Two-dimensional material, and stripping method and application thereof
A technology of two-dimensional materials and solid materials, applied in the direction of luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, binary selenium/tellurium compounds, etc., can solve the problems of producing two-dimensional materials, stripping out two-dimensional materials, and not being able to achieve large-scale production , to achieve the effect of large sheet area, short peeling time and high repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
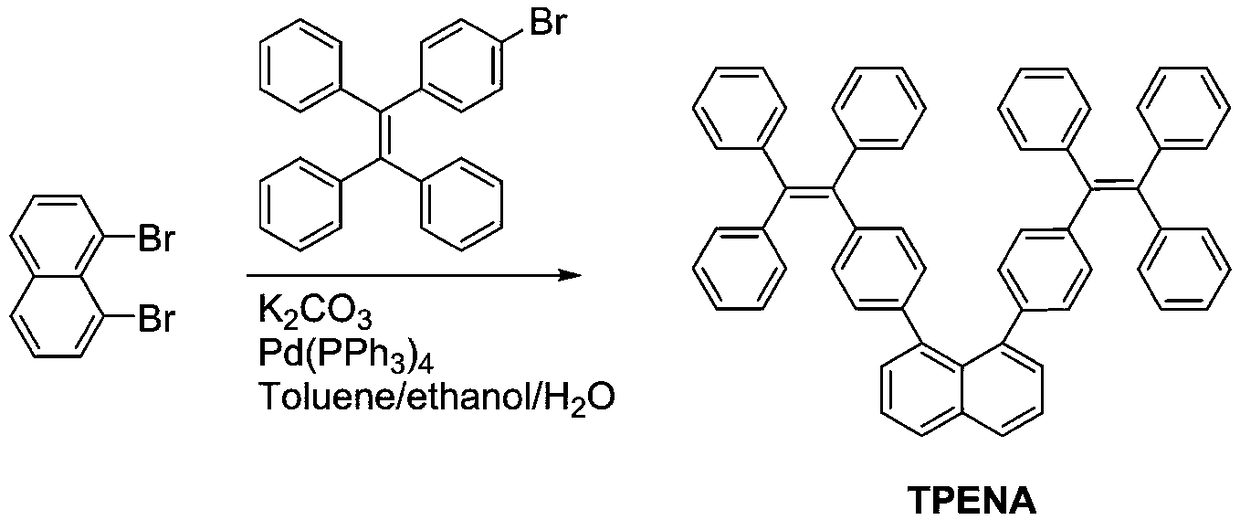
[0039] Example 1 Preparation of 1,8-bis(4-(1,2,2-triphenylethenyl)naphthalene
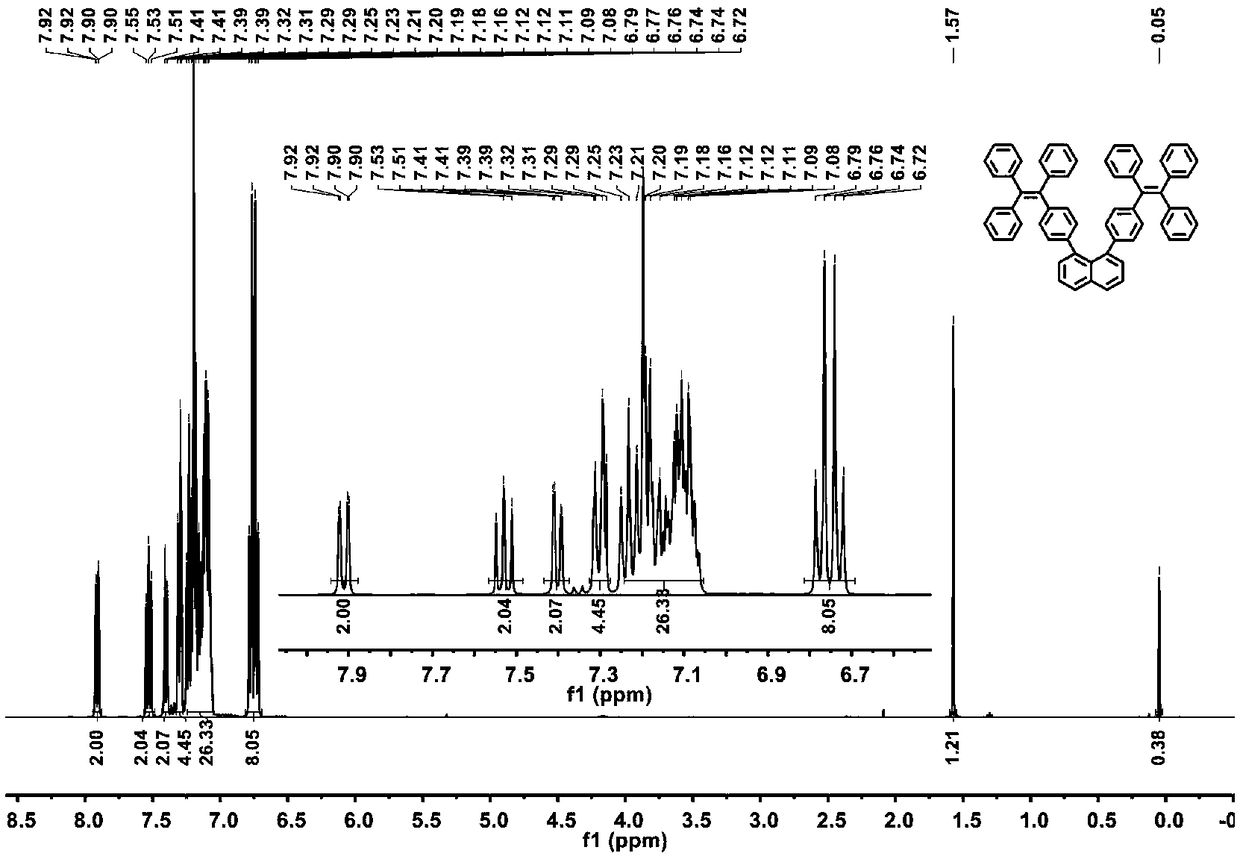
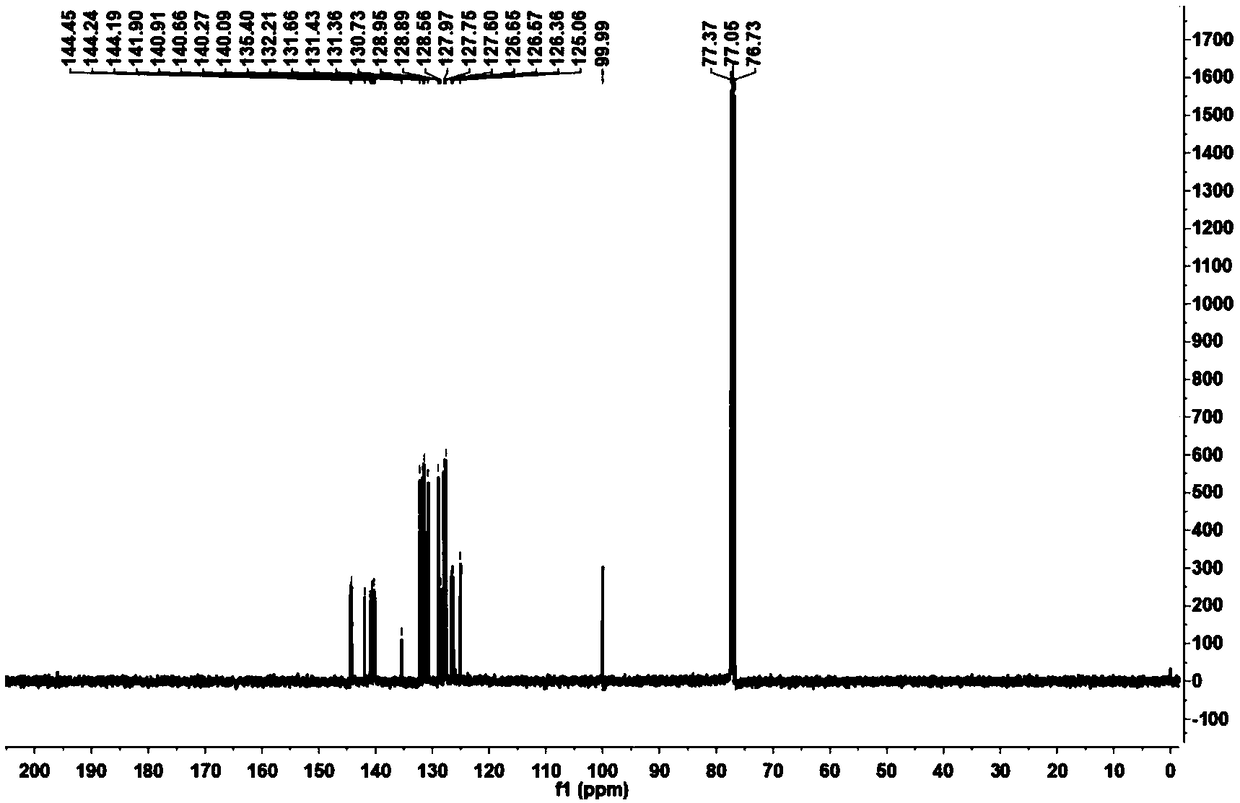
[0040] Under the condition of nitrogen protection, add 1,8-dibromoanthracene and TPE phenyl borate (molar ratio is 1:2.5), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium, potassium carbonate into a single-necked bottle, and then add Appropriate amount of toluene and ethanol, stirred vigorously, kept the temperature at 90°C, refluxed for 24 hours, extracted, washed and filtered to obtain the primary product, and obtained high-purity 1,8-bis(4-(1, 2,2-triphenylethenyl) naphthalene, its synthetic route is as formula figure 1 shown. figure 2 For the 1,8-bis(4-(1,2,2-triphenylvinyl)naphthalene aggregation-induced luminescent material prepared in this example 1 H NMR spectrum. image 3 Obtain 1,8-two (4-(1,2,2-triphenylethenyl) naphthalene for this embodiment 13 C NMR image. Figure 4 The mass spectrum of 1,8-diTPE substituted naphthalene was obtained for this example. From Figure 1-Figure 4 It can be ...
Embodiment 2 2
[0041] The stripping of embodiment 2 molybdenum disulfide
[0042] Figure 6 It is a schematic flow chart of exfoliating two-dimensional materials in the present invention. The stripping method of the present invention is as follows: 1,8-di(4-(1,2,2-triphenylethenyl)naphthalene (0.1~5g) obtained in Example 1 and molybdenum disulfide ( 0.5g to 5g), mixed with 20mL ethanol and ground for 1 hour, then added a certain volume of ethanol (10 to 100mL) and ultrasonicated for 1 to 100 minutes, and then centrifugally filtered to obtain molybdenum disulfide with few layers or a single layer.
[0043] Figure 7 It is an electronic scanning SEM photo of molybdenum disulfide material exfoliated with 1,8-bis(4-(1,2,2-triphenylethenyl)naphthalene-induced luminescent molecules in this example, Figure 8 It is a TEM photo of molybdenum disulfide material exfoliated with 1,8-bis(4-(1,2,2-triphenylethenyl)naphthalene-induced luminescent molecules in this example. From Figure 7 and 8 It can...
Embodiment 3 2
[0044] The stripping of embodiment 3 tungsten diselenide
[0045] Aggregation-induced luminescent molecules and tungsten diselenide with a multi-layer structure are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:0.1, and 1 mL of ethanol is added to grind for 1 min, then a certain volume of ethanol 10 mL is added for ultrasonication for 10 minutes, and then centrifuged to obtain few-layer or single-layer Tungsten diselenide. The target material is characterized by testing methods such as AFM and TEM, and the target material has only a single layer or a few layers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com