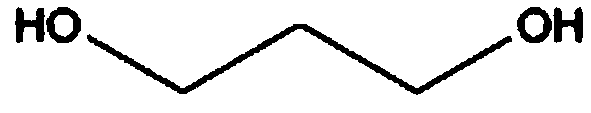
Method for preparing 1,3-propylene glycol by means of methyl 3-methoxypropionate
A technology of methyl methoxy propionate and methoxy propanol, which is applied in the field of chemical synthesis, can solve problems such as unfavorable industrialization, harsh reaction conditions, and complicated operation, and achieve short synthesis routes, low environmental impact, and high reaction selectivity Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Preparation of hydrogenation catalyst
[0031] Dissolve 1 mole of copper nitrate in water, add 40% sodium hydroxide solution and stir, and ensure that the number of moles of sodium hydroxide is twice that of copper nitrate. Then add silica sol with a concentration of 30% and stir, and the addition amount of silica sol is measured according to the weight content of Cu in the final catalyst being 45%. After the mixture was evenly stirred, it was dried at 90°C for 4 hours, then calcined at 550°C for 5 hours, and pressed into tablets to obtain a hydrogenation catalyst. The pressed tablet is crushed and sieved to obtain a 20-40 mesh supported nano-copper-based catalyst. The catalyst can be reduced for 10 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere containing 5% hydrogen at 300 degrees before use, and the purpose of the reduction is to reduce the copper oxide to the active component of the elemental copper catalyst.
[0032] Reduction reaction principle:
[0033] CuO+H 2 → Cu 2 O+H ...
Embodiment 2
[0047]Preparation of hydrogenation catalyst: the specific method is the same as example 1, except that copper acetate is replaced by copper nitrate, and its advantage is that copper acetate is decomposed into carbon dioxide during high-temperature roasting, while copper nitrate is decomposed into nitrogen dioxide during high-temperature roasting, polluted environment.
[0048] Hydrogenation reaction: the specific method is the same as example 1, and the catalyst prepared by adopting copper acetate is compared with copper nitrate, and the reaction conversion rate and selectivity are not much different.
[0049] Demethylation: the specific method is the same as Example 1
Embodiment 3
[0051] Preparation of hydrogenation catalyst: the specific method is the same as Example 1, except that copper oxalate is used instead of copper nitrate. Copper oxalate is a light blue-green powder at room temperature, soluble in ammonia, almost insoluble in water, ethanol and acetic acid. Therefore, in the catalyst preparation process, it should be prepared in an ammonia water system.
[0052] Its advantage is that copper oxalate decomposes into carbon dioxide during high-temperature roasting, while copper nitrate decomposes into nitrogen dioxide during high-temperature roasting, polluting the environment. However, due to the use of ammonia water, ammonia volatilizes during the drying process, which is not as good as copper acetate from the perspective of environmental protection.
[0053] Hydrogenation reaction: the specific method is the same as Example 1, the hydrogen pressure is 4.0MPa, and the catalyst prepared by adopting copper acetate is compared with copper nitrate,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com