L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase and application thereof in catalytic synthesis of rare sugar D-psicose
A phosphate aldolase and amino acid technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of difficult product separation and purification, low yield, difficult refining and purification, etc., and achieve the effects of high synthesis efficiency, cost saving and high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The RhaD coding gene was inserted into the expression vector pET-28a by double digestion with BamHI and SacI to obtain the recombinant expression plasmid pET-28a-rhaD. Using the plasmid pET-28a-rhaD as a template, saturation site-directed mutations were performed on the active region of L-rhamnosan-1-phosphate aldolase RhaD. See SEQ ID NO.1 for the gene sequence of wild-type L-rhamnosan-1-phosphate aldolase.
[0043] The primer sequences are:
[0044] Wild-type rhaD amplification primers:
[0045] Upstream primer rhaD-F GCGC GGATCC ATGCAAAACATTACTCAG (the underlined sequence is the BamHI restriction site);
[0046] downstream primer rhaD-R GCGC GAGCTC TTACAGCGCCAGCGCACTG (the underlined sequence is the SacI restriction site).
[0047] As well as carrying out combined site mutations of more than two RhaD active region sites, the wild-type RhaD recombinant expression plasmid pET-28a-rhaD was used as a blank control in this study. The sites of the saturation site-d...
Embodiment 2
[0063] RhaD aldolase wild type and mutant enzyme activity detection:
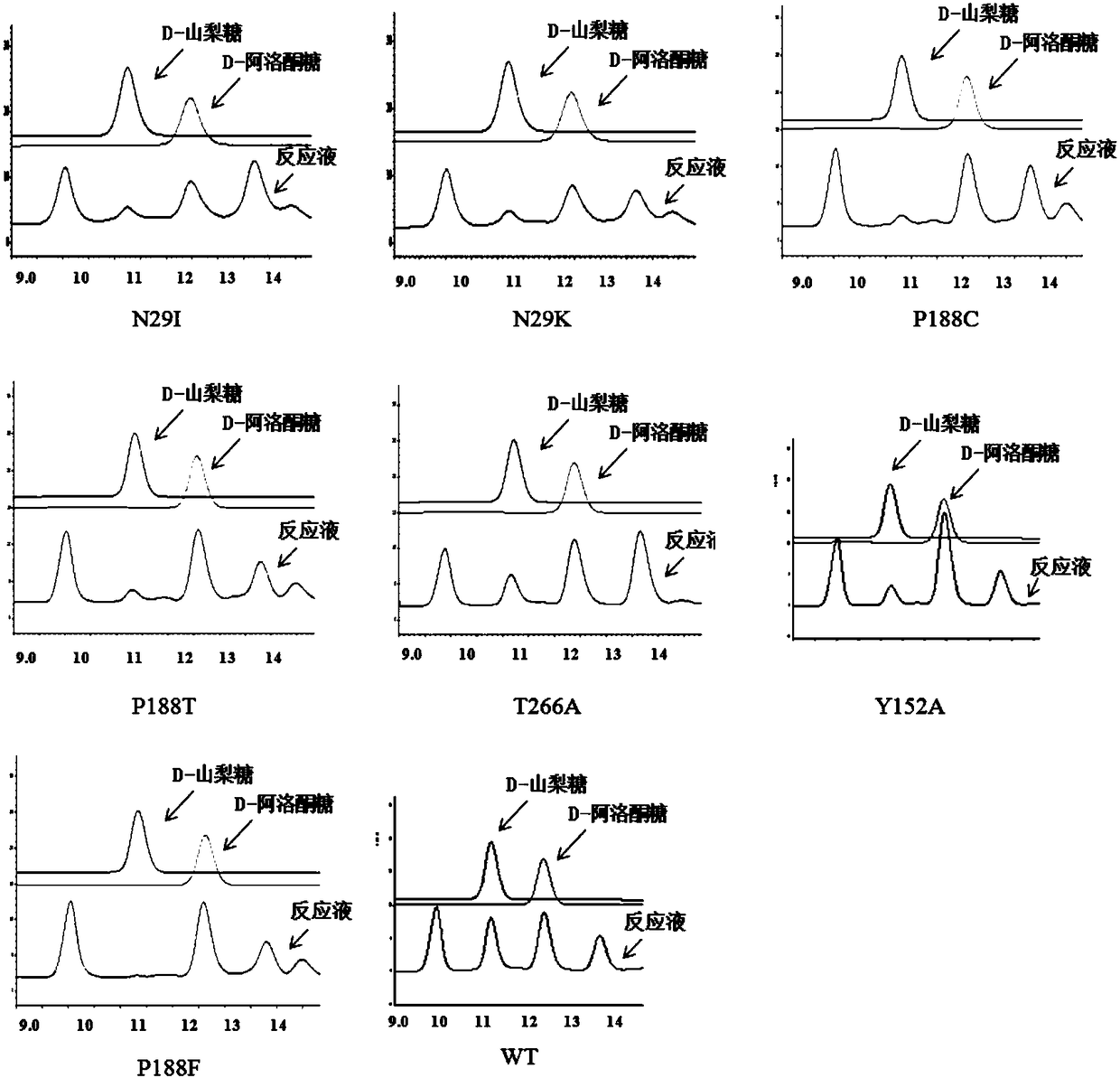
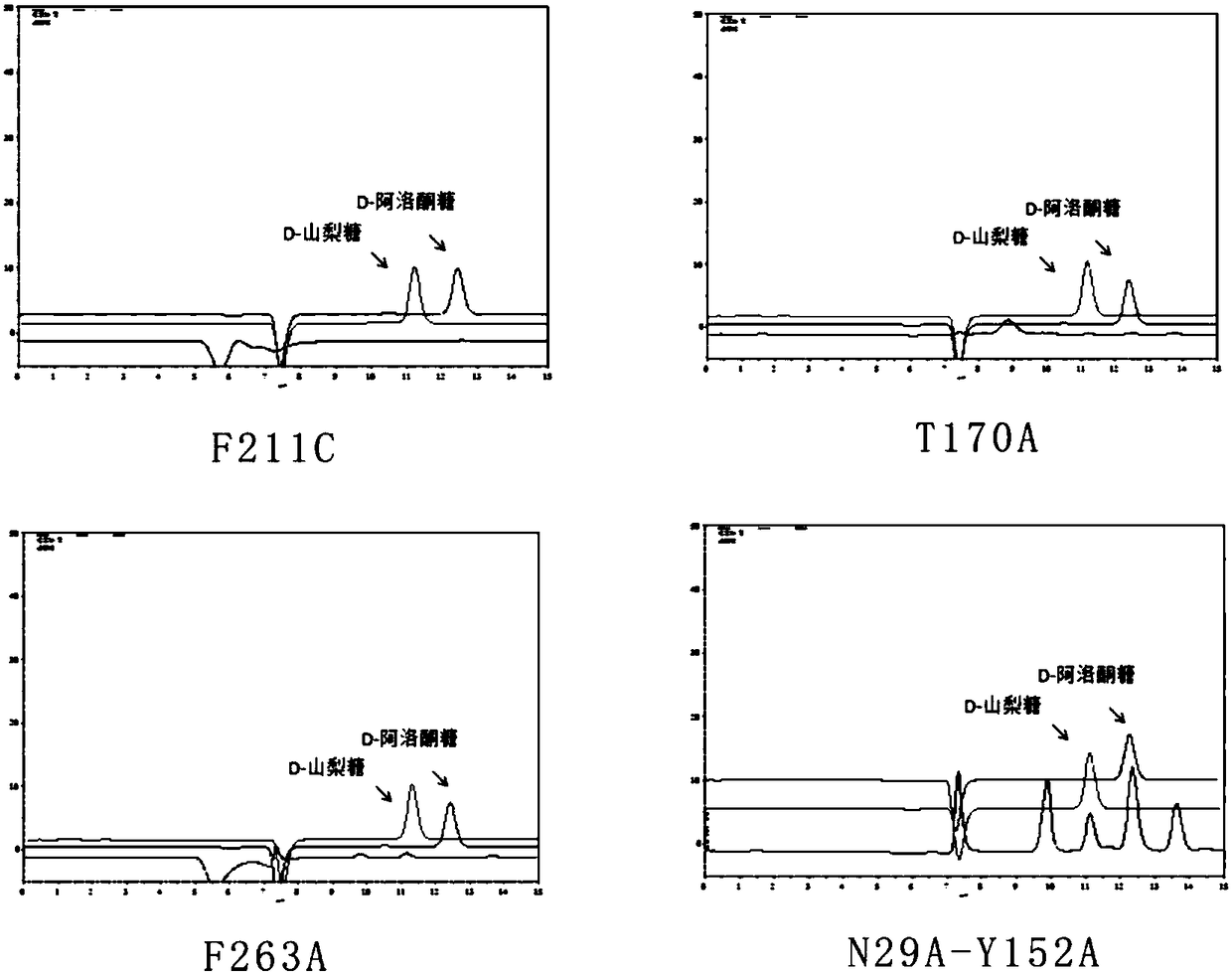
[0064] For the determination of enzyme activity, the 50 μL total volume reaction system is as follows: DHAP (0.2M, 5 μL, 0.02M); D-glyceraldehyde (0.5M, 2 μL, 0.02M), aldolase RhaD wild type or mutant (10mg / mL , 2.5 μL, 0.5 mg / mL) was supplemented with 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) to a volume of 50 μL. The reaction was allowed to stand at 30°C overnight, and the pH was adjusted to 5 with 3M HCl, then 0.25 μL of acid phosphatase AP was added, and the reaction was left to stand at 30°C overnight. At the end of the reaction, 3M NaOH was used to adjust the pH to 7 to terminate the reaction, and then centrifuged at 15000 g for 10 min to collect the supernatant. HPLC detection, such as figure 1 and figure 2 shown.
[0065] The chromatographic conditions of the present invention are: a Hitachi differential detector (HITACHI RI), a chromatographic column Bio-Rad Aminex HPX-87H, a mobile phase of 5 mmol / L dilute sul...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Stereoselective analysis of RhaD aldolase:
[0071] This study found that the L-rhamnosugar-1-phosphate aldolase (RhaD) of the dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)-dependent aldolase family derived from Escherichia coli MG1655 catalyzed two reaction substrates: the first One is dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and the second is aldehydes. When D-glyceraldehyde is used as the aldehyde acceptor, the stereoselectivity of the aldehyde acceptor is lost, and two rare sugars, D-psicose and D-sorbose, are produced, and the ratio of the two is close to 1:1. When the site-directed mutant strains N29I, N29K, P188C, P188T, T266A, and Y152A of MG1655 RhaD used DHAP and D-glyceraldehyde as substrates, D-psicose was mainly produced, while the RhaD site-directed mutant strain of Escherichia coli MG1655 strain P188F can completely synthesize D-psicose, and the specific experimental results are shown in Table 1.
[0072] In this study, site-directed saturation mutations were performed on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com