Molten sample preparation method of molybdenum, manganese, vanadium or chromium iron alloy sample for X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy
A technology of ray fluorescence spectroscopy and ferrochromium alloy, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitability for mass production inspection and analysis, corrosion of precious platinum yellow crucibles, affecting the sufficiency of oxidation, etc., and achieves elimination of mineral effects and particle size. effect, the wall hanging operation is cumbersome and strict, and the effect of easy demoulding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
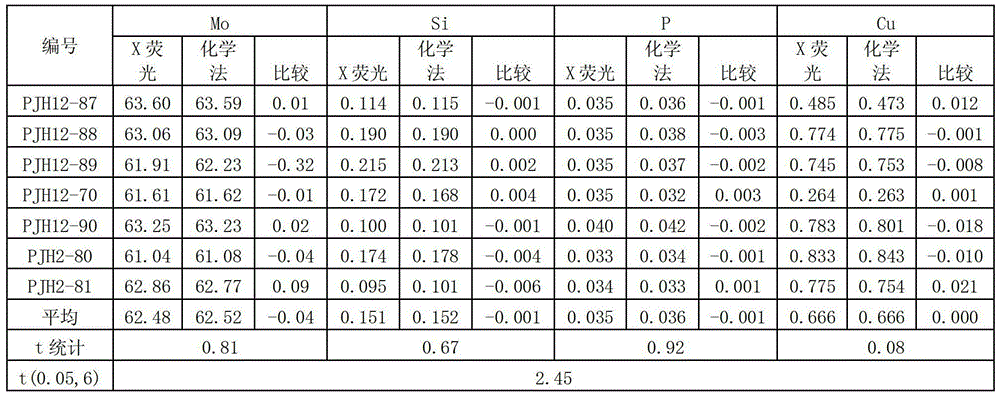
[0030] Embodiment 1 Preparation of ferromolybdenum glass frit
[0031] 1. Pre-oxidation of samples
[0032]Weigh 0.1g ± 0.1mg ferromolybdenum sample, place it in a conical filter paper filled with 2.0000g lithium tetraborate, 1.0000g lithium carbonate, 0.5000 vanadium pentoxide mixed flux, stir the sample evenly, wrap it into a spherical shape, Put it into a graphite-bottomed crucible, place it in a high-temperature furnace at 400°C, leave a 15mm gap in the furnace door, gradually raise the temperature to 850°C-900°C, melt for 15 minutes, take it out, and cool it down.
[0033] 2. Preparation of glass frits
[0034] Take out the molten ball and sweep away the graphite powder, place it in a platinum yellow crucible filled with 4.0000g of lithium tetraborate, and add 0.4mL of 300g / L potassium iodide solution. Melt at 1120±20°C for 15 minutes, take it out, expose the bottom of the crucible and rotate to remove air bubbles, shake well, then melt at 1120±20°C for 15 minutes, take...
Embodiment 2
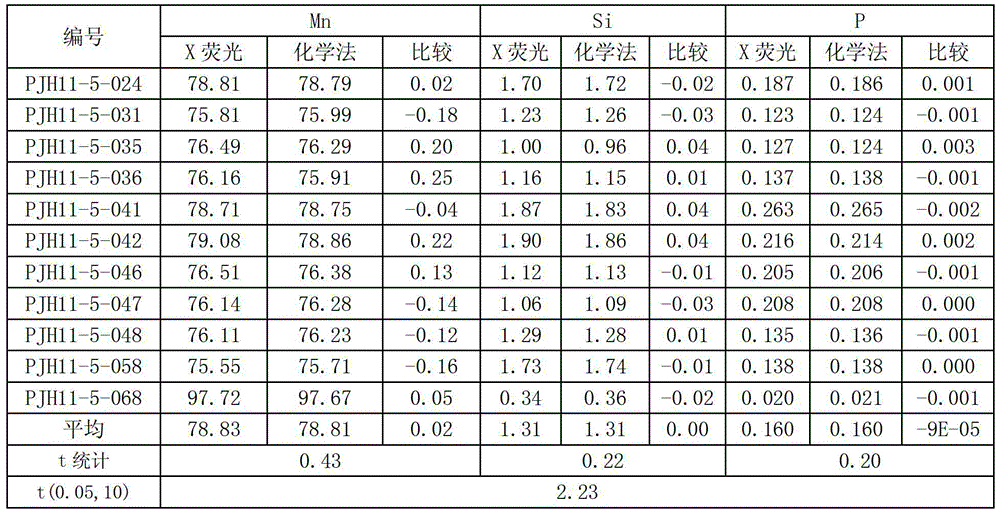
[0035] The preparation of embodiment ferromanganese glass frit
[0036] 1. Pre-oxidation of samples
[0037] Weigh 0.1g ± 0.1mg ferromanganese sample, place it in a conical filter paper filled with 2.0000g lithium tetraborate, 1.0000g lithium carbonate, 0.5000 vanadium pentoxide mixed flux, stir the sample evenly, wrap it into a ball, Put it into a graphite-bottomed crucible, place it in a high-temperature furnace at 400°C, leave a 15mm gap in the furnace door, gradually raise the temperature to 850°C-900°C, melt for 15 minutes, take it out, and cool it down.
[0038] 2. Preparation of glass frits
[0039] Take out the molten ball and sweep away the graphite powder, place it in a platinum crucible filled with 4.0000g of lithium tetraborate, and add 0.5mL of 200g / L lithium bromide. Melt at 1120±20°C for 15 minutes, take it out, expose the bottom of the crucible and rotate to remove air bubbles, shake well, then melt at 1120±20°C for 15 minutes, take it out, expose the bottom ...
Embodiment 3
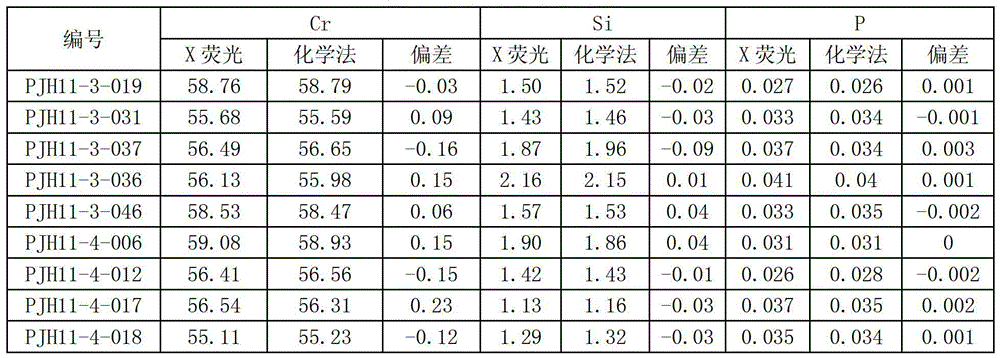
[0040] The preparation of embodiment trichromium ferroglass frit
[0041] 1. Pre-oxidation of samples
[0042] Weigh 0.1g ± 0.1mg ferrochrome sample, place it in conical filter paper filled with 2.0000g lithium tetraborate, 1.0000g lithium carbonate, 1.0000g lithium metaborate, 0.5000g sodium nitrate mixed flux, stir the sample evenly, Wrap it into a spherical shape, put it into a graphite-bottomed crucible, place it in a high-temperature furnace at 400°C, leave a 15mm gap in the furnace door, gradually heat up to 850°C-900°C, melt for 15 minutes, take it out, and cool it down.
[0043] 2. Preparation of glass frits
[0044] Take out the molten ball and sweep away the graphite powder, place it in a platinum yellow crucible filled with 2.0000g of lithium tetraborate and 2.0000g of lithium metaborate, and add 0.4mL of 300g / L potassium iodide. Melt at 1120±20°C for 15 minutes, take it out, expose the bottom of the crucible and rotate to remove air bubbles, shake well, then melt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com