Adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde
A catalyst and formaldehyde technology, applied in the direction of organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem of low formaldehyde conversion efficiency, low formaldehyde conversion rate, and volatile catalysts Live and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
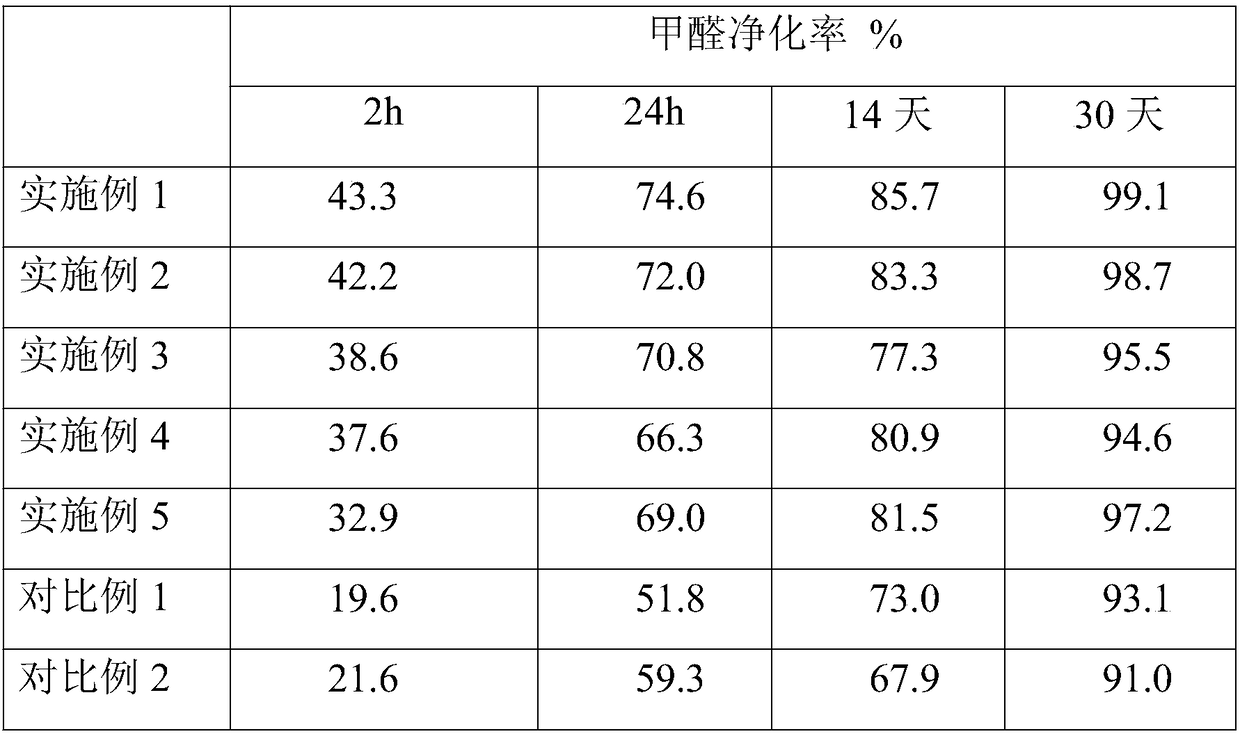
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0010] The present invention also provides a preparation method of the adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde, including the following steps:
[0011] (1) Add a foaming agent to the nylon 66 emulsion and mix uniformly, and then electrostatically spin to obtain nylon 66 fiber, and calcinate the nylon 66 fiber at 300 to 450°C for 2 to 4 hours to obtain porous carbon fiber;
[0012] (2) After mixing the porous carbon fiber, attapulgite, silane coupling agent and organic titanate uniformly in a solvent, ultrasonicate for 15-30 minutes, and then seal and react at 80-120℃ for 3-6 hours to obtain modified porous carbon fiber ;
[0013] (3) Disperse the modified porous carbon fiber in a solvent ultrasonically for 15 to 30 minutes, then add polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, continue ultrasonication for 30 to 45 minutes, then add graphene oxide, and stir for 30 to 45 minutes to obtain Adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde.
[0014] In the presen...
Embodiment 1
[0023] An adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde, made of the following parts by weight: 10 parts by weight of attapulgite, 8 parts by weight of tetraethyl titanate, 3.5 parts by weight of silane coupling agent KH580, and 6 parts by weight of graphene oxide Parts, 5 parts by weight of polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride, 3 parts by weight of sodium carbonate, 100 parts by weight of nylon 66 emulsion, and 50 parts by weight of water.
[0024] The preparation method of the adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde includes the following steps:
[0025] (1) Add sodium carbonate to nylon 66 emulsion and mix uniformly, and then electrospin to obtain nylon 66 fiber. The electrospinning process is: power supply voltage 50kV, spinning temperature 35°C, relative humidity 75%; multi-needle spray The distance between the needles of the silk unit is 35cm, and the number of needles of the spinning unit is 90;
[0026] Calcining nylon 66 fibers at 350°C for...
Embodiment 2
[0031] An adsorption catalyst for in-situ degradation of formaldehyde, made of the following parts by weight: 12 parts by weight of attapulgite, 10 parts by weight of tetramethyl titanate, 3.2 parts by weight of silane coupling agent KH590, and 6 parts by weight of graphene oxide Parts, 6 parts by weight of polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride, 3 parts by weight of N,N'-dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine, 120 parts by weight of nylon 66 emulsion, and 50 parts by weight of ethanol.
[0032] (1) Add N,N'-dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine into nylon 66 emulsion and mix uniformly, and then electrospin to obtain nylon 66 fiber. The electrospinning process is: power supply voltage 50kV, spinning The temperature is 35℃, the relative humidity is 75%; the distance between the needles of the multi-needle spinning unit is 35cm, and the number of needles of the spinning unit is 90;
[0033] Calcining nylon 66 fibers at 400°C for 2.5 hours to obtain porous carbon fibers;
[0034] (2) After grinding...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com