Method for screening multifunctional bacteria for degrading organophosphorus pesticides
A technology of organophosphorus pesticides and screening methods, which is applied in the methods of using microorganisms, methods based on microorganisms, bacteria, etc., can solve problems such as no strain screening methods involved, and achieve the effects of easy survival and reproduction, simple operation, and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0069] Preparation of medium:
[0070] 1) Preparation of LB liquid medium (pH7.0): mix 10g of tryptone, 5g of yeast extract, 10g of sodium chloride and double distilled water, and adjust the volume to 1000mL with double distilled water, adjust the pH with sodium hydroxide When the value reaches 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes after aliquoting.
[0071] 2) Preparation of LB solid medium (pH7.0): mix 10g tryptone, 5g yeast extract, 10g sodium chloride, 17-20g agar powder and double distilled water, and dilute to 1000mL with double distilled water, Adjust the pH value to 7.0 with sodium hydroxide, and sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes after aliquoting.
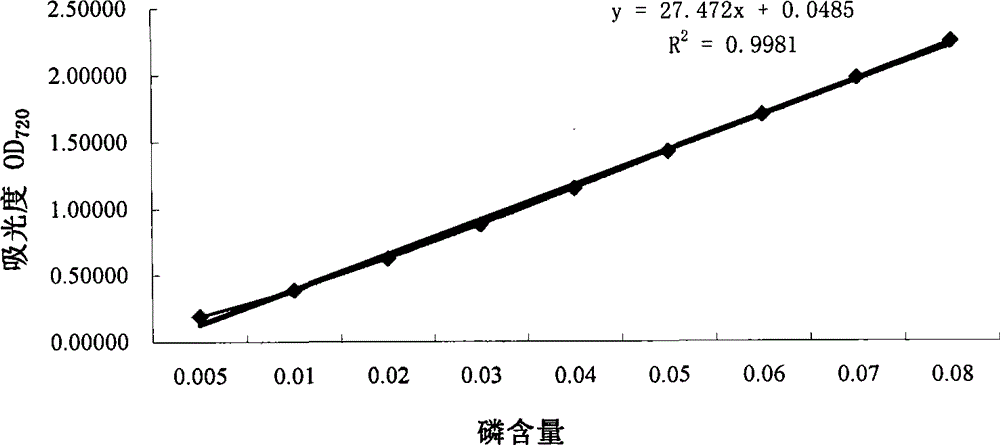
[0072] 3) Preparation of improved MM medium: 40mmol / L 3-(N-morpholino) sodium propanesulfonate (adjust pH 7.4 with KOH), 2mmo / L K 3 PO 4 (pH7.0), glucose 2% (W / V), (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2.0g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.2g / L, sodium citrate 2H 2 O1.0g / L, potassium glutamate 1.0g / L, tryptophan 8.0mg / L, 3.0nmol / L ammonium molybdate, 4...
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Degradation of glyphosate by siderophilic bacteria Bacillus subtilis Bs-15
[0083] 1. Disease prevention and growth promotion of siderophilic bacteria B. subtilis Bs-15
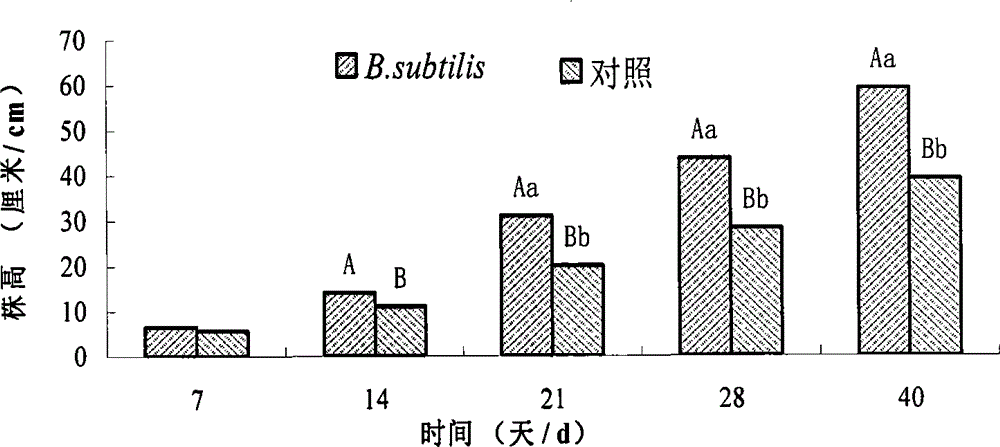
[0084] B. subtilis Bs-15 (originally numbered as CAS15) is screened from the rhizosphere soil of rubber trees, and has strong siderophilic ability. Plant pathogens such as base rot, mango anthracnose, and Pythium melon fruit have a strong inhibitory effect [Yu Xianmei, Zheng Fucong, Lin Chao, et al. Isolation and identification of soil siderophilic antagonistic bacterium CAS15. Journal of Plant Protection, 2009, 36(2): 129-135].
[0085] The pot experiment was used to study the biocontrol effect of siderophilic bacteria B. subtilis Bs-15 on sweet pepper wilt and the promotion effect on sweet pepper growth. This part has been published [Yu Xianmei, Zhou Guangfang, Xin Li. The conditions for Bacillus subtilis Bs-15 to produce siderophore and its effect on disease prevention and growth pro...
Embodiment 2
[0179] Example 2: Isolation and identification of siderophilic bacteria CAS17 and degradation of chlorpyrifos
[0180] 1. Isolation and screening of strain CAS17
[0181] The rhizosphere soil of fruit trees such as apples, pears, and walnuts was collected, brought back to the laboratory, and sieved through a 20-mesh sieve after natural air-drying.
[0182] Take 1g of soil sample, add 50mL of sterilized distilled water, shake and culture at room temperature 150r / min for 2h, stand still to get supernatant, and separate and screen by CAS detection plate method and plate dilution method. According to the presence and size of the orange halo, the strains with strong siderophilic ability were screened out. CAS17 has a strong siderophilic ability and produces a larger orange halo ( Figure 13 ). Store at 4°C after purification.
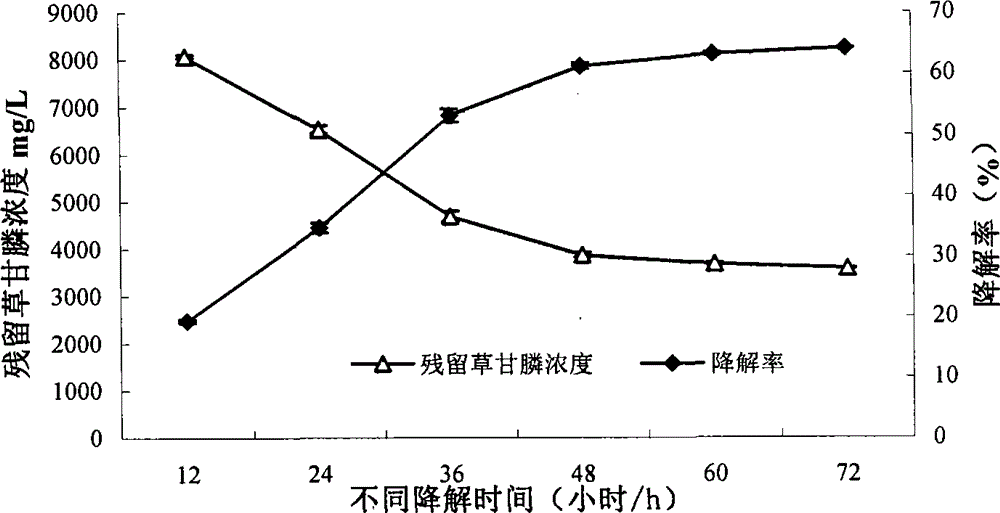
[0183] 2. The domestication of strain CAS17 to chlorpyrifos
[0184] Inoculate strain CAS17 in LB liquid medium containing chlorpyrifos (concentration:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com