Preparation method of carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles
A technology of carboxylated cellulose and nanoparticles, which is applied in the field of cellulose, can solve the problems of complex and time-consuming preparation process, insufficient operation, toxicity, etc., and achieve the effects of simple and easy operation, environmental protection in the preparation process, and poor dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
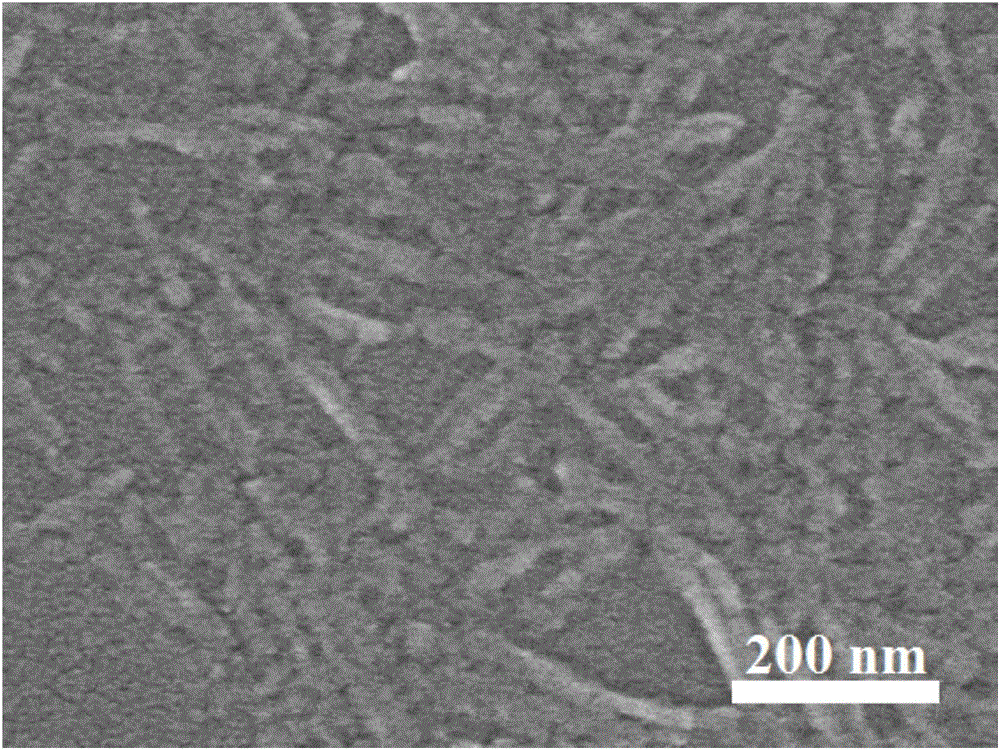
[0036] Fully infiltrate commercially available microcrystalline cellulose in a mixed solution of 5 mol / L aqueous hydrochloric acid and 3 mol / L aqueous nitric acid, where the volume ratio of hydrochloric acid to nitric acid is 3:1, and then transfer it to a hydrothermic tank with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner. In the kettle; wherein, the solid content of microcrystalline cellulose in the mixed solution is 0.04g / mL. The reaction was carried out at 120° C. for 3 h. After the hydrothermal kettle was naturally cooled, the reaction product was poured out and diluted with deionized water. The solution is washed to be close to neutral by suction filtration to obtain a uniformly distributed dispersion of carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles; freeze-dried to obtain carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles. like figure 1 Scanning electron microscope observation shows that the prepared cellulose nanoparticles are rod-shaped, with a length of 100-300nm and a diameter of 5-20nm. figure 2 ...
Embodiment 2
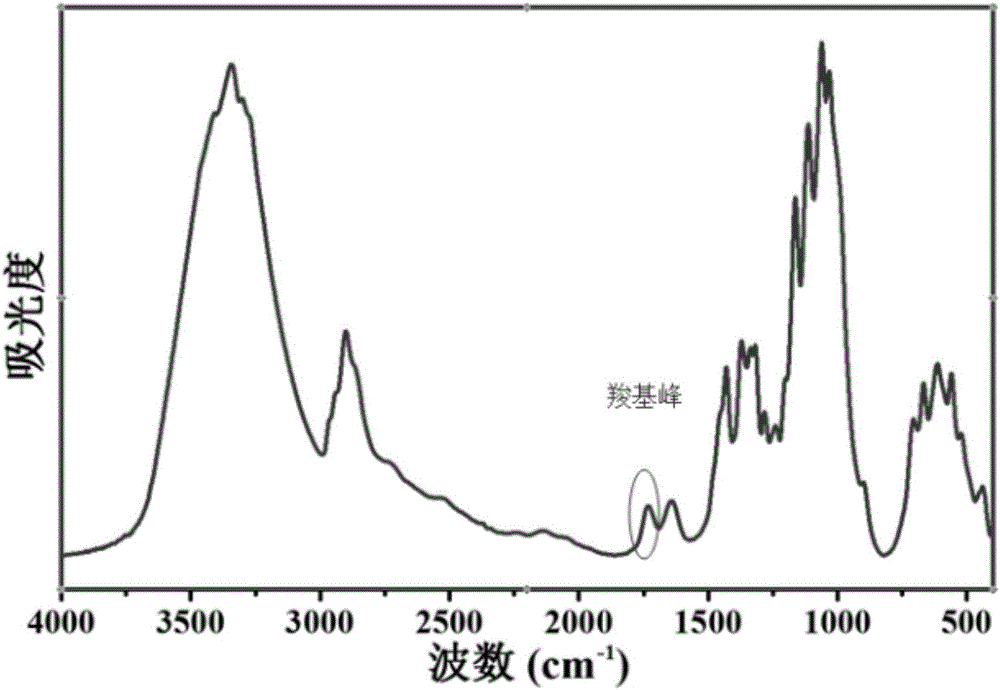
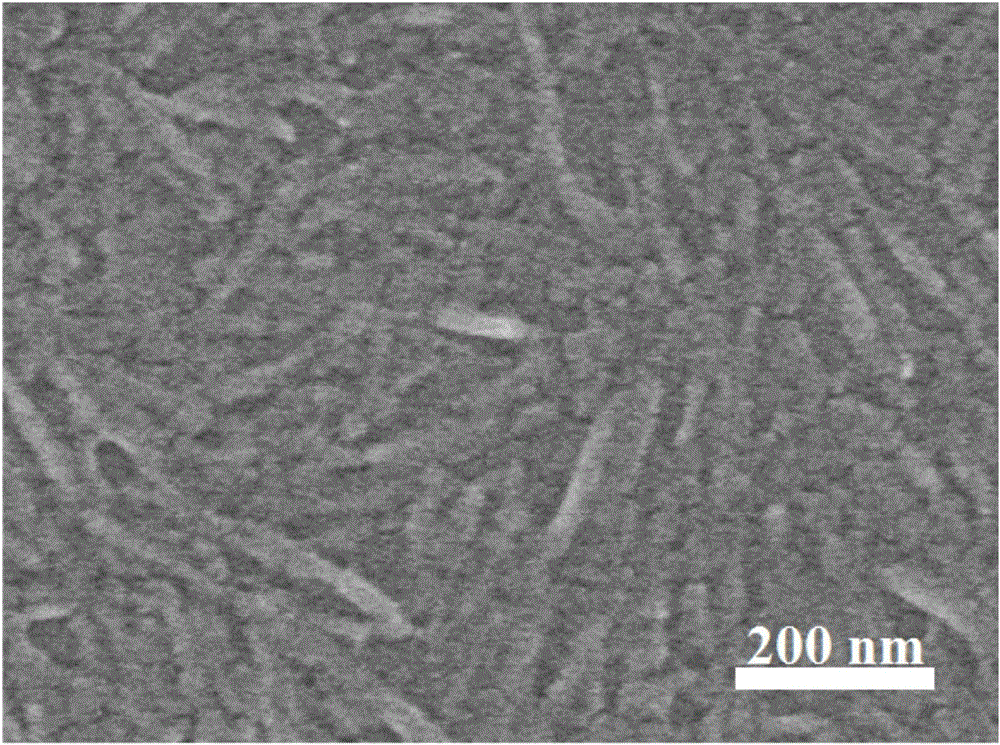
[0038] Fully soak the manufactured paper in a mixed solution of 2mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution and 1mol / L perchloric acid aqueous solution, wherein the volume ratio of hydrochloric acid to perchloric acid is 1:1, and then transfer it to a hydrothermal kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene Medium; Among them, the solid content of the paper in the mixed solution is 0.02g / mL. The reaction was carried out at 80° C. for 6 h. After the hydrothermal kettle was naturally cooled, the reaction product was poured out and diluted with deionized water. The solution is washed to be close to neutral by suction filtration to obtain a uniformly distributed dispersion of carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles; freeze-dried to obtain carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles. like image 3 Scanning electron microscope observation shows that the prepared cellulose nanoparticles are rod-shaped, with a length of 140-310nm and a diameter of 6-25nm. Figure 4 The carboxyl peak appeared in t...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The wood pulp is fully soaked in the mixed solution of 1mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution and 5mol / L hypochlorous acid aqueous solution, wherein the volume ratio of hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid is 2:3, and then transferred to a hydrothermal kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene Medium; wherein, the solid content of wood pulp in the mixed solution is 0.01g / mL. The reaction was carried out at 100° C. for 0.5 h. After the hydrothermal kettle was naturally cooled, the reaction product was poured out and diluted with deionized water. The solution is washed to be close to neutral by suction filtration to obtain a uniformly distributed dispersion of carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles; freeze-dried to obtain carboxylated cellulose nanoparticles. like Figure 5 Scanning electron microscope observation shows that the prepared cellulose nanoparticles are rod-shaped, with a length of 120-310nm and a diameter of 8-22nm. Image 6 The carboxyl peak appeared i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com