Preparation method of high-purity algal polyphenol
A seaweed polyphenol, high-purity technology, applied in the field of preparation of high-purity seaweed polyphenol, can solve the problems of long production time, high equipment requirements, complex production process, etc., to shorten production time, improve product quality, and simplify the process flow Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
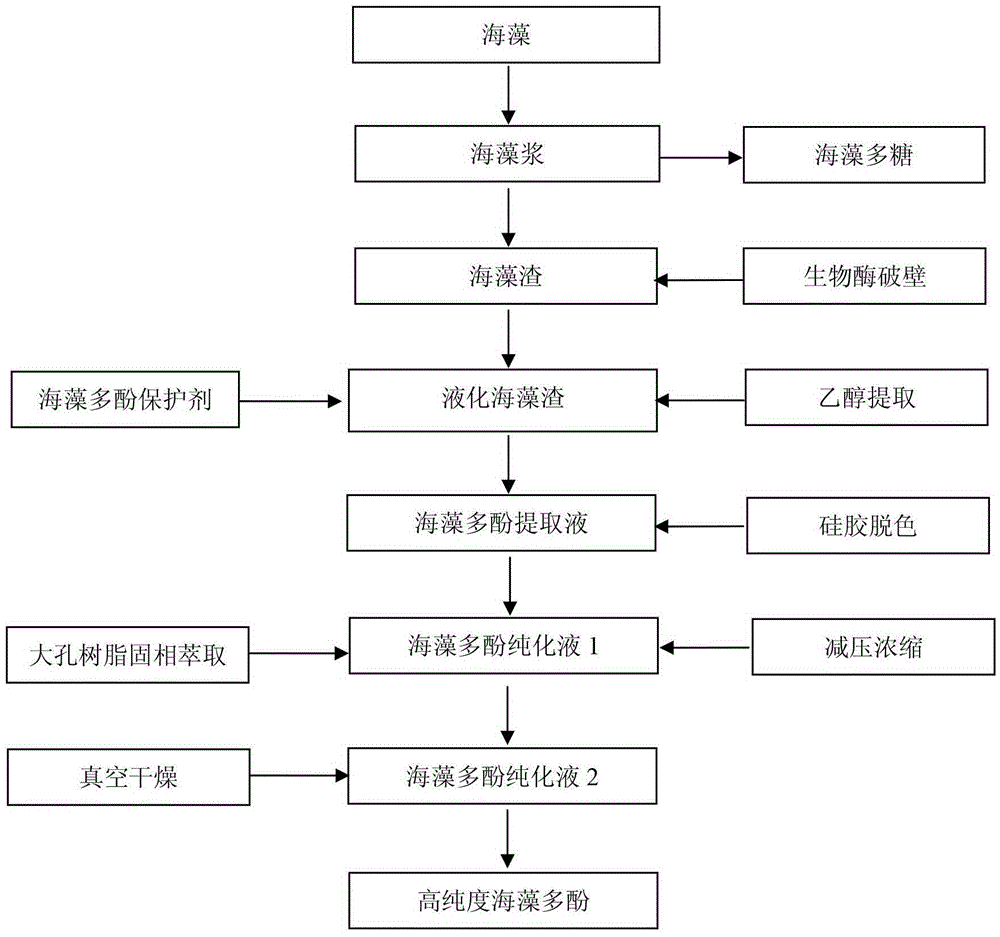
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Preparation of high-purity seaweed polyphenols from kelp
[0027] (1) Get water content and be 20 mass % dry sea-tangle 1kg, after soaking and rinsing with tap water to remove impurities such as silt, beating with a beater to obtain 0.6L of seaweed slurry; send it into the agitator, and add 3L deionized water, under temperature Stir at a speed of 120 rpm for 30 minutes; then use a low-speed centrifuge to centrifuge the seaweed slurry at a speed of 1000 rpm for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant and seaweed residue; the seaweed residue is stirred by a mixer and centrifuged in a centrifuge according to the above steps and conditions Afterwards, the supernatant and seaweed residue were collected again. The two supernatants were combined and spray-dried to obtain seaweed polysaccharides; 342 g of seaweed residue was collected for extraction and preparation of seaweed polyphenols.
[0028] (2) Mix the wet kelp slag with 1.71 g of compound enzyme evenly, and hyd...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Preparation of high-purity seaweed polyphenols from wakame
[0033] (1) Take 1 kg of dried wakame with a water content of 20% by mass, soak, rinse, and beat with tap water to obtain 0.55 L of seaweed pulp; add 2.75 L of deionized water after sending it into the agitator, and stir at a speed of 120 rpm under temperature 30 min; then centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 min, collect the supernatant and seaweed residue respectively; repeat the above steps, the supernatant is used to prepare seaweed polysaccharide; collect 313 g of seaweed residue, which is used to extract and prepare seaweed polyphenols.
[0034] (2) Mix the above-mentioned wet wakame residue with 1.565 g of compound enzyme evenly, and hydrolyze it at room temperature for 5 hours, so as to break the cell wall of seaweed.
[0035] (3) 80% by volume ethanol aqueous solution containing 0.05% by mass, 0.01% by volume of phytic acid and 0.1% by volume of acetic acid is used as the extract. Add 1.565L of ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: Sea millet prepares high-purity seaweed polyphenols
[0039] (1) Take 1 kg of dry sea millet with a water content of 20% by mass, soak, rinse, and beat with tap water to obtain 0.5 L of seaweed slurry; add 2.5 L of deionized water after sending it into the agitator, and use 120 rpm under temperature. Stir for 30 minutes; then centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes to collect the supernatant and seaweed residue; repeat the above steps, the supernatant is used to prepare seaweed polysaccharides; collect 410 g of seaweed residue, which is used to extract and prepare seaweed polyphenols.
[0040] (2) Mix the above-mentioned wet wakame residue with 2.05 g of compound enzyme evenly, and hydrolyze it at room temperature for 5 hours, so as to break the cell wall of seaweed.
[0041] (3) 80% by volume ethanol aqueous solution containing 0.05% by mass, 0.01% by volume of phytic acid and 0.1% by volume of acetic acid is used as the extract. Add 2.05L of the extract to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com