Preparation methods of compound fermenting microbial agent and water-soluble fish protein amino acid fertilizer
A technology of composite fermentation bacteria and fish protein, applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, methods based on microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of easy pollution of the environment, corruption, and volatility, and achieve low cost, The effect of short production cycle and stable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
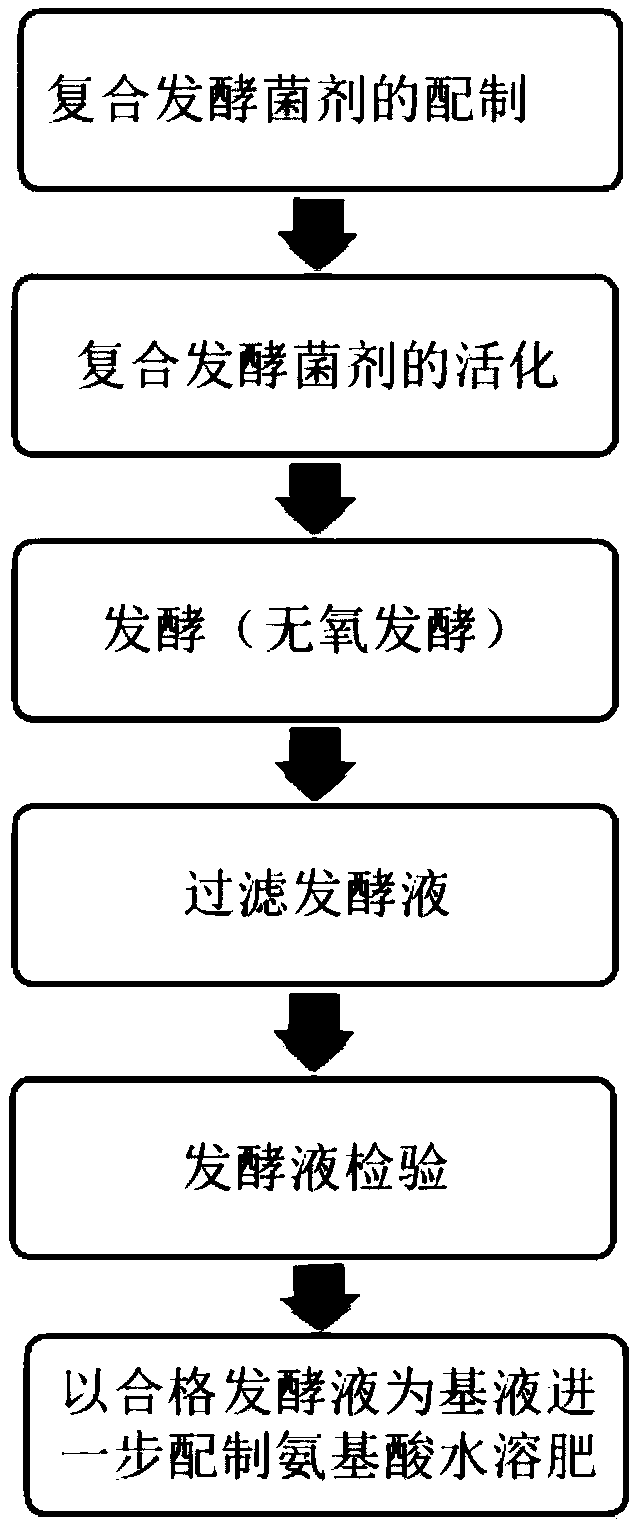
[0028] 1. Take Bacillus subtilis or Bacillus licheniformis 60% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g); Lactobacillus acidophilus or plantarum 20% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g ); Bifidobacterium bifidum or Bifidobacterium breve 20% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 * 108CFU / g). The above three kinds of bacteria are mixed to form a composite fermentation bacterial agent;
[0029] 2. Get corn starch 10% (weight ratio); Ammonium tartrate 5% (weight ratio); Disodium hydrogen phosphate 1% (weight ratio); Glucose 5% (weight ratio); Composite fermentation bacteria agent 3% (weight ratio) ; Water 76% (by weight). Stir the above raw materials evenly, control the temperature at 30°C, and activate the composite fermentation agent for 5 hours.
[0030] 3. Grinding the low-value fish and aquatic product processing waste into a homogenate with a pulverizer, after removing impurities, measure and add it to the fermenter; add the activated co...
Embodiment 2
[0034]1. Get 70% of Bacillus subtilis or Bacillus megaterium (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g); Lactobacillus acidophilus or Lactobacillus brevis 15% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g ); Bifidobacterium bifidum or Bifidobacterium longum 15% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 * 108CFU / g). The above three kinds of bacteria are mixed to form a composite fermentation bacterial agent.
[0035] 2. Get corn starch 15% (weight ratio); Ammonium tartrate 3% (weight ratio); Disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.5% (weight ratio); Glucose 5% (weight ratio); Composite fermentation bacteria agent 2.5% (weight ratio) ; Water 74% (by weight). Stir the above raw materials evenly, control the temperature at 32°C, and activate the composite fermentation agent for 3 hours.
[0036] 3. Grinding the low-value fish and aquatic product processing waste into a homogenate with a pulverizer, after removing impurities, measure and add it to the fermenter; add th...
Embodiment 3
[0040] 1. Get Bacillus subtilis or Bacillus megaterium 65% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g); Lactobacillus acidophilus or Lactobacillus casei 25% (weight ratio, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108CFU / g ); Bifidobacterium bifidum or Bifidobacterium longum 10% (by weight, live bacteria content ≥ 100 × 108 CFU / g). The above three kinds of bacteria are mixed to form a composite fermentation bacterial agent.
[0041] 2. Get corn starch 8% (weight ratio); Ammonium tartrate 2% (weight ratio); Disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.8% (weight ratio); Glucose 4% (weight ratio); Composite fermentation bacteria agent 1.2% (weight ratio) ; Water 84% (by weight). Stir the above raw materials evenly, control the temperature at 35°C, and activate the bacteria for 3 hours.
[0042] 3. Use a pulverizer to pulverize low-value fish and aquatic product processing waste into a homogenate, remove impurities and add it to the fermenter; add the activated composite bacterial agent to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com