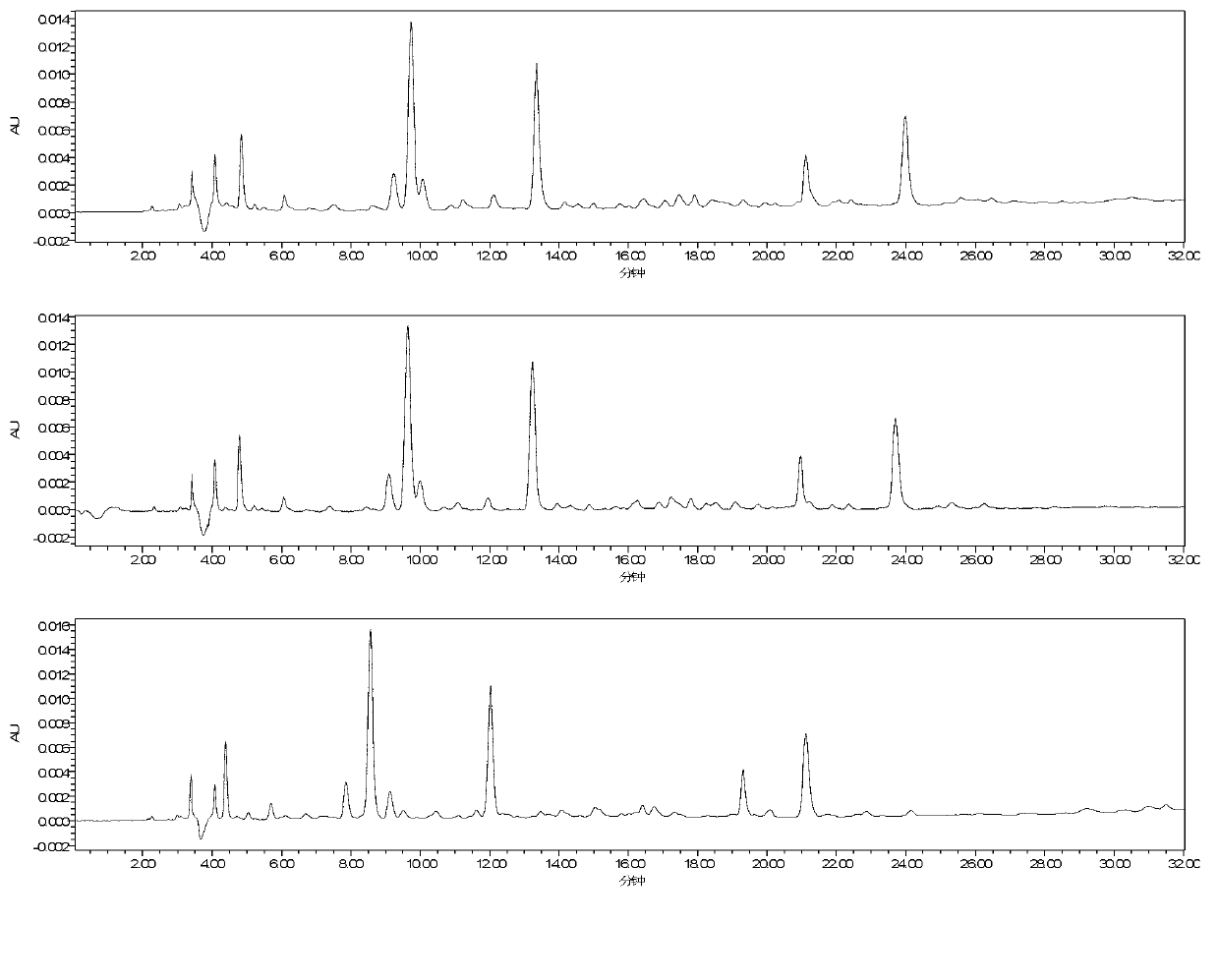
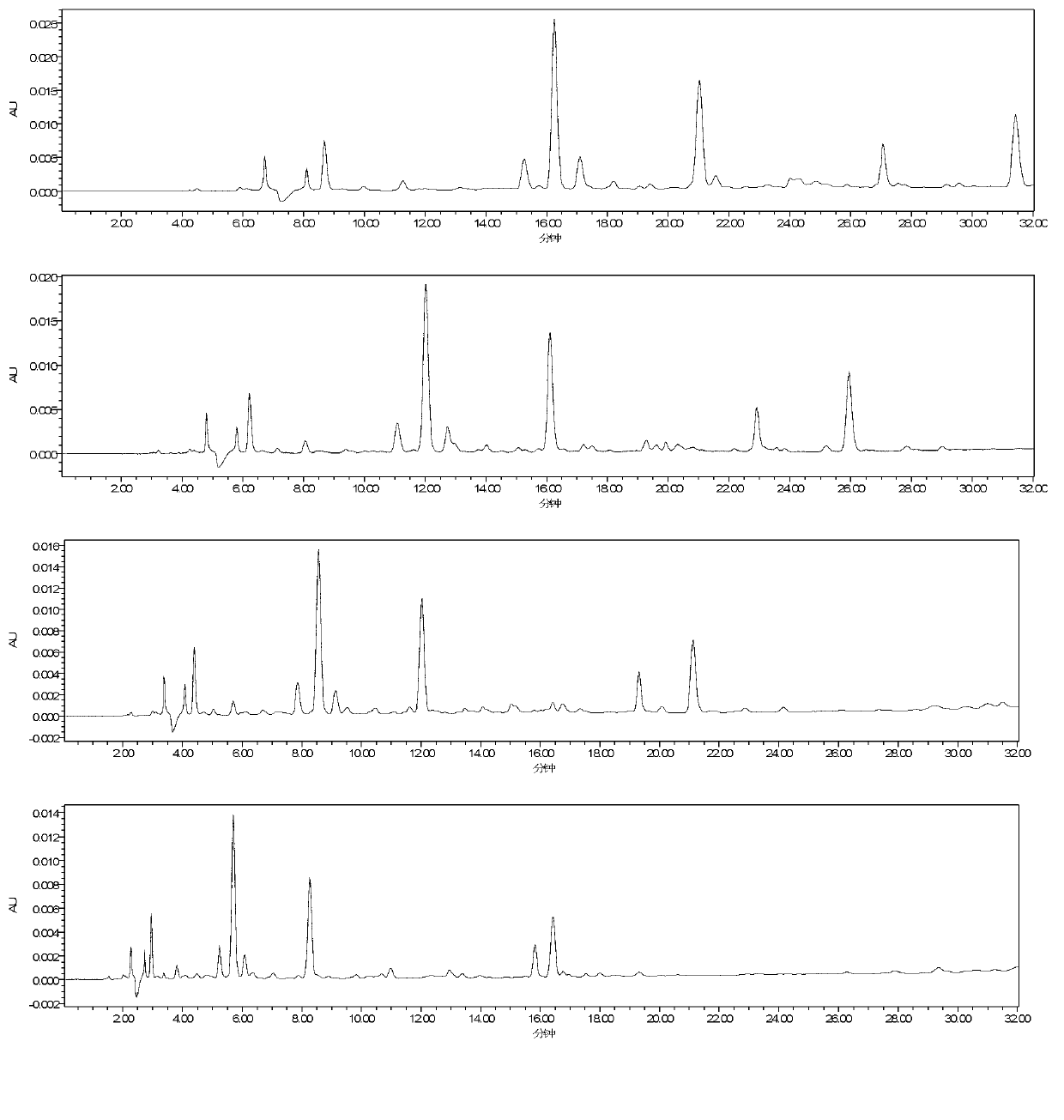
[0060] Investigated mobile phase systems such as acetonitrile-water, acetonitrile-0.1% phosphoric acid, acetonitrile-0.3% glacial acetic acid, methanol-water, methanol-0.1% phosphoric acid, and the results are as follows: figure 1 As shown, through test comparison, it is finally determined that the content determination of the above four components is completed by acetonitrile-0.3% glacial acetic acid gradient elution.
[0061] Investigated different column temperatures of 25°C, 30°C, and 40°C, the results are as follows figure 2 shown; and the influence of different flow rates of 0.5, 0.7, 1.0, 1.5mL / min on the separation of each compone...
Embodiment 3
[0069] [Example 3] Content detection of gallic acid, salidroside, tyrosol and p-coumaric acid in Rhodiola rosea extract Chromatographic conditions and system adaptability:
[0070] Column is Phenomenex Luna C 18 Column (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm), the mobile phase is acetonitrile (A)-0.3% glacial acetic acid solution (B), the elution program is: 0~5min, 9%A; 5~30min, 9%~25%A , 30~35min, 25%~40%A; column temperature: 40℃; volume flow: 0.7mL min -1 ; Detection wavelength: 275nm, 308nm; Injection volume 10μl. Take the solution of the test product and inject it under the above-mentioned chromatographic conditions for analysis. The resolution of each component to be tested and the adjacent peak in the sample is greater than 1.5, the tailing factor is between 0.95 and 1.05, and the number of plates is calculated according to Rhodiola rosea. Glycoside calculations are greater than 20,000. Chromatograms such as Figure 8 shown.
[0071] Preparation of reference solution
[0072] Take app...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com