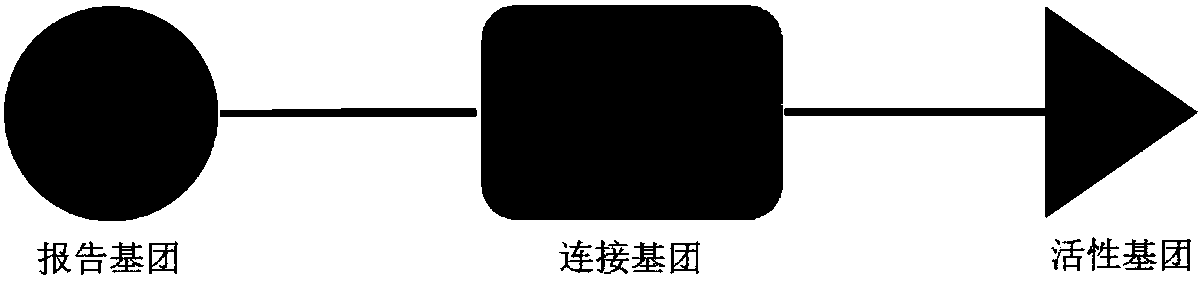
Analytical method for related enzymes in biosynthesis pathway of plant secondary metabolites
A technology of substrates and compounds, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biomaterial analysis, biological testing, etc., can solve problems such as incompatibility, heavy workload, and incomplete protein expression levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
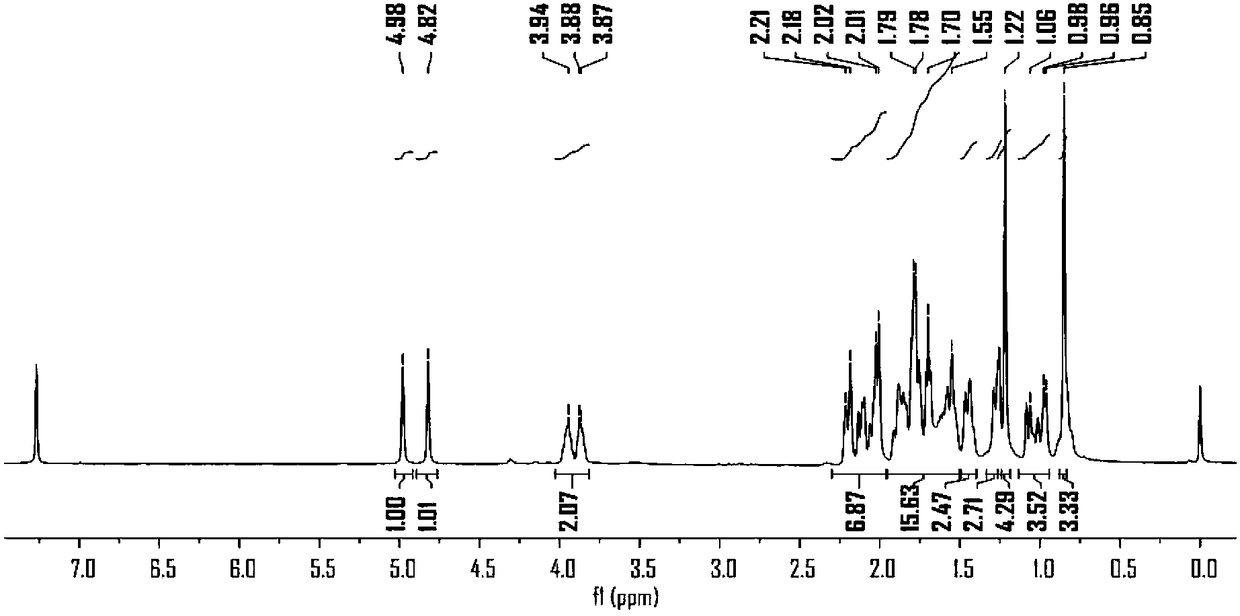
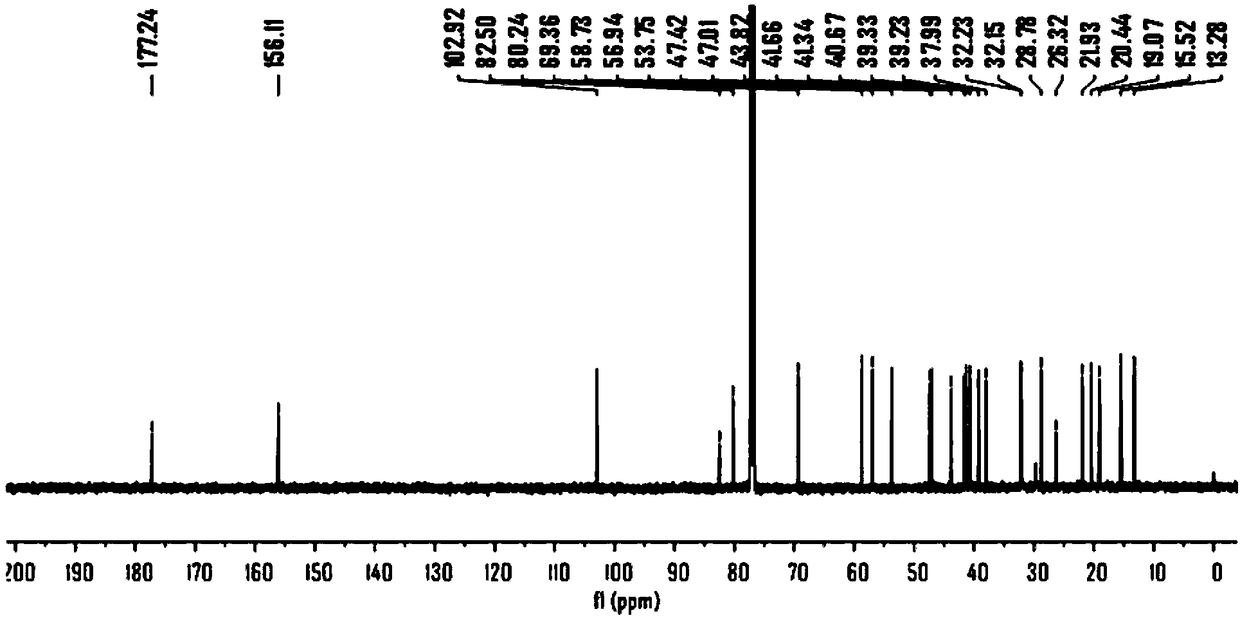
[0089] Experimental Example 1: Synthesis of Probe Molecule 1
[0090] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0091] Compound 1-1 was synthesized in this laboratory according to the method of reference (Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(33):8551-8556.); the reagents used for chemical synthesis were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, TCI or aladdin respectively .
[0092] 2. Synthesis of probe molecule 1
[0093] The synthetic route of probe molecule 1 is as follows:
[0094]
[0095] Add steviol (30mg, 0.1mmol) in the dry flask, K 2 CO 3 (27mg, 0.2mmol), pumped nitrogen, added 2mL of anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), 3-(but-3-ynyl)-3-(2-iodoethyl)-3H -Diaziridine (1-1) (33mg, 0.13mmol) was dissolved in 1mL N,N-dimethylformamide, added to the reaction under ice-cooling, heated to 70°C, reacted for 6hr, thin layer chromatography (TLC) For detection, wash with 10% HCl and saturated saline, dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and separate by column chromat...
experiment example 2
[0100] Experimental Example 2: Extraction of Active Stevia Plant Protein
[0101] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0102] Stevia rebaudiana was collected from Jining City, Shandong Province, China. DEAE column material was purchased from Aogma.
[0103] Plant cell extract: 50mM HEPES (pH 7.8), 150mM sodium chloride, 5mM magnesium chloride, 1mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 10mM dithiothreitol, 1g sodium ascorbate, 10g cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone, 5g polyvinylpyrrolidone.
[0104] 2. Extraction of active stevia plant protein
[0105] Grind the fresh stevia leaf and stem tissue by liquid nitrogen grinding method, add 2mL of pre-cooled plant cell lysate added with protease inhibitors per 1g of stem and leaf tissue, and incubate on ice to fully dissolve the stevia protein , use ammonium sulfate gradient salting out to obtain protein precipitation, then use pre-cooled protein solution to redissolve the precipitated protein, after dialysis and desalination, use D...
experiment example 3
[0106] Experimental example 3: Verifying the catalytic activity of stevia protein
[0107] 1. Experimental materials and reagents
[0108] Steviol was synthesized by our laboratory, and product standards and reagents were purchased from Sigma, TCI, Sinopharm and Yuanye.
[0109] 2. Verification of the catalytic activity of stevia protein
[0110] Take 300 μL of the protein solution prepared in Example 2, add 1 mM steviol, 5 mM uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG), react at 30 ° C for 4 hours, extract with n-butanol, spin dry, redissolve in methanol, LC-MS analysis, stevia Steviol monoside, steviol bioside, stevioside, and rebaudioside A are all produced.
[0111] Gel electrophoresis, staining. Figure 6 Silver staining analysis of extracted stevia protein after electrophoresis is shown. Cut off the gel blocks with a size around 50kD and perform protein spectrum analysis after in-gel digestion. Figure 8 Protein profiling after electrophoresis of extracted stevia proteins is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com