Method for separating potassium oxide from potassium-containing sodium aluminate solution
A potassium-containing sodium aluminate and potassium oxide technology, which is applied in the direction of alkali metal oxides, can solve the problems of complicated process, aggravated evaporation scaling, and high processing costs, and achieves mild and easy-to-control reaction conditions, improved crystallization particle size, and product The effect of structural optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
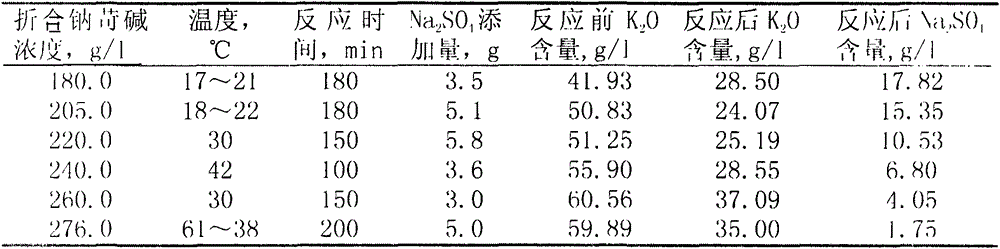
[0017] The Bayer method evaporated the mother liquor and diluted it to the equivalent sodium caustic concentration of 180g / l, and analyzed k 2 O41.93g / l, Na 2 SO 4 2.11g / l, take 50ml mother liquor and add 3.5g analytical pure anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 , Stir the reaction at room temperature of 17°C to 21°C for 180 minutes, let it stand for 10 hours, take the supernatant and analyze k 2 O28.50g / l, Na 2 SO 4 17.82g / l. Add analytical pure NaOH to 30ml clear liquid to Na 2 o k Up to 280g / l, plus 0.5g Na 2 SO 4 , stirred for 150 minutes, drip filtered, and analyzed Na in the filtrate 2 SO 4 1.71g / l.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Filter the high-distilled mother liquor of the Bayer process, dilute the filtrate to a concentration of 220g / l equivalent to sodium caustic, and analyze k 2 O51.25g / l, Na 2 SO 4 2.13g / l, take 50ml of mother liquor and add 5.8g of analytically pure powdered anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 , stirred the reaction at 30°C for 150 minutes, let it stand for 10 hours, and took the supernatant to analyze k 2 O 25.19g / l, Na 2 SO 4 10.53g / l.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Filter the high-distilled mother liquor of the Bayer process, and analyze the converted sodium caustic concentration to be 276g / l, K 2 O 59.89g / l, Na 2 SO 4 2.01g / l, take 50ml of mother liquor and add 5.0g of analytically pure powdered anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 , stirred and reacted for 200 minutes under the condition of 61°C~38°C, drip filtered, and the filtrate was analyzed k 2 O 35.00g / l, Na 2 SO 4 1.75g / l.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com