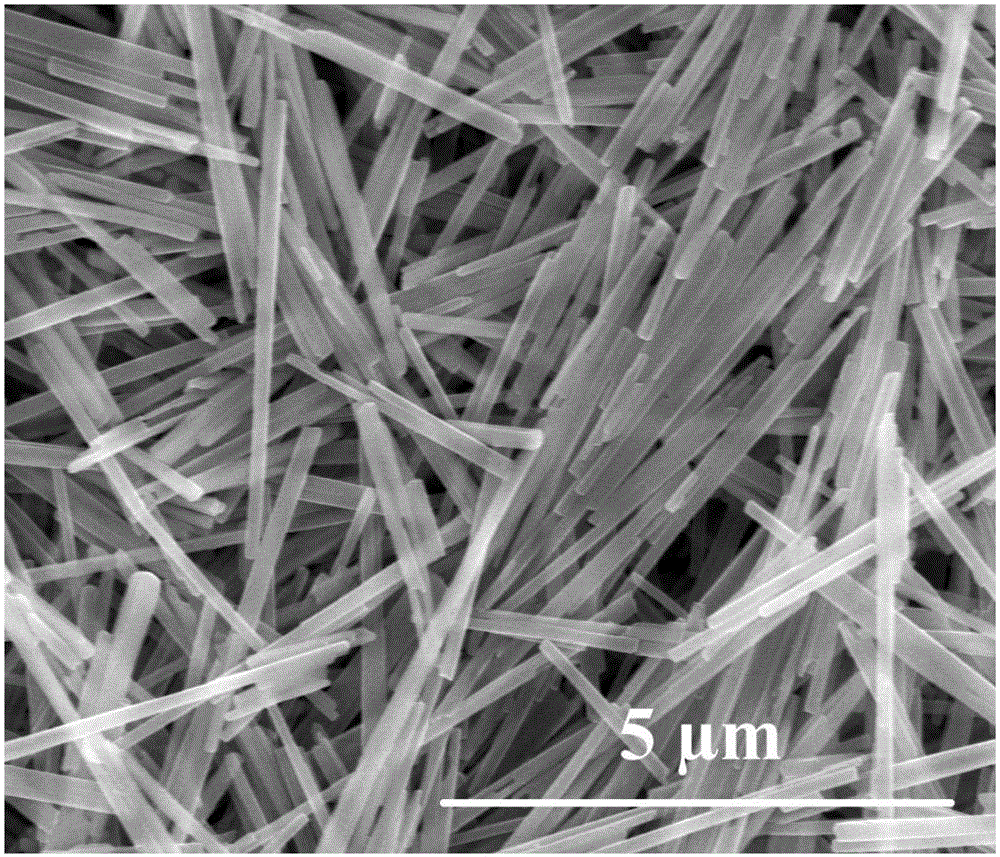
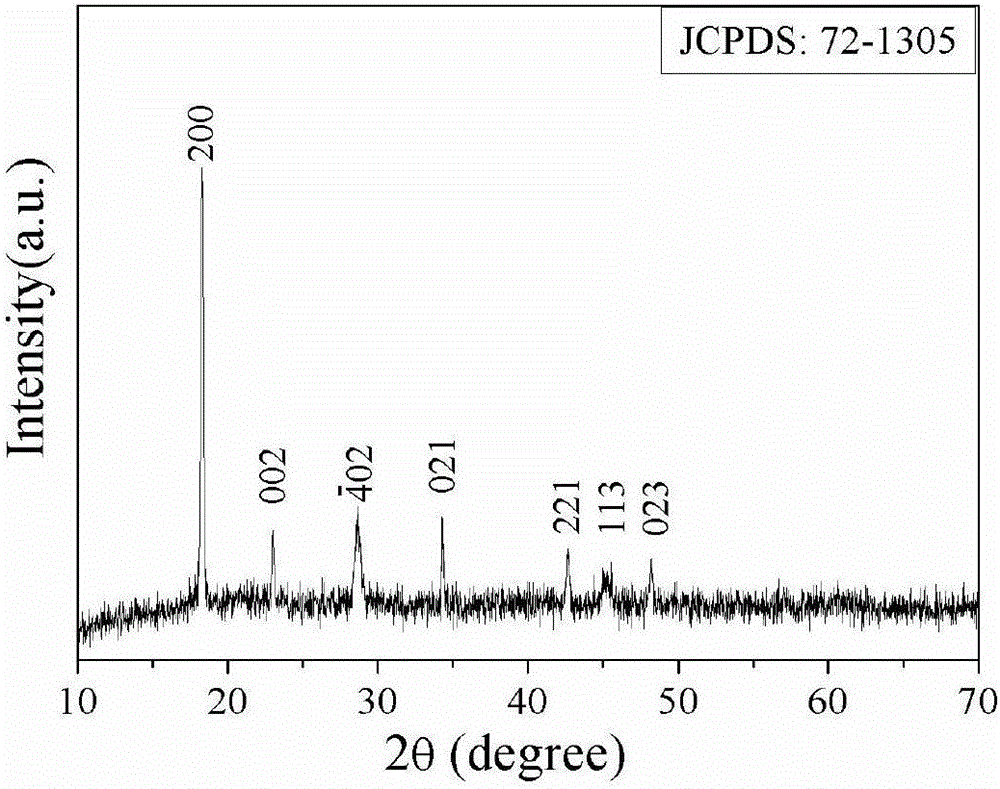
Ferric oxide nano material, preparation method of ferric oxide nano material, lithium ion battery negative pole and lithium ion battery
A ferric oxide and lithium ion battery technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of ferric oxide reversible cycle capacity attenuation, low storage capacity of graphite lithium, excessively long dendrite piercing, etc. Denaturation, good product quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
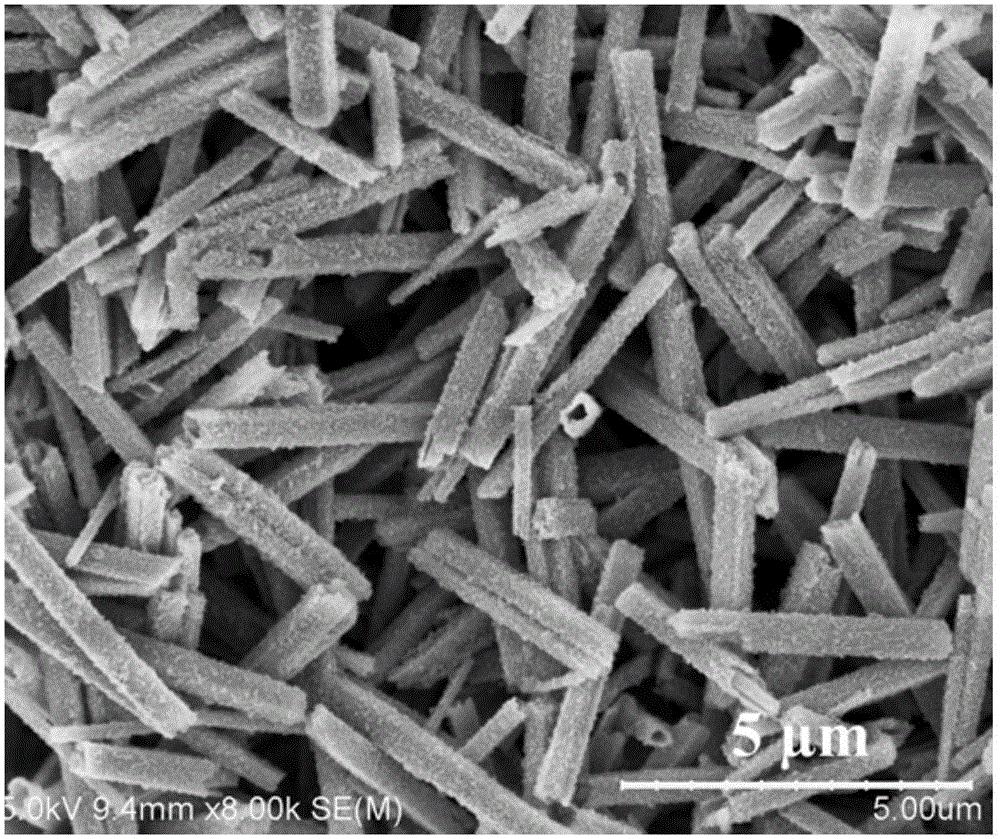
[0048]1. Mixing process: Dissolve 0.1g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate in a mixed solution of 16mL of ethylene glycol and 8mL of distilled water, then add 20 microliters of hydrazine hydrate solution with a mass fraction of 50% as an antioxidant to obtain a green solution, marked It is solution a; dissolve 0.046g and 0.02g of oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide in a mixed solution of 16mL ethylene glycol and 8mL distilled water successively, and mark it as solution b. After placing the above two solutions of a and b in a water bath at 30°C for 2 minutes, quickly pour the solution of a into the solution of b in a 30°C oven with stirring, and continue to stir for 2 minutes to obtain a light yellow turbid solution. The cloudy solution was left to age at 30°C for 12 hours, and then the precipitate was filtered, washed, and vacuum-dried at 30°C for 12 hours to obtain light yellow ferrous oxalate dihydrate precursor powder.
[0049] 2. Transformation process: Disperse 0.1g of ferrous o...
Embodiment 2
[0052] 1. Mixing process: Dissolve 0.5g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate in a mixed solution of 16mL of ethylene glycol and 8mL of distilled water, then add 25 microliters of hydrazine hydrate solution with a mass fraction of 50% as an antioxidant to obtain a green solution, marked Liquid b; 0.23 g and 0.1 g of oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide were successively dissolved in a mixed solution of 16 mL of ethylene glycol and 8 mL of distilled water, and marked as liquid a. After placing the above two solutions of a and b in a water bath at 50°C for 10 minutes, quickly pour liquid b into liquid a under the condition of stirring in an oven at 50°C, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain a light yellow turbid solution. The cloudy solution was left to age at 50°C for 8 hours, and then the precipitate was filtered, washed, and vacuum-dried at 50°C for 8 hours to obtain light yellow ferrous oxalate dihydrate precursor powder.
[0053] 2. Transformation process: Disperse 0.1g of f...
Embodiment 3
[0056] 1. Mixing process: Dissolve 1.5g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate in a mixed solution of 32mL of ethylene glycol and 10mL of distilled water, and then add 35 microliters of hydrazine hydrate as an antioxidant to obtain a green solution, which is marked as liquid b; 0.8g and 0.5g of oxalic acid and sodium hydroxide were successively dissolved in a mixed solution of 32mL of ethylene glycol and 10mL of distilled water, marked as liquid a. After placing the above two solutions of a and b in a water bath at 60°C for 10 minutes, quickly pour liquid b into liquid a under the condition of stirring in an oven at 60°C, and continue stirring for 5 minutes to obtain a light yellow turbid solution. The cloudy solution was left to age at 70°C for 4 hours, and then the precipitate was filtered, washed, and vacuum-dried at 70°C for 6 hours to obtain light yellow ferrous oxalate dihydrate precursor powder.
[0057] 2. Conversion process: Disperse 0.2 g of ferrous oxalate dihydrate precur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com