A molybdenum ion-imprinted amino-functionalized chitosan adsorbent and its preparation method and application
A technology of amino function and chemical chitosan, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as high operating costs, secondary pollution, and cumbersome operations, and achieve low cost and reduced Pollution, the effect of improving economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 A molybdenum ion-imprinted amino-functionalized chitosan (I-EDA-CS) adsorbent
[0038] The preparation method is as follows:
[0039] 1) Dissolve 2g of solid ammonium molybdate in a mixed solution of water and ethanol (water:ethanol=1:1), stir, and react at 20-25°C for 3h to obtain a colorless transparent liquid;
[0040] 2) Slowly drop 30 mL of ethylenediamine into the colorless transparent liquid, keep stirring at room temperature, and react for 2 hours to obtain solution A, then add 50 mL of epichlorohydrin to solution A, and stir under reflux at 40°C for 12 hours, then Add 25 g of chitosan, continue to stir under reflux for 24 hours at 50 °C, wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry at 50 °C to obtain an intermediate product;
[0041] 3) Remove molybdenum imprinted ions in the intermediate product with HCl of a certain acidity, then wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry to obtain a molybdenum ion imprinted amino-functionalized chitosan ...
Embodiment 2-5
[0043] Example 2-5 A molybdenum ion-imprinted amino-functionalized chitosan (I-EDA-CS) adsorbent
[0044] The preparation method is the same as that of Example 1, except that the addition amount of ammonium molybdate in step 1) is changed by 1g, 3g, 4g, and 5g.
[0045] The I-EDA-CS adsorbents prepared in Examples 1-5 were tested and compared, and the results showed that when the mass ratio of ammonium molybdate to chitosan was 1-3:25, the adsorption rate reached more than 94%.
Embodiment 6
[0046] Example 6 Application and Comparison
[0047] Take the imprinted adsorbent: the I-EDA-CS adsorbent prepared in Example 1.
[0048] Take the unimprinted adsorbent: N-EDA-CS adsorbent. The preparation process of the unimprinted adsorbent is the same as that of the imprinted adsorbent, except that ammonium molybdate is not added in the reaction process, that is, in the reaction process prepared in Example 1, no ammonium molybdate is added. The N-EDA-CS adsorbent was finally obtained by adding ammonium molybdate.
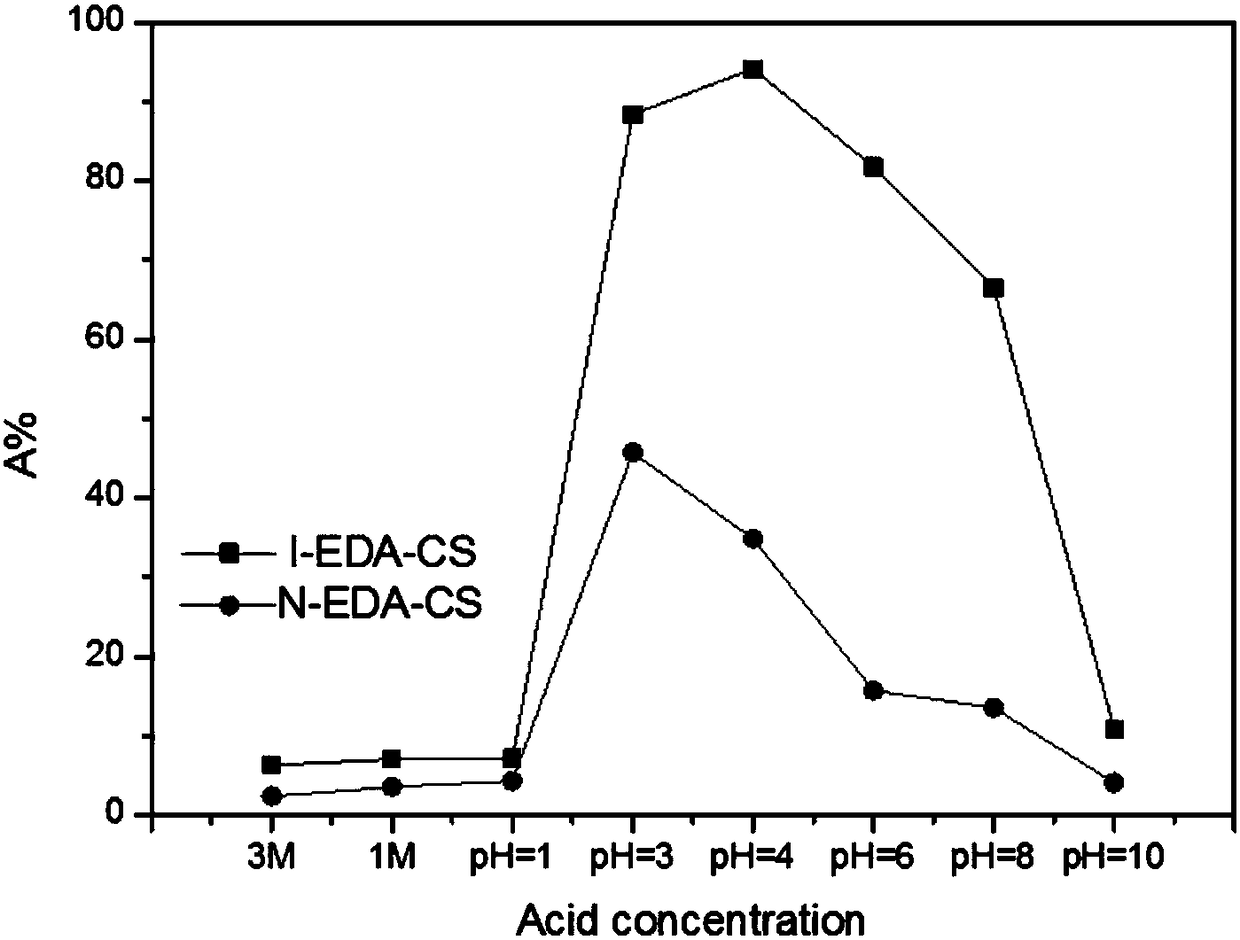
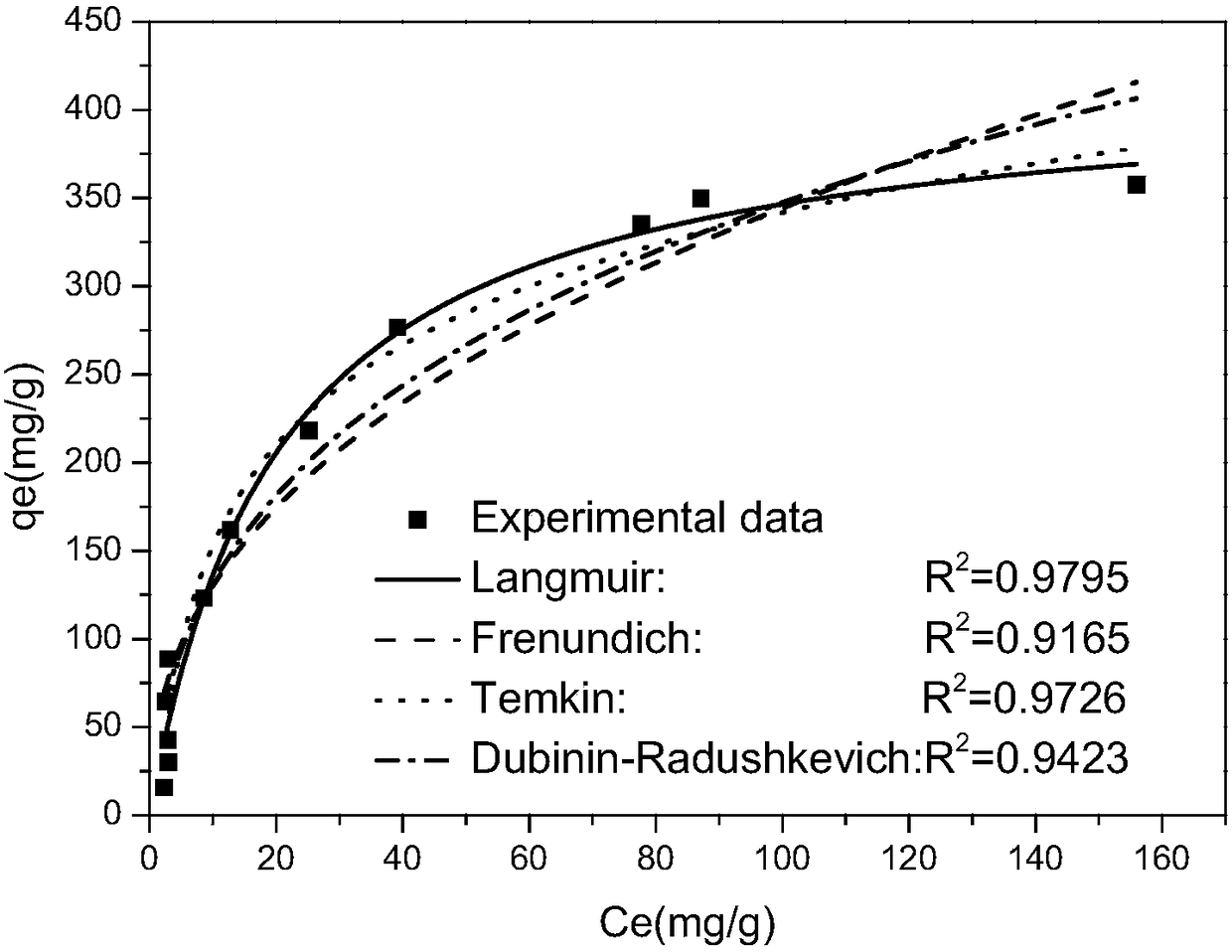
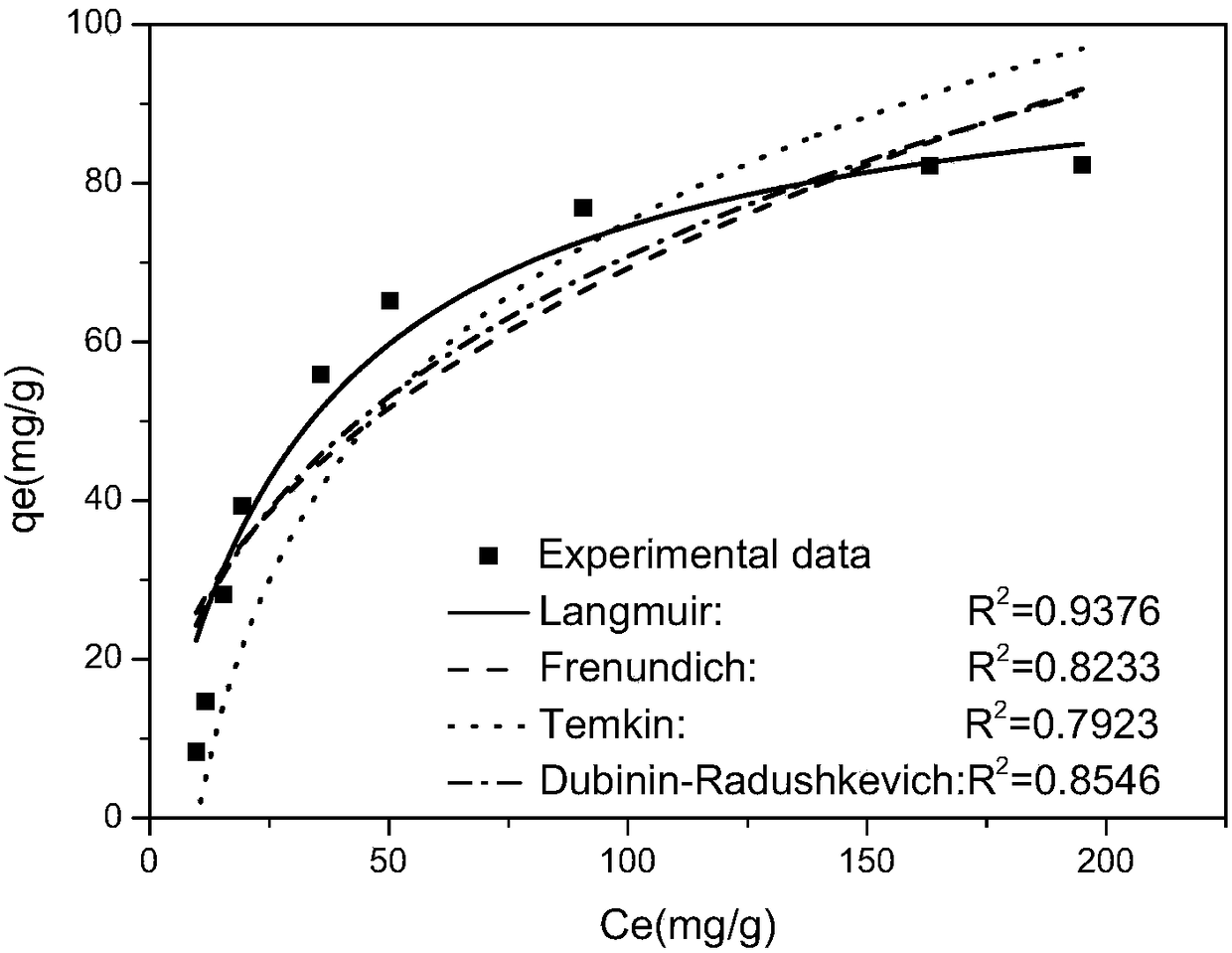
[0049] The I-EDA-CS adsorbent and N-EDA-CS adsorbent were oscillated and adsorbed on a 20ppm rhenium solution with pH=4 with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:1, and oscillated at 303K for 24h. The results are as follows figure 1 As shown, the adsorption efficiency of I-EDA-CS adsorbent for rhenium can reach 94.11%. While the unimprinted N-EDA-CS adsorbent was only 45.7%. The maximum adsorption capacity of I-EDA-CS adsorbent can reach 357.52g / kg, and the maximum adsor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com