Method for recycling metal in tungsten carbide waste through fluoride electrolysis
An electrolytic recovery and fluoride technology, applied in the field of molten salt electrolysis, can solve the problems of inability to increase the voltage value and current value, impure cathode product, large volatilization loss, etc., to reduce the electrochemical precipitation potential, ensure electrochemical separation, The effect of improving electrochemical activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The setting of the electrolysis device is as follows: the electrolysis cell is a graphite crucible, which is placed in a closed container, and the closed container provides gas protection and electric heating. The cathode and anode extend into the molten salt in the electrolytic cell.
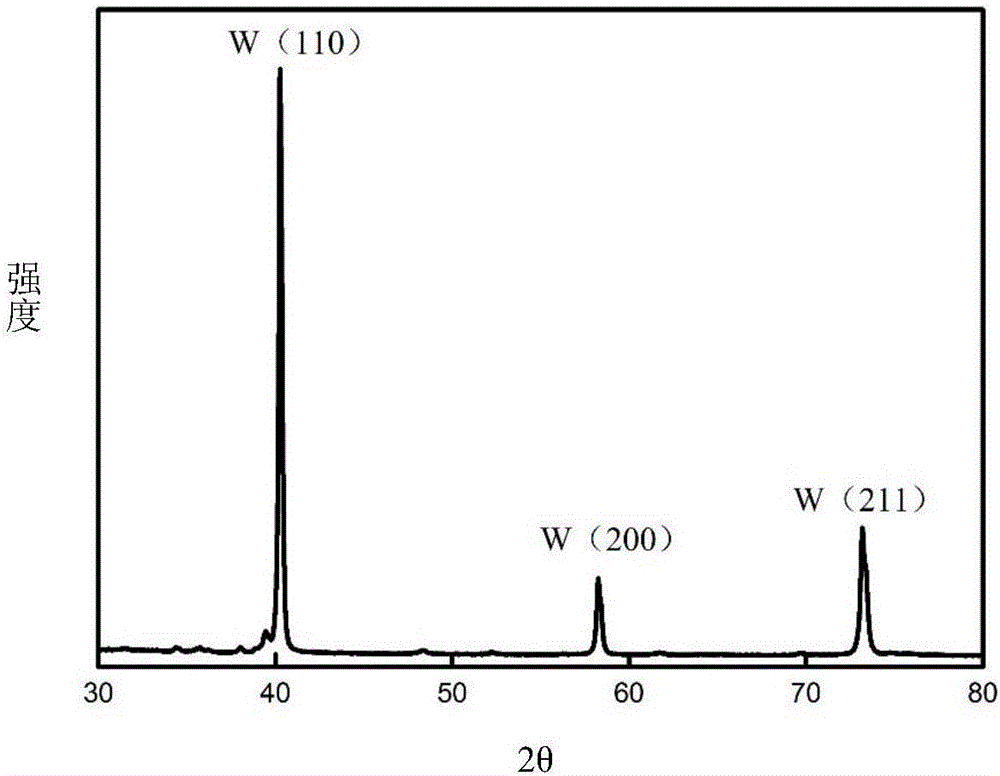
[0048] Using tungsten carbide waste as a consumable anode, nano-tungsten powder was prepared by molten salt electrolysis. The size of the tungsten carbide waste is 4mm×4mm×18mm, the depth of the interface inserted into the molten salt is 6mm, and the electrolytic cell is protected by 99% high-purity argon gas. The molten salt system is composed of NaF-KF (39.7% mol-60.3% mol), the electrolysis temperature is 800°C, the metal nickel sheet (8mm×40mm×0.3mm) is used as the cathode, the electrode spacing is 25mm, the voltage is controlled for electrolysis, and the electrolysis voltage is controlled at 2V, tungsten powder is precipitated from 2 hours, and the electrolysis time is 4 hours.
...
Embodiment 2
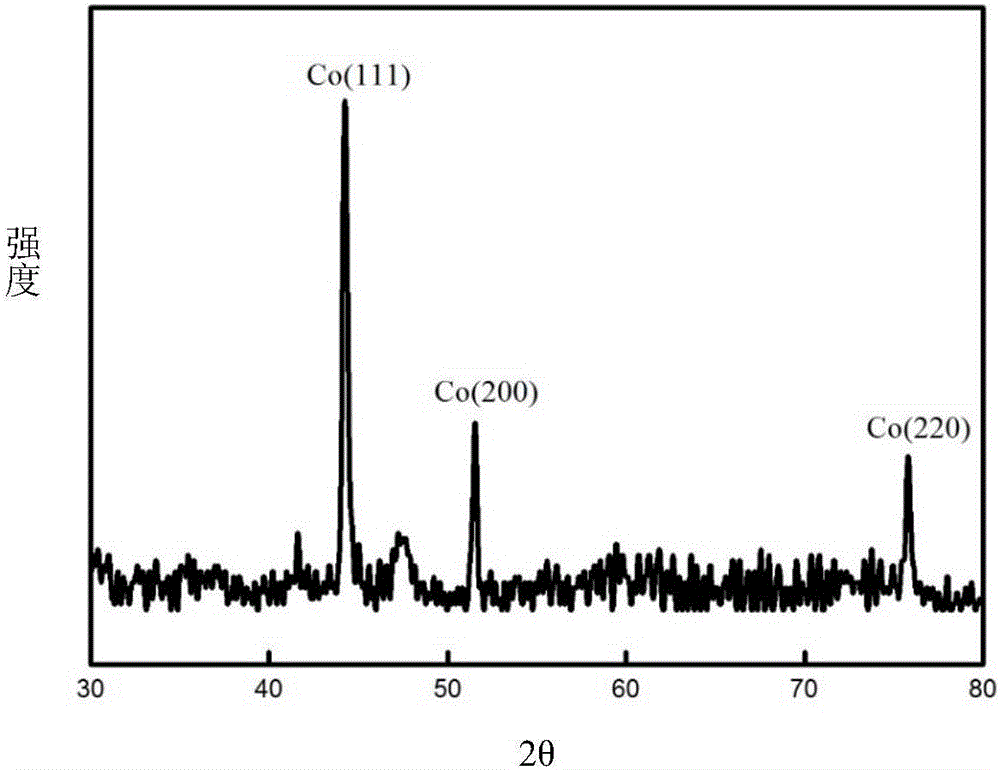
[0054] The setting of the electrolysis device is the same as in Example 1. Using waste cemented carbide as a consumable anode, pure cobalt metal powder was prepared by molten salt electrolysis. The waste cemented carbide is WC-6% Co, the size is 4mm×4mm×18mm, the depth of the interface inserted into the molten salt is 6mm, and the electrolytic cell is protected by 99% high-purity argon gas. The composition of the molten salt system is NaF-KF (39.7% mol-60.3% mol), the electrolysis temperature is 750°C, the metal nickel sheet (8mm×40mm×0.3mm) is used as the cathode, the electrode distance is 35mm, the current is controlled for electrolysis, and the electrolysis current is controlled at 20mA (That is, the initial current density of the anode is 0.0178A / cm 2 , as the electrolysis proceeds, the anode current density increases; the cathode current density is 0.02A / cm 2 , the cathode is inserted 6mm deep), and the electrolysis time is 2h. During electrolysis, the cell voltage is ...
Embodiment 3
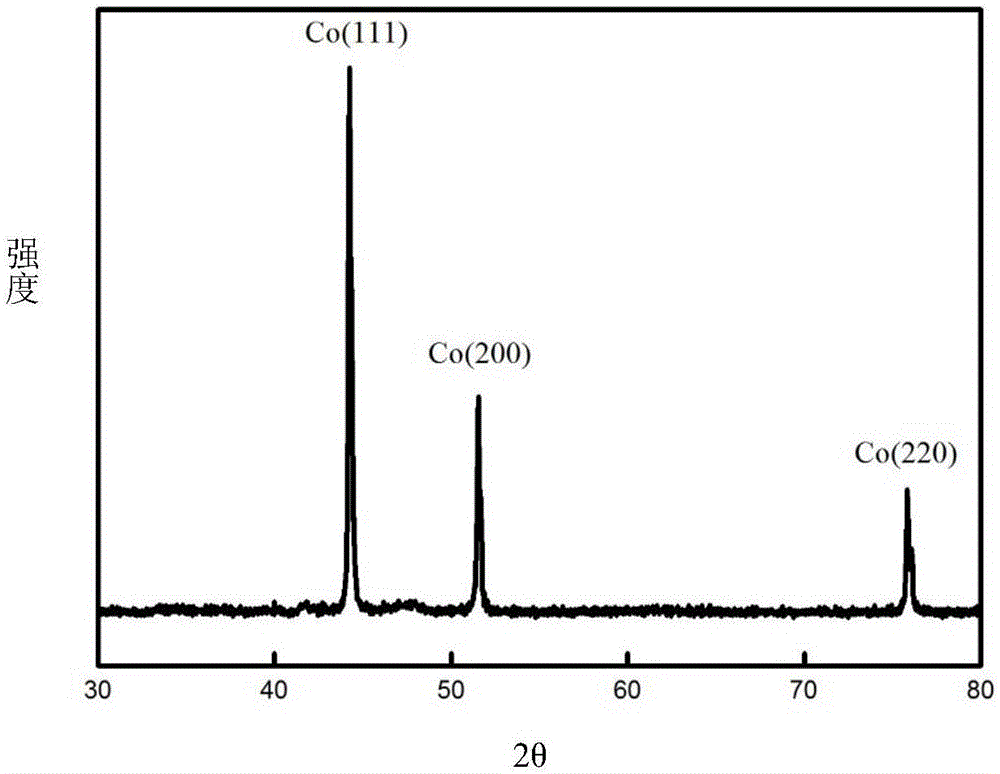
[0063] Using waste cemented carbide as a consumable anode, pure cobalt metal powder was prepared by molten salt electrolysis. The waste cemented carbide is WC-16% Co, the size is 4mm×4mm×18mm, the depth of the interface inserted into the molten salt is 10mm, and the electrolytic cell is protected by 99% high-purity argon gas. The composition of the molten salt system is NaF-KF (39.7% mol-60.3% mol), the electrolysis temperature is 850°C, the metal nickel sheet (8mm×40mm×0.3mm) is used as the cathode, the electrode distance is 40mm, the current is controlled for electrolysis, and the electrolysis current is controlled at 60mA , Electrolysis time 4h. The products obtained by electrolysis are collected by washing with water, centrifuging, and blowing and drying. The blast drying temperature is 40°C, and the drying time is 10 hours.
[0064] The cobalt powder obtained by electrolysis has a purity of 98.9%, a cathode current efficiency of 53.57%, and an anode electrochemical diss...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com