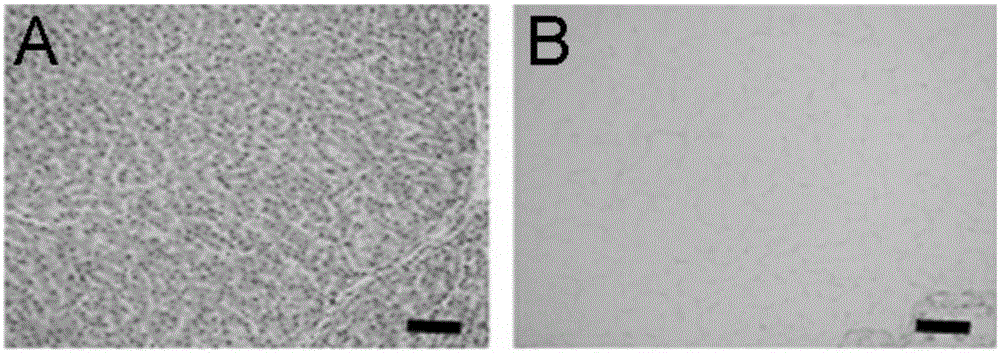
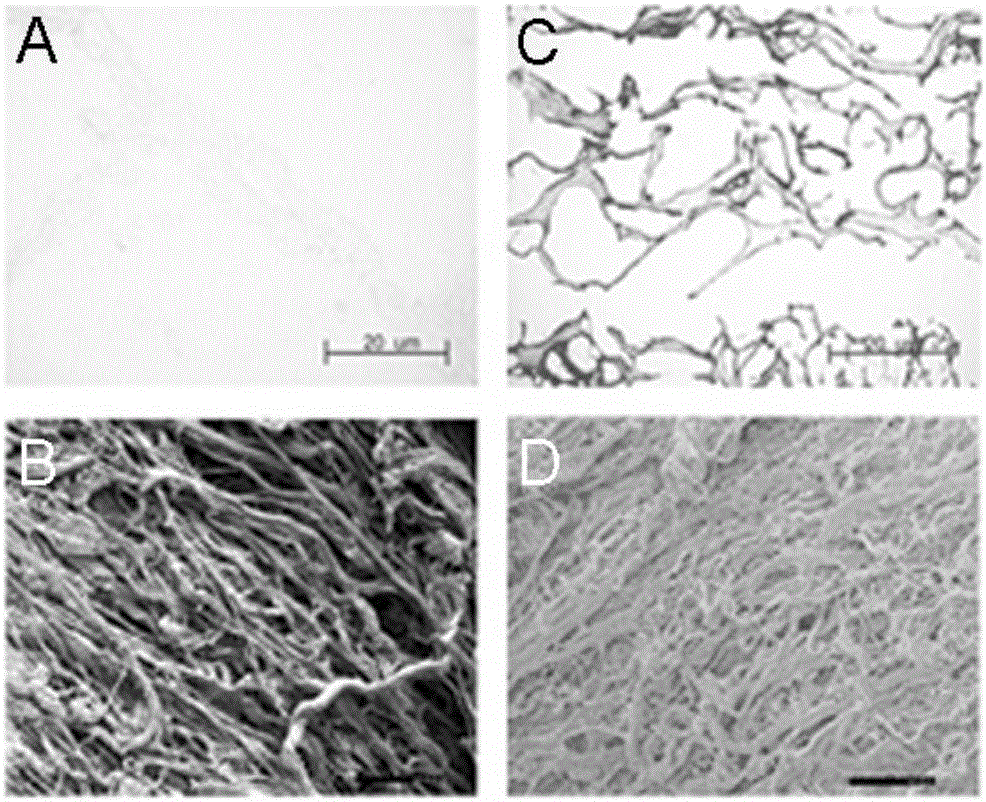
A decellularized liver bioscaffold with anticoagulant properties and preparation method thereof
A decellularization and bioscaffold technology, applied in the fields of clinical medicine, biomedicine and regenerative medicine, can solve the problems of high preparation cost, poor blood compatibility, and insufficient binding, and achieve strong anticoagulant performance and anticoagulant effect. Uniform and beneficial for long-term anticoagulation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Preparation of decellularized liver bioscaffold with anticoagulant properties of the present invention
[0041] 1. Experimental method
[0042] (1) Obtaining decellularized porcine liver bioscaffold
[0043] The decellularized liver bioscaffold of the present invention can be obtained by using the isolated porcine liver as a raw material and processed by a conventional decellularization method. For example, it can be prepared according to the following method:
[0044] The liver was taken out from a Bama pig weighing 15-25 kg, and perfused with 0.1% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) until the blood in the liver drained completely to obtain the isolated pig liver, which was stored at -20°C .
[0045] The isolated porcine liver was taken, thawed at 4°C, and perfused with 1% Triton X-100 solution at a flow rate of 200 mL / min for 3 h and 1% sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) solution at a flow rate of 200 mL / min for 6 h. Then lavage with 1% Triton X-100 solution...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 Preparation of decellularized liver bioscaffold with anticoagulant properties of the present invention
[0073] 1. Experimental method
[0074] (1) Preparation of decellularized porcine liver bioscaffold: According to the method in Example 1, a decellularized porcine liver bioscaffold was prepared.
[0075] (2) Anticoagulant modification
[0076] a. Anticoagulant modification
[0077] Preparation of heparin sodium perfusion solution: prepare a heparin sodium aqueous solution with a concentration of 3.3 g / L at 0° C., and adjust the pH value to 2.7. Then add sodium nitrite to a final concentration of 33mg / L, stir at 0°C for 2 hours, and adjust the pH value to 7.0. Then add NaBH 3 The final concentrations of CN and NaCl were 10 mg / L and 0.15 mol / L, respectively, and the pH was adjusted to 3.5.
[0078] At room temperature, the prepared heparin sodium perfusion solution was poured into the decellularized porcine liver scaffold, and the perfusion was circulate...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 Preparation of decellularized liver bioscaffold with anticoagulant properties of the present invention
[0090] 1. Experimental method
[0091] (1) Preparation of decellularized porcine liver bioscaffold: According to the method in Example 1, a decellularized porcine liver bioscaffold was prepared.
[0092] (2) Anticoagulant modification
[0093] a. Anticoagulant modification
[0094]Preparation of heparin sodium perfusion solution: prepare a heparin sodium aqueous solution with a concentration of 2 g / L at 0°C, and adjust the pH value to 2.7. Then add sodium nitrite to a final concentration of 33mg / L, stir at 0°C for 2 hours, and adjust the pH value to 7.0. Then add NaBH 3 The final concentrations of CN and NaCl were 10 mg / L and 0.15 mol / L, respectively, and the pH was adjusted to 3.5.
[0095] At room temperature, the prepared heparin sodium perfusion solution was poured into the decellularized porcine liver scaffold, and the perfusion was recirculated f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com