Cell culture method using plant epidermis as tissue engineering scaffold material
A technology of tissue engineering scaffold and plant epidermis, which is applied in the field of cell culture, can solve the problems of spreading diseases, causing inflammatory reactions, accumulation of local acid products, improper handling, etc., and achieves good transparency and is conducive to the growth and arrangement of stratification tight effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Rabbit Primary Corneal Epithelial Cell Culture
[0032] Among the present embodiment, the medium and reagents used are as follows:
[0033] SHEM medium: 5% FBS (fetal bovine serum), 0.5g / mL hydrocortisone, 1% ITS (insulin, transferrin and selenium solution), 0.5% DMSO (di methyl sulfoxide), 10 ng / mL human EGF (human epidermal growth factor), 1% PS (P means Penicillin penicillin, S means Streptomycin streptomycin, and the respective concentrations of penicillin and streptomycin are 1%).
[0034] Dispase (neutral protease) II digestion solution: commercially available, working concentration 2U / mL.
[0035] 10×PBS: NaCl 20g, KCl 2g, NaCl 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O 18.2g, KH 2 PO 4 2.4g, stir evenly with a stirrer, adjust the pH to 7.2-7.4, dilute it into 1×PBS and sterilize before use.
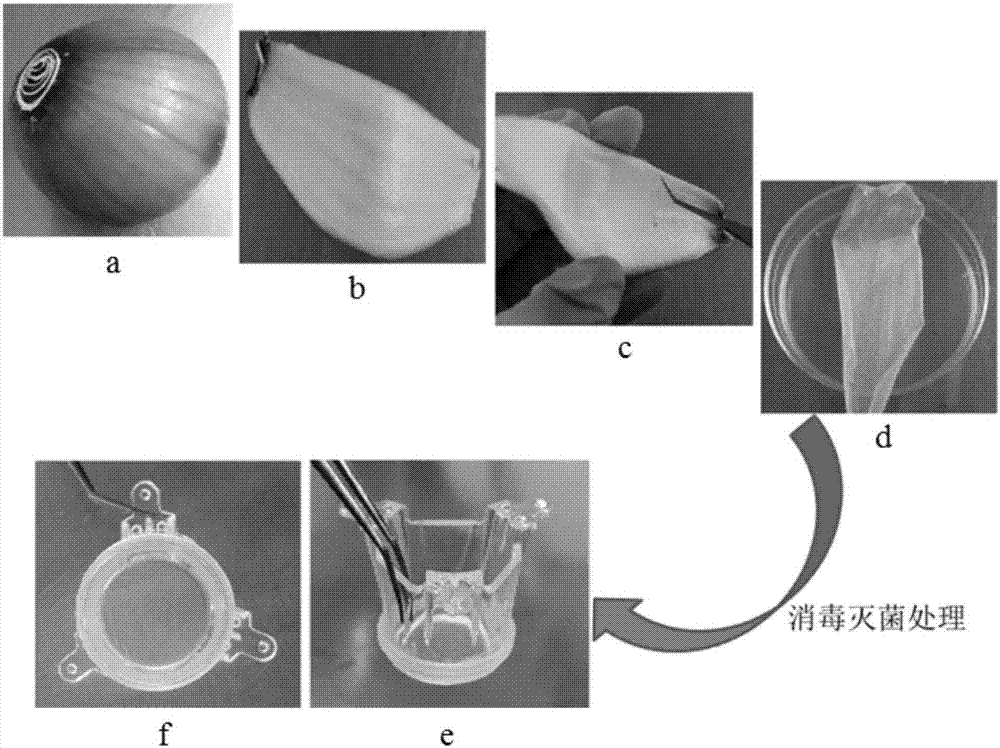
[0036] Among the present embodiment, the onion bulb inner epidermis is selected, and the rabbit primary corneal epithelial cell culture method using the onion bulb inner epidermis ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Rabbit Primary Corneal Stromal Cell Culture
[0048] Among the present embodiment, the culture medium and culture conditions adopted are as follows:
[0049] Medium: DMEM (basic), 10% FBS, 1% PS; culture conditions: 37°C, 5% CO 2 incubator.
[0050] In this example, the preparation method of the onion epidermal scaffold is the same as step 1) in Example 1.
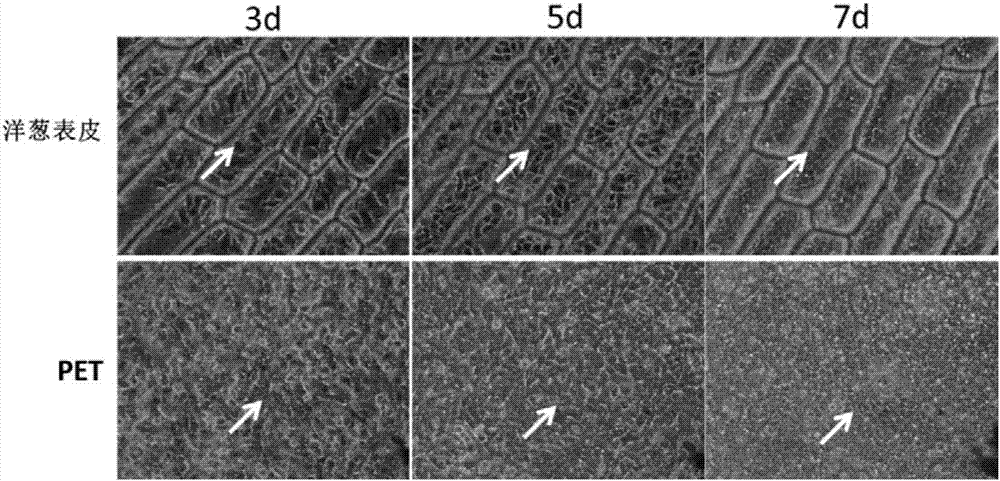
[0051] Such as Figure 6 Shown on the left side of the middle is a schematic diagram of the comparison of cell culture of rabbit primary corneal stromal cells (Rabbit Corneal StromaCells P0) on onion epidermal scaffolds and ordinary culture dishes in this embodiment. After 4-6 days of culture, the primary rabbit keratocytes grown on the onion epidermis could well maintain the shape of the keratocytes, and there was no obvious difference in shape compared with the cells on the culture dish, but the cell fusion rate was higher.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3: breast cancer cell culture
[0053] Among the present embodiment, the culture medium and culture conditions adopted are as follows:
[0054] Medium: DMEM (basic), 10% FBS, 1% PS; culture conditions: 37°C, 5% CO 2 incubator.
[0055] In this example, the preparation method of the onion epidermal scaffold is the same as step 1) in Example 1.
[0056] Breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 was cultured and digested by conventional cell culture methods according to the above conditions to obtain a cell suspension, and then 5-8×10 4 piece / cm 2 Inoculated on the onion epidermis support, cultivated according to the method of step 6) in Example 1. At the same time, cells cultured in ordinary culture dishes were used as a control.
[0057] After culturing for 1 to 2 days, the results are as follows: Figure 6 As shown in the middle right, the cell morphology of the onion epidermal scaffold group has not changed compared with that of the ordinary culture dish group, in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com