Printing and dyeing wastewater treatment method
A technology for printing and dyeing wastewater and mixed wastewater, applied in energy wastewater treatment, textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long hydraulic retention time, high investment cost and high equipment requirements, and achieve equipment investment And the effect of low operating cost, simple operation and management, and high chroma removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Simulated printing and dyeing wastewater: 150mg / L reactive blue X-BR aqueous solution (prepared with distilled water), its water quality COD cr It is 134mg / L, the chromaticity (dilution factor method) is 110, the absorbance at the maximum absorption wavelength is 640nm is 0.964, and the pH is 6.5.
[0074] Domestic sewage was collected from a community in Nanchang City, and its water quality characteristics are shown in Table 1.
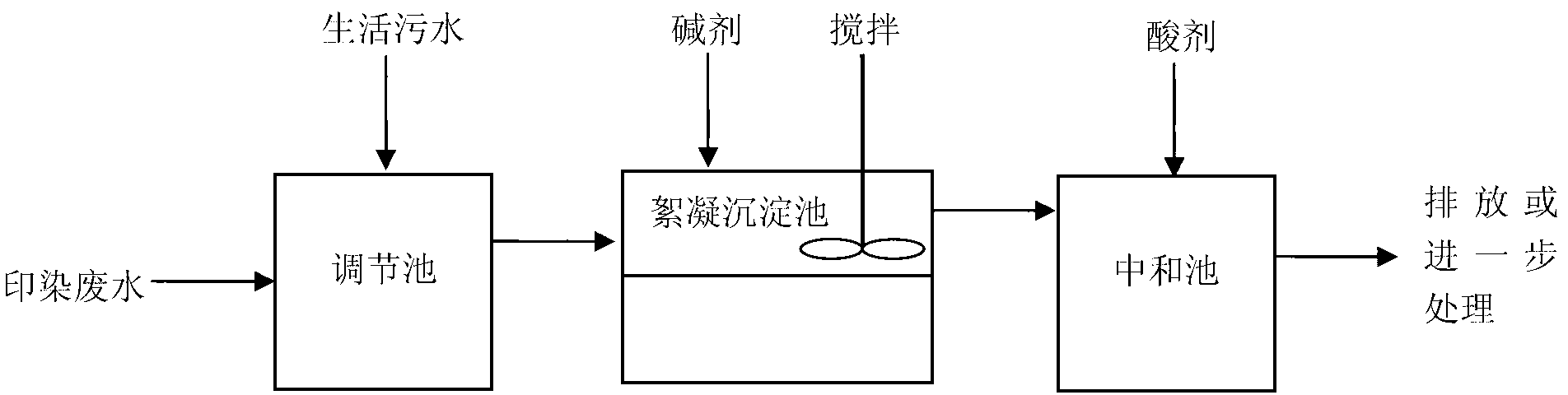
[0075] Step 1: Mix 10ml of simulated printing and dyeing wastewater and 10ml of domestic sewage evenly in a mass ratio of 1:1.
[0076] The second step: adding 4 mg of sodium hydroxide therein to adjust the pH to 11.9.
[0077] The third step: the fast stirring speed is 300 rpm, and the fast stirring time is 2 minutes. The slow stirring speed is 100 rpm. The slow stirring time was 5 minutes.
[0078] Step 4: The static free settling time is 60 minutes.
[0079] The fifth step: adjust the pH value to 8.9 with sulfuric acid.
[0080] The s...
Embodiment 2
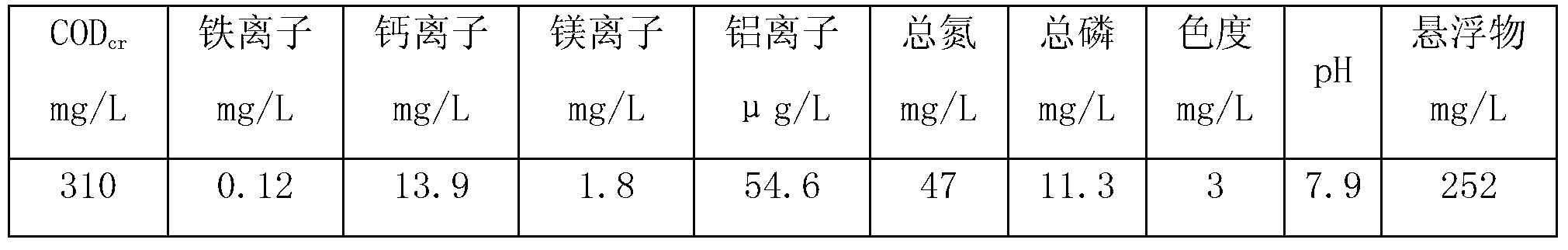
[0087] Simulated printing and dyeing wastewater: 200mg / L disperse ruby S-2GFL aqueous solution (prepared with distilled water), its water quality COD cr It is 310mg / L, the chromaticity (dilution factor method) is 300, the absorbance at the maximum absorption wavelength is 470nm is 2.316, and the pH is 6.9. Domestic sewage was collected from a residential area in Dezhou City, and its water quality characteristics are shown in Table 3.
[0088] Step 1: Mix 10ml of simulated printing and dyeing wastewater and 15ml of domestic sewage evenly in a mass ratio of 1:1.5.
[0089] Step 2: Add 6 mg of sodium hydroxide therein to adjust the pH to 12.0.
[0090] The third step: the fast stirring speed is 300 rpm, and the fast stirring time is 2 minutes. The slow stirring speed is 100 rpm. The slow stirring time was 5 minutes.
[0091] Step 4: The static free settling time is 60 minutes.
[0092] The fifth step: adjust the pH value to 8.9 with sulfuric acid.
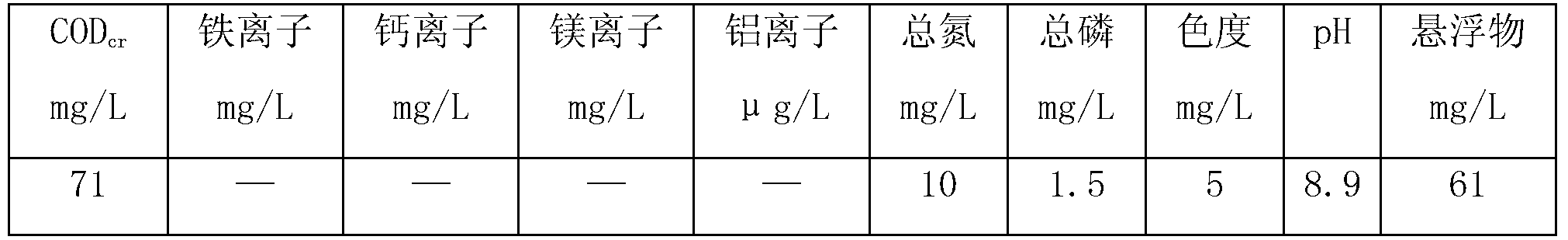
[0093] The water quali...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Simulated printing and dyeing wastewater containing mixed dyes: respectively containing 100mg / L reactive blue X-BR and 200mg / L dispersed ruby S-2GFL mixed aqueous solution (prepared with distilled water), the water quality COD cr It is 430mg / L, the chromaticity (dilution factor method) is 400, and the maximum pH is 6.7.
[0101] Domestic sewage is collected from a community in Yantai City, and its water quality characteristics are shown in Table 5.
[0102] Step 1: Mix 10ml of simulated printing and dyeing wastewater and 20ml of domestic sewage evenly in a mass ratio of 1:2.
[0103] Step 2: Add 0.4g of calcium hydroxide therein to adjust the pH to 12.3.
[0104] The third step: the fast stirring speed is 300 rpm, and the fast stirring time is 2 minutes. The slow stirring speed is 100 rpm. The slow stirring time was 5 minutes.
[0105] Step 4: The static free settling time is 60 minutes.
[0106] The fifth step: adjust the pH value to 8.9 with hydrochloric acid. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com