Preparation method and application of ZnO/ZnFe2O4 nano-composites
A nanocomposite material, zinc ferrite technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of inability to meet green chemistry, numerous operation steps, and inappropriate preparation in large quantities, and achieve good sensitivity, raw materials, etc. The effect of easy availability and short response time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Preparation of Zinc-Fe Prussian Blue Analog Nanomaterials
[0022] Dissolve zinc nitrate (0.089g, 0.3mmol) in 50mL deionized water to form solution A, add potassium ferricyanide (0.066g, 0.2mmol), sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (0.05g) into 50mL deionized water Form a clear solution B, add solution A dropwise to solution B under stirring, continue to stir for half an hour after the drop, keep away from light for 3 days, centrifuge, wash with water and ethanol, collect the yellow precipitate at the bottom of the beaker; place in Dry at 60° C. for 18 hours in a vacuum oven to obtain zinc-iron Prussian blue analogue nanomaterials.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Preparation of Zinc-Fe Prussian Blue Analog Nanomaterials
[0025] Zinc chloride (0.041g, 0.3mmol) was dissolved in 50mL deionized water to form solution A, and potassium ferricyanide (0.066g, 0.2mmol) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (0.08g) were added to 50mL deionized water to form a clear solution B. Add solution A to solution B dropwise under stirring, continue to stir for half an hour after the drop is completed, and age in the dark for 4 days, centrifuge, wash with water and ethanol, and collect the yellow precipitate at the bottom of the beaker. After washing with deionized water or ethanol, dry in a vacuum oven at 80° C. for 24 hours to obtain zinc-iron Prussian blue analogue nanomaterials.
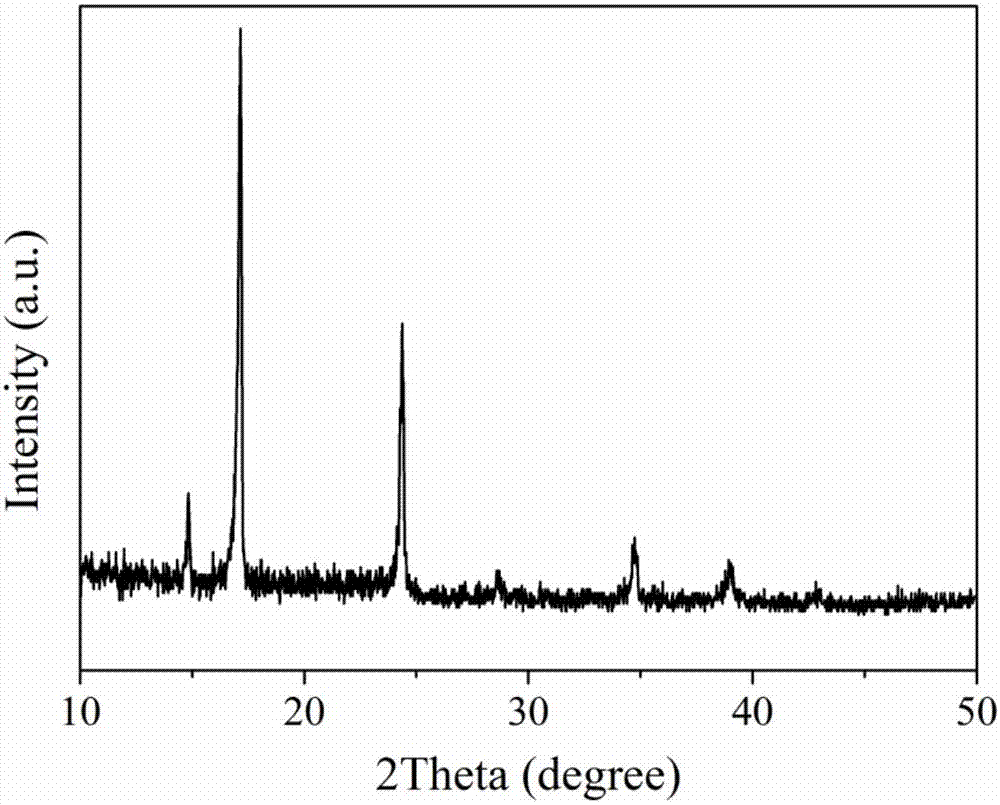
[0026] The structure was confirmed by X-ray powder diffractometer analysis, such as figure 1 The zinc-iron Prussian blue analogue nanomaterial shown is Zn 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ] 2 ·xH 2 O.
[0027] The morphology of the obtained ZnFe Prussian blue analog nanomaterials was characteriz...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Preparation of ZnO / ZnFe 2 o 4 Nanocomposite
[0030] Weigh 20 mg of the zinc-iron Prussian blue analogue nanomaterial in Example 1 or Example 2 into a crucible, place it in a muffle furnace, and perform high-temperature calcination in an air atmosphere. The calcination temperature is 450°C, the heating rate is 2°C / min, and the calcination time is 3h.
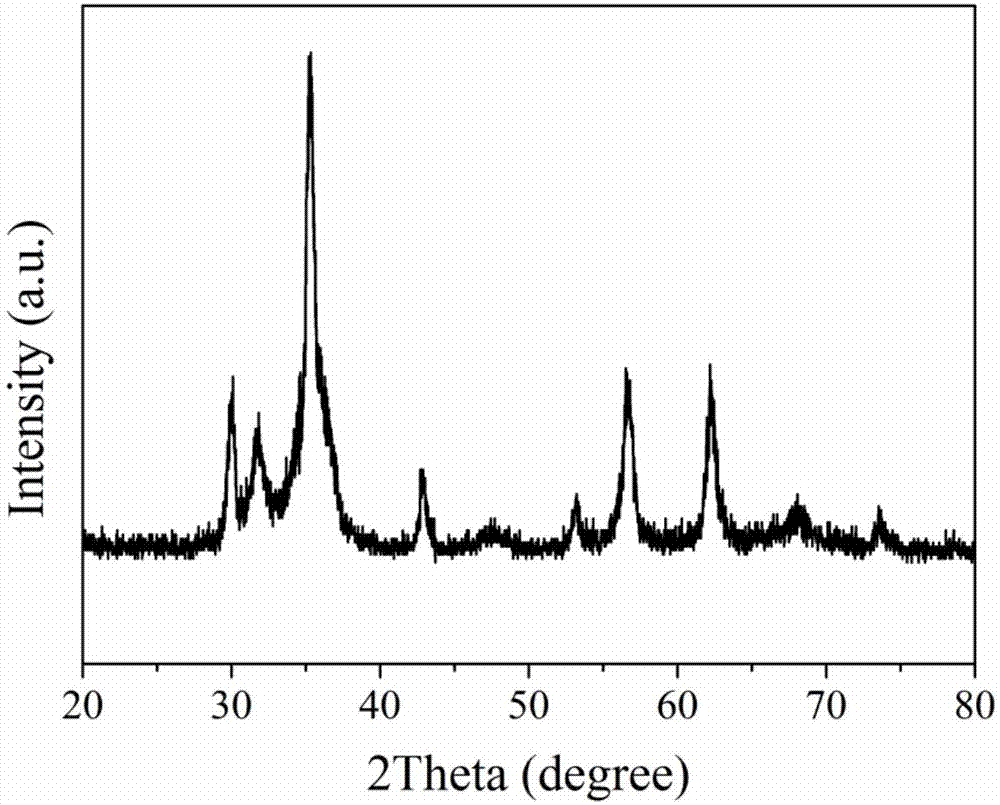
[0031] The structure was confirmed by X-ray powder diffractometer analysis, such as figure 2 The material structure composition of the composite material shown is ZnO / ZnFe 2 o 4 nanocomposites.
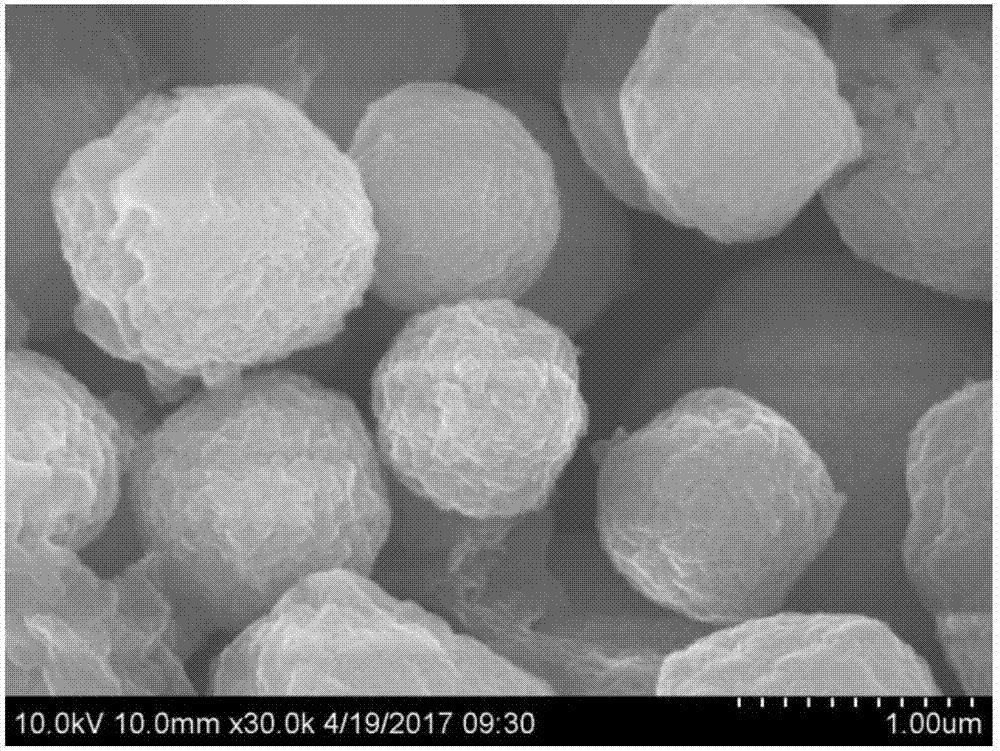
[0032] Characterization of ZnO / ZnFe obtained by scanning electron microscopy 2 o 4 Morphology of nanocomposites. Such as figure 2 As shown, the resulting ZnO / ZnFe 2 o 4 Nanocomposites are hollow spherical structures with rough surfaces.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com