Novel temperature-response inorganic pyrophosphatase conjugate synthesis and application of conjugate to enhanced polymerase chain reaction
An inorganic pyrophosphatase, temperature-responsive technology, used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, hydrolase, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of screening and extraction of thermophilic microorganisms denaturation inactivation and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving the optimum reaction temperature and heat resistance, easy control of the process, and simple process method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
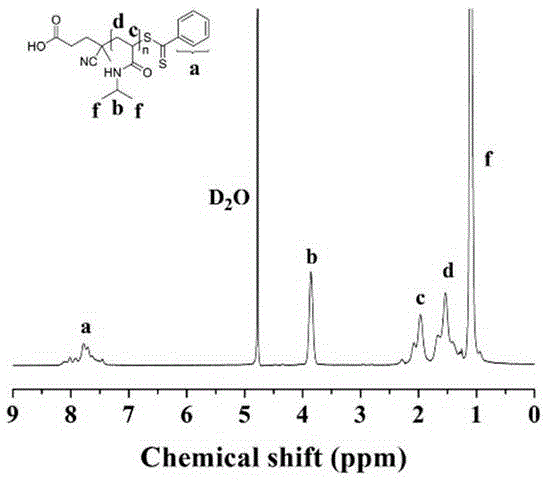
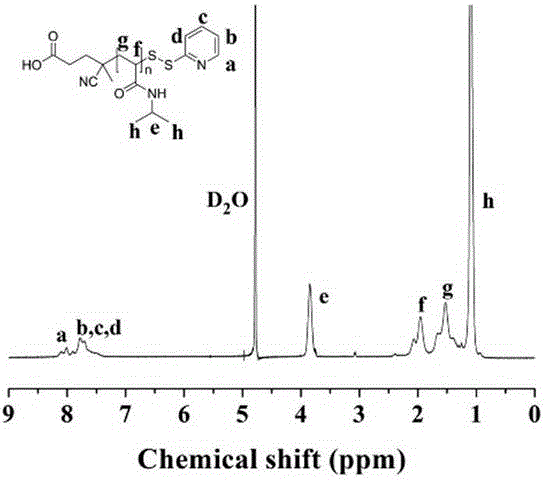
[0040] Embodiment one, the result is as figure 1 with 2 shown.
[0041] (1) Expression and extraction of the mutant (K148C): a site-directed mutagenesis method was used to introduce a cysteine containing a sulfhydryl group near the active center of the protein.
[0042] (2) Preparation of polymer PNIPAM: adjust NIPAM and CTA seasoning ratio at 65 o C for 24 h, followed by dialysis and lyophilization to obtain polymers with different molecular weights. Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT)
[0043] (3) Preparation of polymers with thiopyridine: add ethanolamine and dithiobipyridine, react at room temperature for 4 h, dialyze and freeze-dry to obtain the modified polymer Pydl-PNIPAM.
[0044] (4) Preparation of PNI-PPase conjugate: Combine in 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH=8.0), the molar ratio of PNIPAM / PPase is 50 / 1, and react overnight to obtain the conjugate PNI-PPase.
Embodiment 2
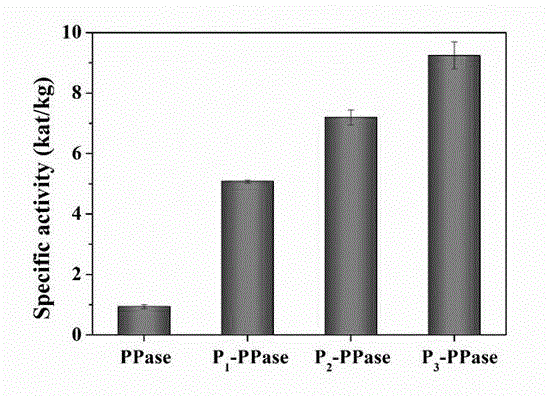
[0045] Embodiment two, the result is as image 3 Shown is the activity test of the conjugate at different temperatures and 60 o Activity test after different incubation times at C.
[0046] (1) Determination of the activity of the conjugate at different temperatures: the conjugate was heated at 25-90 o C for 10 min heat treatment, and then with the substrate sodium pyrophosphate (Na 4 P 2 o 7 ) at the corresponding temperature for 10 min, measure the Pi content of the product, and calculate the specific activity value (kat / kg).
[0047] (2) Determination of the thermal stability of the conjugate at different times: the conjugate was heated at 60 o After heat treatment at C for 10-180 min, the activity was measured, and the specific activity value and relative activity were calculated (the specific activity value at the time of heat treatment for 10 min was 100%).
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment three, the result is as Figure 4 Shown is the enhancement effect of the conjugate added to the PCR system and the activity test after different cycles of heat treatment in the PCR instrument.
[0049] (1) PCR enhancement effect test: PPase, PNIPAM, and PNI-PPase were added to the PCR system, and ordinary PCR was used as a control to measure the amplification after 20 cycles.
[0050] (2) Changes in the activity of the conjugate under different cycles of the PCR instrument: place the conjugate in the PCR instrument for 20-100 cycles, measure the activity of the conjugate, and calculate the specific activity value (kat / kg) , which is sodium pyrophosphate (Na 4 P 2 o 7 ) as the substrate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com