Method for removing by-product in a palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction in situ
A coupling reaction, palladium-catalyzed technology, used in organic chemistry methods, chemical instruments and methods, purification/separation/stabilization of organic compounds, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of reducing concentration, reducing precipitation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
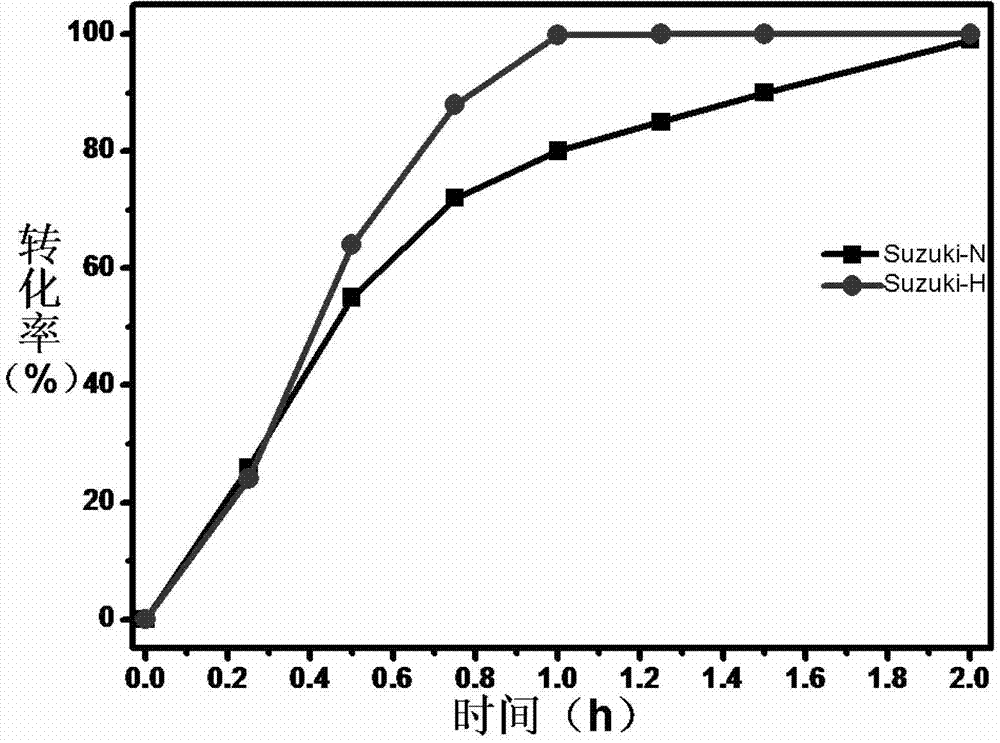
[0027] Embodiment 1, remove by product in the Suzuki reaction
[0028] Two reaction systems were prepared: 5 mmol of iodobenzene and 10 mmol of phenylboronic acid were dissolved in 50 mL of toluene, 0.1 g of 5 wt % Pd / C catalyst was added, and the acid-binding agent was triethylamine.
[0029] In order to illustrate the impact of the inventive method on the Suzuki reaction, one part does not add any substance, which is recorded as the Suzuki-N system; the other part adds 2g of water content and is 80% wet activated carbon solid powder, which is recorded as the Suzuki-H system , in this system, the addition amount of wet activated carbon solid powder is 1 time of the total mass of iodobenzene and phenylboronic acid. Subsequently, the temperature of the two reaction systems was raised to 80° C., and 10 mmol of triethylamine was added to start the reaction. Sampling was performed at intervals of 15 minutes, and the conversion rate was analyzed by Shimadzu 10A-VP-PLUS liquid chrom...
Embodiment 2
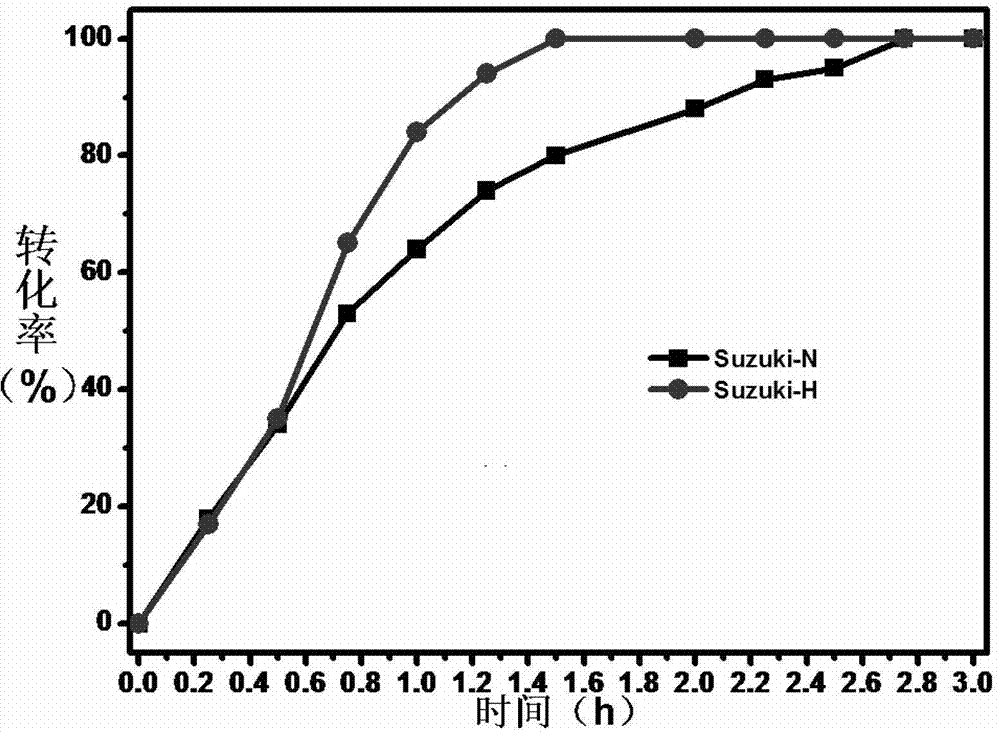
[0031] Embodiment 2, remove the by product in the Suzuki reaction
[0032] Two reaction systems were prepared: 5 mmol of iodobenzene and 10 mmol of phenylboronic acid were dissolved in 50 ml of chloroform, and 0.1 g of 5 wt % Pd / C catalyst was added, and the acid-binding agent was ethylenediamine.
[0033] In order to illustrate the impact of the inventive method on the Suzuki reaction, one part does not add any substance, which is recorded as the Suzuki-N system; another part of the porous silicon oxide that adds 2g of water content is 100%, and is recorded as the Suzuki-H system. In the system, the amount of porous silicon oxide added is 1 time of the total mass of iodobenzene and phenylboronic acid. Subsequently, the temperature of the two reaction systems was raised to 60° C., and 10 mmol of triethylamine was added to start the reaction. Sampling was performed at intervals of 15 minutes. The conversion rate was analyzed by Shimadzu 10A-VP-PLUS liquid chromatography.
[00...
Embodiment 3
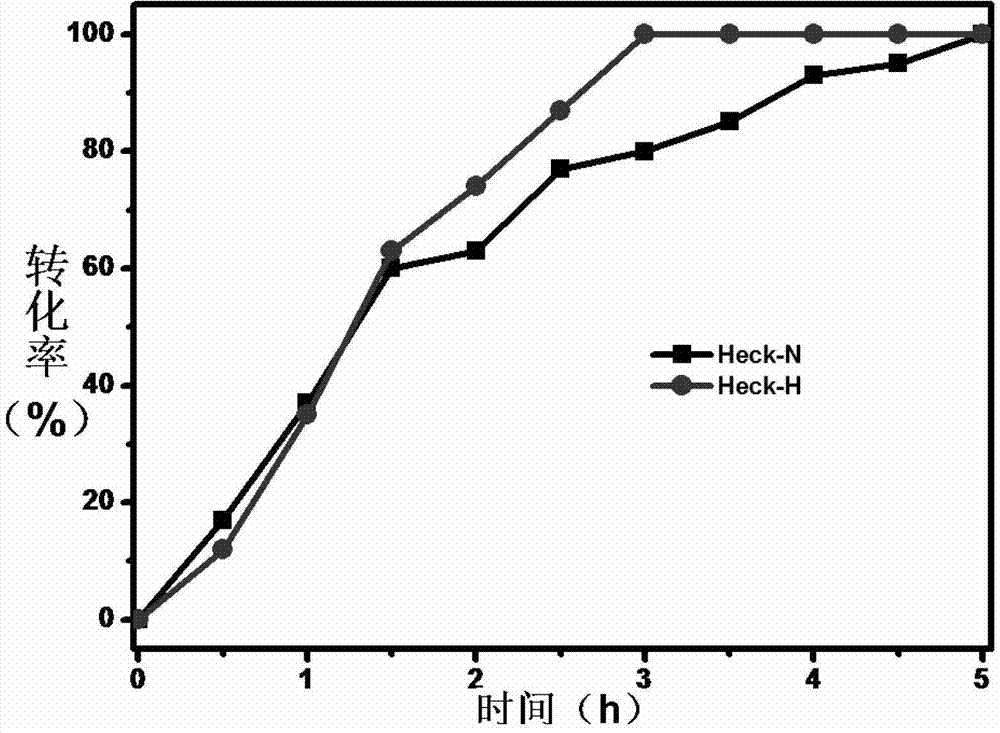
[0035] Embodiment 3, remove the by product in the Heck reaction
[0036] Prepare two reaction systems: dissolve 5mmol iodobenzene and 10mmol styrene into 30ml toluene, add 0.1g 5wt% Pd / C catalyst, and use pyridine as the acid-binding agent.
[0037] In order to illustrate the impact of the inventive method on the Heck reaction, one part does not add any substance, which is recorded as the Heck-N system; the other part adds 3g of gac with a water content of 100%, which is recorded as the Heck-H system, and in this system , the amount of activated carbon added is 3 times the total mass of iodobenzene and styrene. Subsequently, the temperature of the two reaction systems was raised to 90°C, 10 mmol of triethylamine was added to start the reaction, samples were taken at intervals of 0.5 h, and the conversion rate was analyzed by Shimadzu 10A-VP-PLUS liquid chromatography.
[0038] image 3 It is a comparison of the catalytic kinetic curves of the Heck reaction system. It can be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com