Hydrophobic functional micromolecule-hydrophilic polyamino acid based biodegradable polymer and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for degrading polymers and functional small molecules is applied in the field of amphiphilic biodegradable materials and their preparation, and can solve the problems of difficult surface functionalization and low stability of nano-microspheres.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
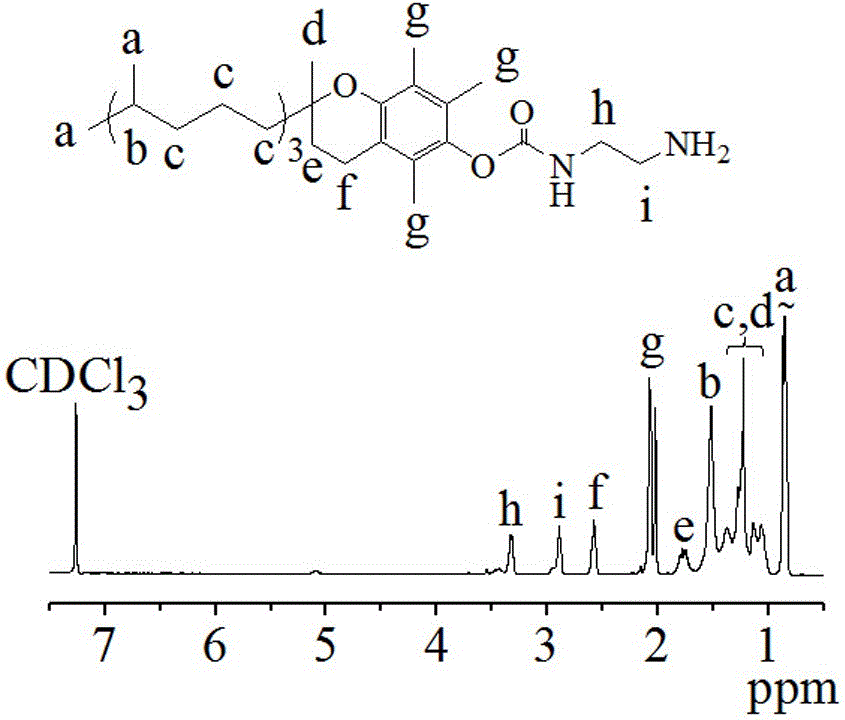
[0067] Embodiment one initiator vitamin E amino (VE-NH 2 )Synthesis
[0068] (1) Preparation of intermediate VE-4-NC: Under nitrogen atmosphere, dichloromethane (30 mL) solution of p-nitrophenyl chloroformate (4-NC, 1.98 g, 9.8 mmol) was heated at 0°C It was added dropwise to a solution of vitamin E (VE, 2.12 g, 4.9 mmol) and pyridine (1.98 mL, 24.5 mmol) in dichloromethane (10 mL) at a rate of 5 seconds. After the dropwise addition was completed, it was transferred to a 30° C. oil bath to react for 24 hours. After the reaction, the by-product pyridinium salt was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was spin-dried by a rotary evaporator to obtain a light yellow viscous crude product of VE-4-NC. Then dissolve the crude product with petroleum ether (b.p: 60-90 ℃), centrifuge to remove impurities, rotary evaporate, and finally vacuum-dry to obtain the yellow viscous oily product VE-4-NC, with a yield of 93.4%;
[0069] (2) Initiator vitamin E amino (VE-NH 2 ) preparation: ...
Embodiment 2
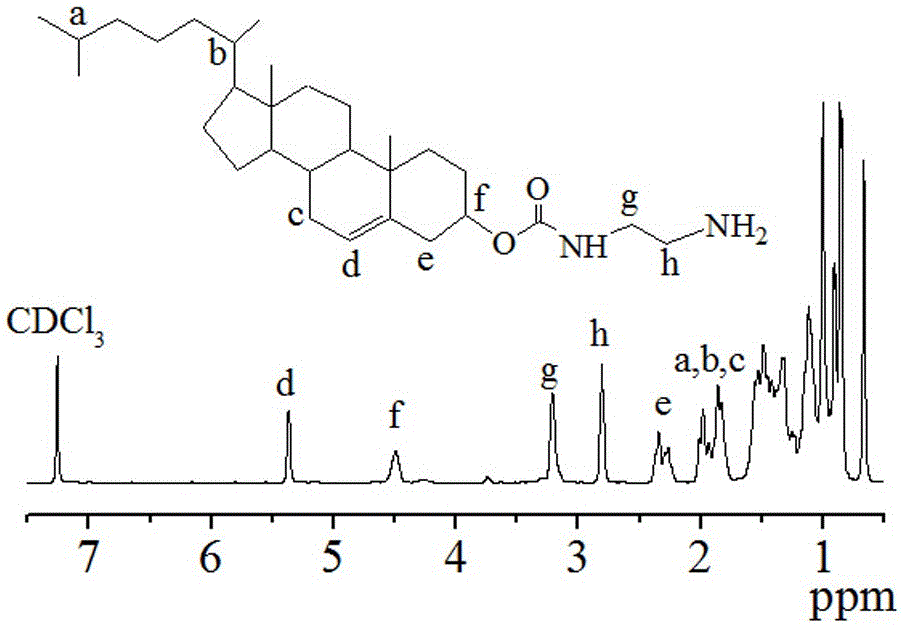
[0071] Embodiment two initiator cholesteryl amino (Chol-NH 2 )Synthesis
[0072] (1) Preparation of intermediate Chol-4-NC: Under nitrogen protection, a solution of p-nitrophenyl chloroformate (4-NC, 1.61 g, 8.0 mmol) in dichloromethane (about 30 mL) was Add slowly dropwise (about 5 seconds per drop) to cholesterol (Chol, 1.55 g, 4.0 mmol) and pyridine (1.56 mL, 20.0 mmol) in dichloromethane (10 mL) under bath conditions. Then, it was reacted in an oil bath at 30°C for one day, the pyridinium salt was removed by filtration, and the crude product was obtained as a white solid by rotary evaporation. Finally, the crude product was purified by washing with ice acetone to obtain the Chol-4-NC product. Yield: 50.4%;
[0073] (2) Initiator cholesteryl amino (Chol-NH 2 ) preparation: Chol-4-NC (1.05 g, 1.9 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (30 mL), and then slowly added dropwise to a twenty-fold excess of ethylenediamine ( 2.57 mL, 38.0 mmol) in dichloromethane (7 mL), react...
Embodiment 3
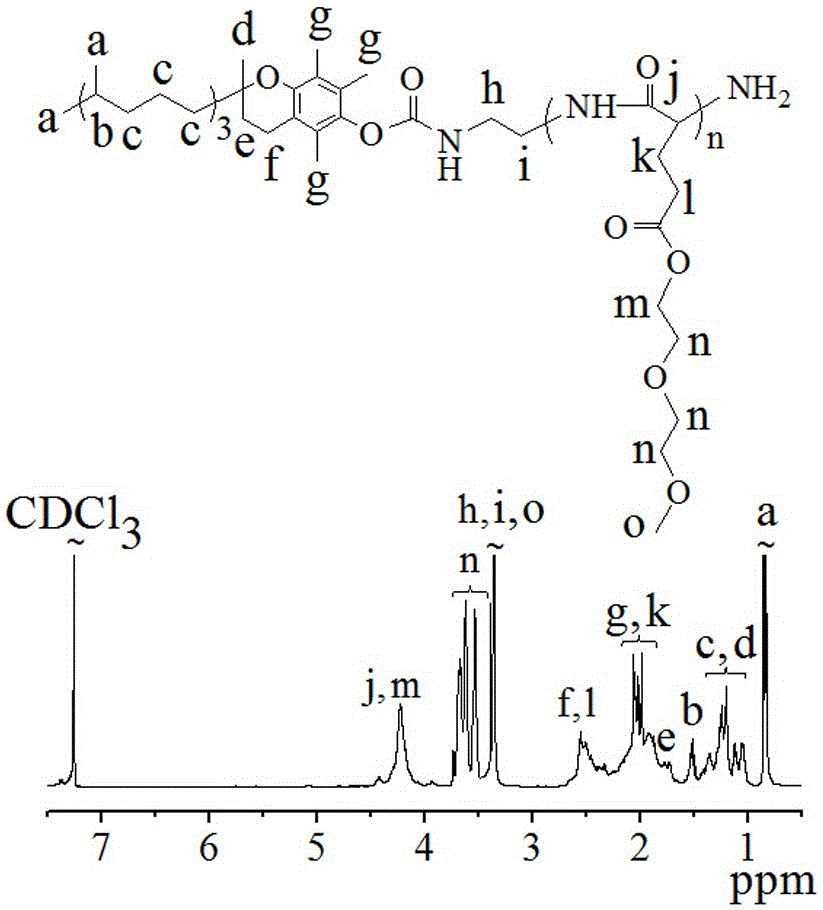
[0075] Example 3 Vitamin E-poly(γ-diethylene glycol monomethyl ether-L-glutamic acid) (VE-poly(EG 2 -Glu)) synthesis
[0076] Taking n as 5 as an example: the initiator vitamin E amino VE-NH 2 (1.16 g, 2.25 mmol) was dissolved in 37 mL of dichloromethane solvent and placed in a closed reactor. Under nitrogen atmosphere, γ-diethylene glycol monomethyl ether-L-glutamic acid-N-carboxy internal acid anhydride (EG 2 -Glu-NCA) (3.71 g, 13.50 mmol) in dichloromethane (37 mL) was quickly added to the initiator and reacted at 25 °C for 12 hours. The reaction process was monitored by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. After the reaction, the reaction solution was concentrated by rotary evaporation to about 18 ml, precipitated with glacial ether, and centrifuged at low temperature (-5°C, 5000 rpm) to collect the precipitate. Finally, it was washed three times with glacial ether and dried in vacuum for 48 hours to obtain a pale yellow product with a yield of 55.8%.
[0077] VE-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com