Green synthesis method of acrylonitrile polymer
A green synthesis, acrylonitrile technology, applied in the field of polymer synthesis, can solve the problems of difficult control of ray irradiation polymerization, and achieve the effects of avoiding complex side reactions, narrow molecular weight distribution, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of RAFT reagent
[0059] Add 1-bromonaphthalene (22.5 g, 0.11 mol) and tetrahydrofuran (90 mL) slowly into a 250 mL three-necked flask with magnesium strips (2.88 g, 0.12 mol) and a small amount of iodine for about 1 hour. React for 3 hours at 40~50°C. At room temperature, carbon disulfide (8.36 g, 0.11 mol) was added to the reaction system, and then the reaction was continued for 8 hours. The reaction solution was poured into water, acidified with 2 mol / L aqueous hydrochloric acid, and then extracted with dichloromethane (40 mL×3). The organic layer was washed with saturated brine and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, the crude product was dissolved in 50 mL ethyl acetate, and reacted with 2.53 g DMSO and a small amount of iodine overnight. Under ventilation, AIBN (10.8 g, 0.066 mol) and 40 mL of benzene were added to the system, and reacted at 70 °C for 15 hours. After the solvent ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: A kind of green synthetic method of acrylonitrile polymer
[0061]
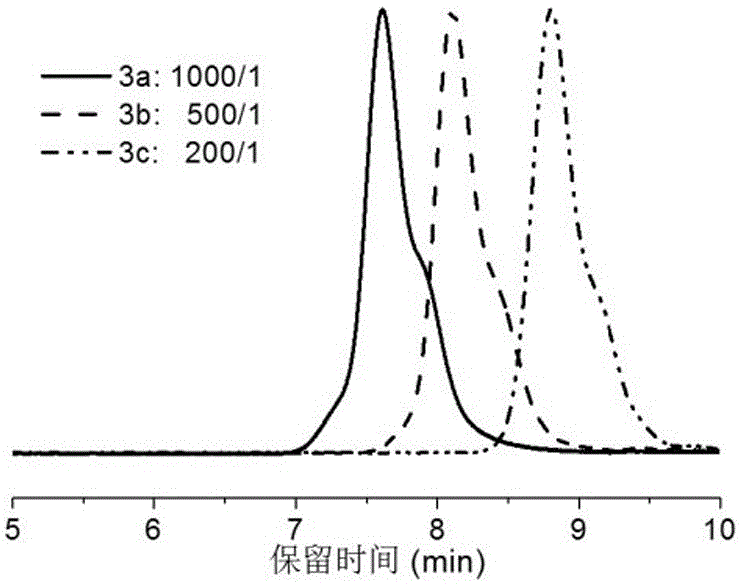
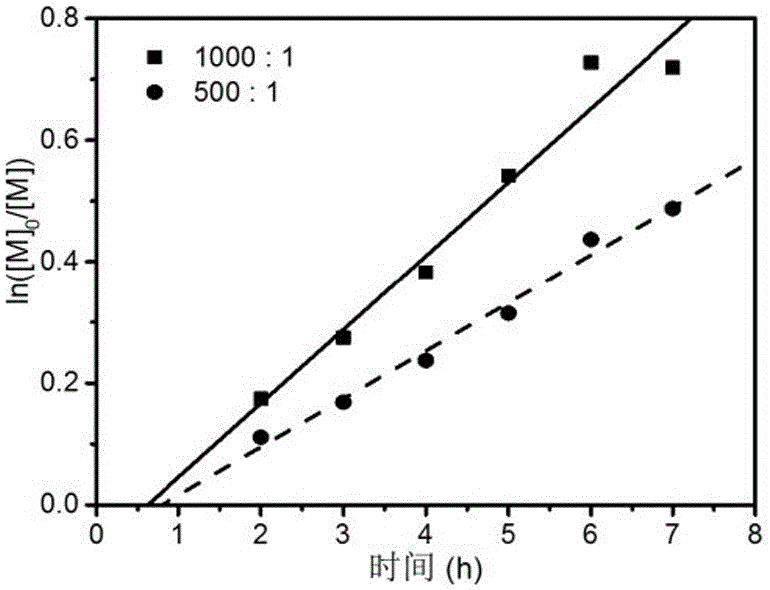
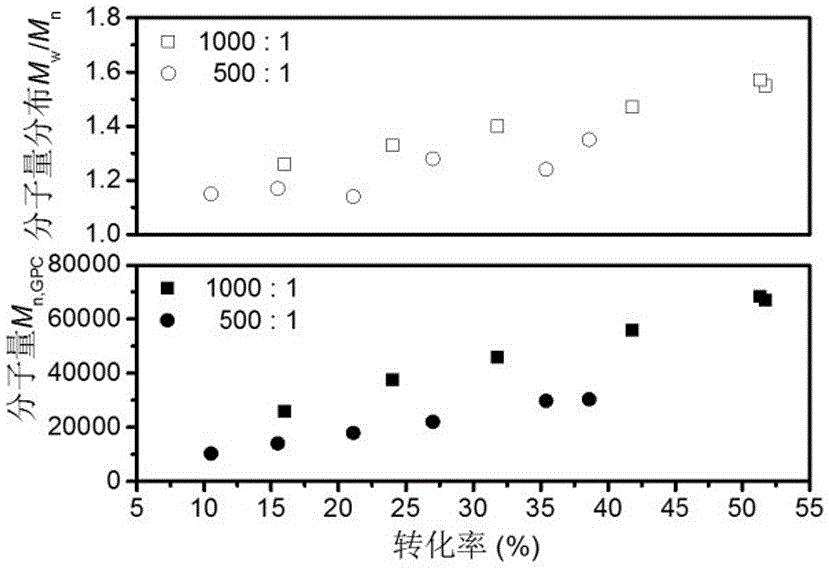
[0062] Add the RAFT reagent obtained in Example 1, acrylonitrile (AN), and solvent ethylene carbonate (EC, 2.64 g) into a 5 mL ampoule, deoxygenate with nitrogen bubbling, and 60 The polymerization reaction occurs under the irradiation of Co-γ rays, and the acrylonitrile polymer reacts at room temperature. Stop the reaction to obtain polyacrylonitrile polymer. Table 1 shows the results of radiation-induced free radical polymerization of acrylonitrile under different conditions.
[0063] Table 1 Radiation-induced free radical polymerization results of acrylonitrile under different conditions
[0064]
[0065] Polystyrene is used as a standard sample in the GPC test; the conversion rate is calculated by weighing method; the theoretical molecular weight calculation equation is:
[0066] .
[0067] Table 1 shows some radiation-induced free radical polymerization results of acrylon...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3: A kind of green synthetic method of acrylonitrile polymer
[0073] Add 15.26 mg of PAN (1c in Table 1), 0.41 g of acrylonitrile (AN), and 1.32 g of ethylene carbonate (EC) into a 5 mL amber bottle, deoxygenate with nitrogen bubbling, 60 The polymerization reaction occurs under the irradiation of Co-γ rays, and the reaction time is 4 hours. Then the reaction solution was dissolved in DMF (2 mL), and then dissolved in 200 mL of methanol; suction filtered, and the obtained polymer was dried in a vacuum oven at 30°C for 24 hours to obtain 123.0 mg of acrylonitrile polymer.
[0074] Figure 8 It is the GPC efflux curve before and after the polymerization of acrylonitrile monomer initiated by polyacrylonitrile as RAFT reagent, Figure 9 It is the NMR spectra of polyacrylonitrile before and after the polymerization of acrylonitrile monomer initiated by RAFT reagent; as can be seen from the figure, the molecular weight of polyacrylonitrile has changed before and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com