Facultative anaerobic acinetobacter with cellulose degrading capability and application of facultative anaerobic acinetobacter
A cellulose degradation, facultative anaerobic technology, applied in the field of new strains, can solve problems such as production difficulties, obligate anaerobic bacteria poisoning, restrictions, etc., to reduce process costs, improve cellulose decomposition efficiency, and ensure the effect of fermentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Isolation and purification of strains
[0015] Compost samples were collected from vegetable straw compost in Qingzhou Compost Plant, Shandong Province.
[0016] Take 10 g of compost samples at the maturity stage, add them to a conical flask filled with 100 ml of sterile water (with glass beads), and shake for 20 minutes. Take 5ml of the sample suspension and put it into a Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml of liquid LB medium, culture at 37°C and shake at 180r / min for 8 hours: take 1ml of the cultured bacterial solution, add it to 9ml of sterile water, and use sterile water to The serial dilution method made a dilution of 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 Take 100 μl of each sample solution and spread it on the culture medium with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as the only carbon source, and make three parallel samples for each dilution. Under the condition of 37°C, they were cultured in the aerobic and anaerobic incubators at constant temperature for 48 h...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Identification of strains
[0021] The strains with higher D / d values under aerobic and anaerobic culture were selected for genomic DNA extraction respectively. DNA was extracted using TIANGEN Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit. Take 5 μl spotting sample, use λEcoT14 as Marker, and detect by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the electrophoresis picture is as follows figure 1 As indicated, the rest were stored at -20°C.
[0022] The extracted genomic DNA was amplified by 16s rDNA PCR. Using 16s rDNA universal primers, using the extracted strain genomic DNA as a template, amplify according to the following reaction system and amplification conditions. Primer sequence: upstream primer P1 (008F) AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG downstream primer P2 (1392R) CGGGCGGTGTGTRC The reaction system is shown in the table below. PCR products were detected by 1% agarose electrophoresis.
[0023] Table 1 PCR amplification reaction system and reaction procedure of 16s rDNA
[0024]
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Determination of cellulolytic enzyme activity under aerobic conditions
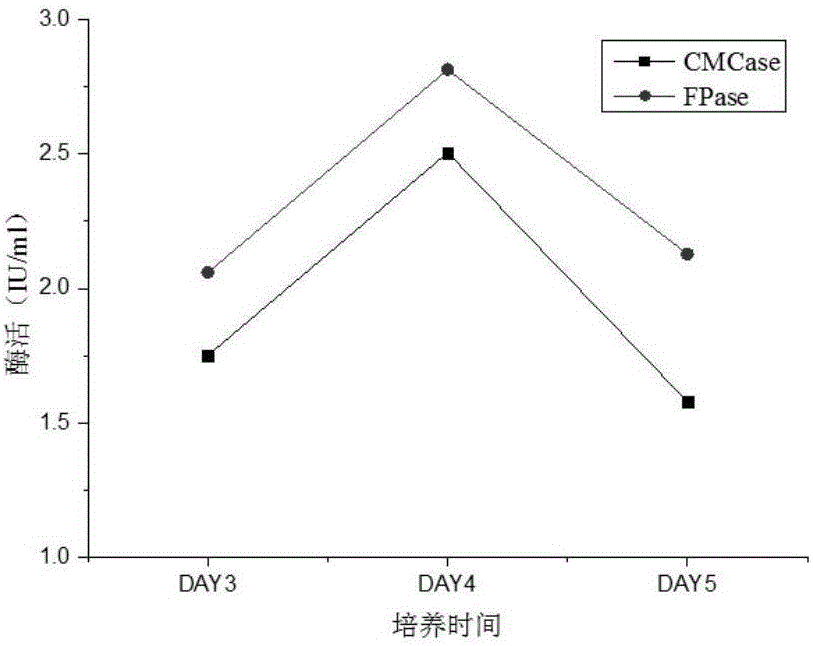
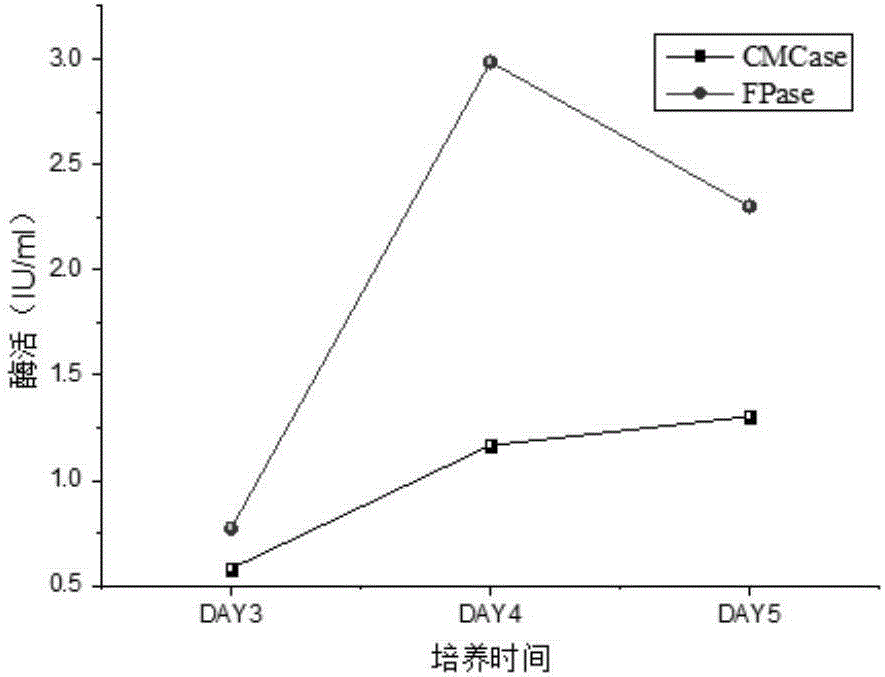
[0029] A single colony of Acinetobacter sdwt001 was picked with an inoculation loop and inserted into LB liquid medium, and cultured at 37°C and 160r / min for 24h. Each 10ml seed solution was transferred to 90ml PCS medium with filter paper or sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as the carbon source and cultured at 160r / min at 37°C. On the 3rd, 4th, and 5th days of fermentation, 10ml of the fermentation broth was taken and centrifuged at 5000r / min for 10min, and the supernatant was taken as the crude enzyme solution for the corresponding enzyme activity to be tested.
[0030] Take 2ml of 1% sodium carboxymethylcellulose (prepared with 0.1M citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution with pH=4.8) as the substrate, take 0.5ml of the corresponding crude enzyme solution, and incubate in a stoppered graduated test tube at 50°C For 1 h, the heat-inactivated crude enzyme solution was used as a control, and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com