Preparation method for organic phase carbon dots
An organic phase, carbon dot technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology, nano-optics, etc., can solve the problems of complex sample separation, long experiment time, limited, etc., and achieve simple and fast process methods, simple and environmentally friendly reaction conditions. , the effect of reducing the reaction time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
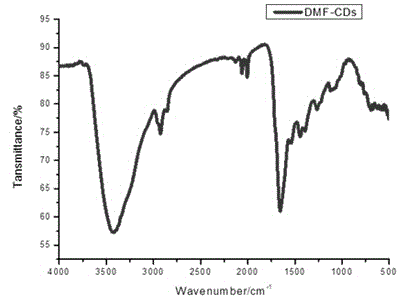
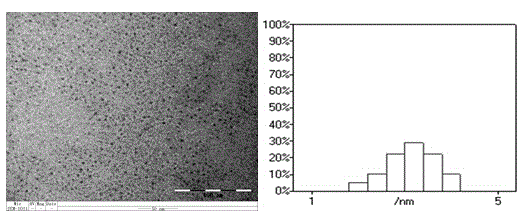
[0028] Take 20mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), put it into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and heat the solvent for 12 hours at 300°C to obtain a carbon dot solution. Filter the obtained liquid with a 0.2 μm microporous membrane, collect the distilled solvent DMF through rotary distillation, and dry it in a vacuum oven to obtain carbon dot solids (named DMF-CDs). Put the separated DMF into the hydrothermal reactor, and continue the reaction under the same conditions to obtain DMF-CDs. To detect carbon dots, such as Figure 1-5 As shown, among them, figure 1 It is the infrared spectrum of DMF-CDs carbon dots. It can be seen from the figure that there is a strong peak at around 1700, indicating that there are carbonyl groups in the carbon dots; figure 2 It is the transmission electron micrograph and particle size distribution diagram of DMF-CDs carbon dots. It can be seen from the figure that the size distribution of carbon dots is 2-4 nm, with an average size of about 3 nm...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Take 20mL of n-hexane (H), put it into the autoclave, and heat the solvent for 10h at 150°C to obtain the carbon dot solution. Filter the obtained liquid with a 0.2 μm microporous membrane, collect the distilled solvent through rotary distillation, and dry it in a vacuum oven to obtain n-hexane carbon dot solids (H-CDs). Put the separated n-hexane into the high-pressure reactor, continue the reaction under the same conditions, and continue to obtain H-CDs. The normal hexane obtained by the rotary steaming of the raw material n-hexane and the product is determined by gas chromatography, and the spectra are compared, as shown in Image 6 shown, from Image 6 It can be seen that there is no significant difference between the two spectra. Therefore, the separated solvent can also continue to react.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Take 20mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), put it into the autoclave, and heat the solvent at 200°C for 24 hours to obtain the carbon dot solution. The obtained liquid was filtered with a 0.2 μm microporous membrane, and the obtained liquid was collected by rotary distillation to collect the evaporated solvent, and then dried in a vacuum oven to obtain DMAc carbon dot solids (named DMAc-CDs). Put the separated DMAc into the autoclave and continue the reaction under the same conditions to obtain DMAc-CDs. To detect carbon dots, such as Figure 7 Shown, TEM image and particle size distribution of DMAc carbon dots. It can be seen from the figure that the size of DMAc carbon dots is uniform, and the average size is about 3 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com