Temperature sensitive polymer material with biodegradability and biocompatibility and preparation method thereof
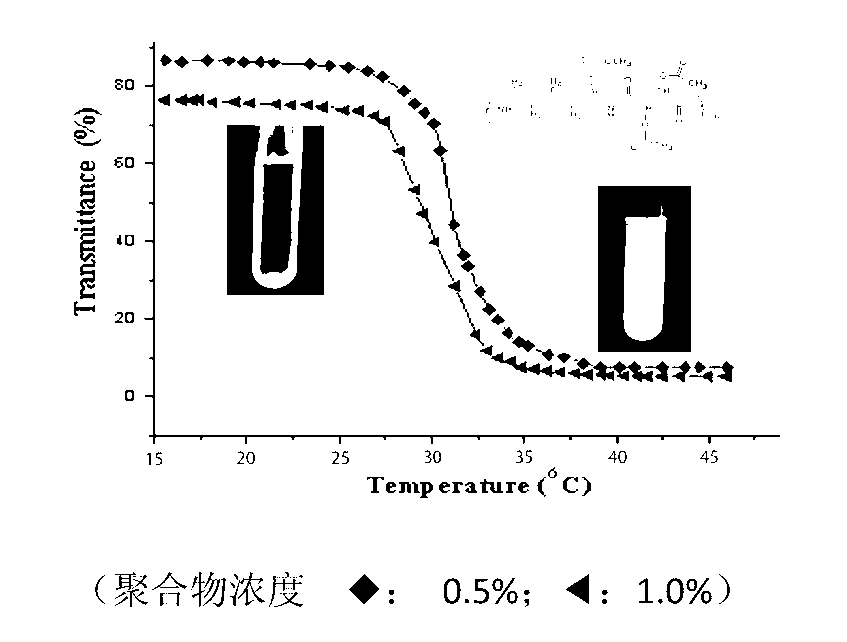
A technology of biocompatibility and polymer materials, which is applied in the field of biodegradable and biocompatible temperature-sensitive polymers and their preparation, can solve the problem of not taking into account the biodegradability and biocompatibility of polymer materials Sexual temperature-sensitive properties, inability to obtain biodegradability, biocompatibility, lack of biocompatibility and other problems, to achieve good biodegradability and biocompatibility, excellent temperature-sensitive properties, to avoid the effect of reducing or disappearing temperature-sensitive properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
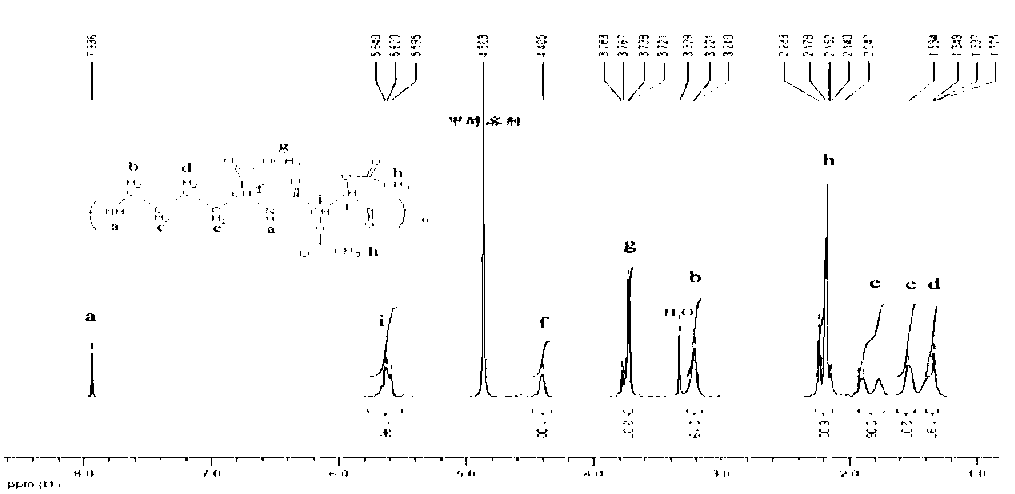
[0044] Embodiment 1: the preparation of poly(lysine methyl ester-diacetoxy tartaric acid)
[0045] (1) Preparation of 2,3‐diacetoxytartaric acid chloride
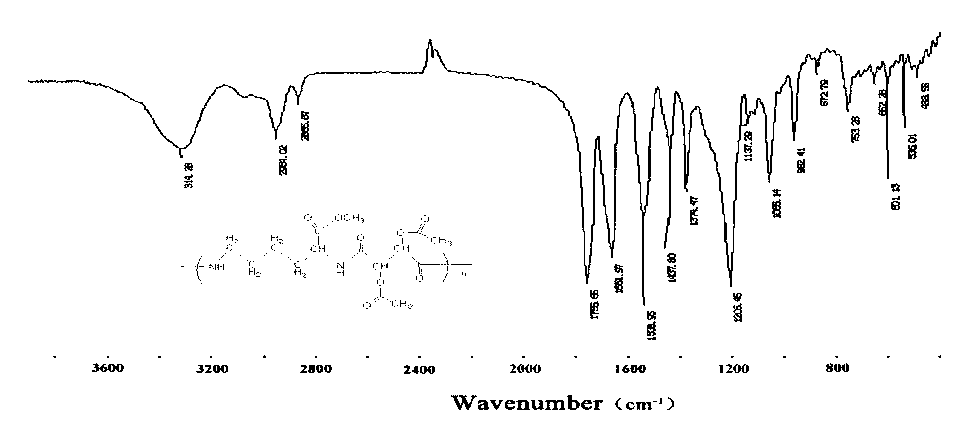
[0046] Add 20 g of tartaric acid and 44 ml of acetic anhydride into a round bottom flask, heat in an oil bath to 140° C., reflux for 2 h, and confirm the completion of the reaction by TLC to obtain a light yellow liquid. The light yellow liquid was cooled to crystallize the target compound. Subsequently, the crystals were washed several times with diethyl ether and dried under vacuum at 80°C to obtain 26.5 g of a white crystalline solid with a yield of 85%. Recrystallize 10 g of the crude product obtained in the previous step with a mixed solvent of acetone and petroleum ether to obtain 6.8 g of pure 2,3‐diacetoxytartaric acid, with a yield of 68%. The reaction equation is as follows:
[0047]
[0048] Add 2g of 2,3-diacetoxytartaric acid and 10ml of thionyl chloride into a 100ml single-necked bottle, and add two drop...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2: the preparation of poly(ethyl lysine-diacetoxy tartaric acid)
[0063] (1) Preparation of 2,3‐diacetoxytartaric acid chloride
[0064] The preparation of 2,3-diacetoxy tartaric acid chloride is the same as in Example 1.
[0065] (2) Synthesis of lysine ethyl ester hydrochloride
[0066] Add 150ml of ethanol to the four-neck bottle, add 21.60ml of thionyl chloride dropwise under the condition of stirring at -10°C, and continue to react for 1h after dropping for about 1.5h. Naturally rise to room temperature to obtain 150 ml of 2 mol / l HCl ethanol solution. Transfer the above solution to a brown reagent bottle, seal it and keep it away from light for later use.
[0067] Add 50ml of ethanol to the four-neck bottle, and slowly add 12ml of thionyl chloride dropwise under the condition of stirring at -10°C. The dropping time is about 20min, and the stirring is continued for 1h after the dropping is completed. Add 5 g of lysine hydrochloride and heat to reflu...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Embodiment 3: the preparation of poly(lysine methyl ester-diethoxytartaric acid)
[0078] (1) Preparation of 2,3‐diethoxytartaric acid chloride
[0079] 4.6g of sodium tartrate and 10ml of ethyl bromide under the action of 0.2g of sodium hydride (or sodium amide) as a catalyst to obtain 2,3-diethoxydiethyl tartrate, the resulting product is acidified and hydrolyzed with dilute hydrochloric acid for 3 hours to obtain 2,3‐diethoxytartaric acid. 2,3-diethoxy tartaric acid was refluxed with thionyl chloride under the catalysis of DMF for 1.5h. After separation and purification, 2,3-diethoxy tartaric acid chloride monomer was obtained with a yield of 45 %.
[0080]
[0081] (2) Synthesis of lysine methyl ester hydrochloride
[0082] The synthetic method of lysine methyl ester hydrochloride is with embodiment 1.
[0083] (3) Preparation of thermosensitive poly(lysine methyl ester‐diethoxy tartaric acid)
[0084] Add 10ml of methanol into the reaction bottle, and cool ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com