A method for improving dewatering performance of citric acid wastewater sludge by using Penicillium oxalicum
A technology of citric acid wastewater and Penicillium oxalate, applied in water/sludge/sewage treatment, dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problem of biological conditioning that has not been reported and the source of bacteria has not been specified , long culture cycle and other problems, to achieve the effect of short separation and purification cycle, easy operation, and improved dehydration performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 for testing sludge sample
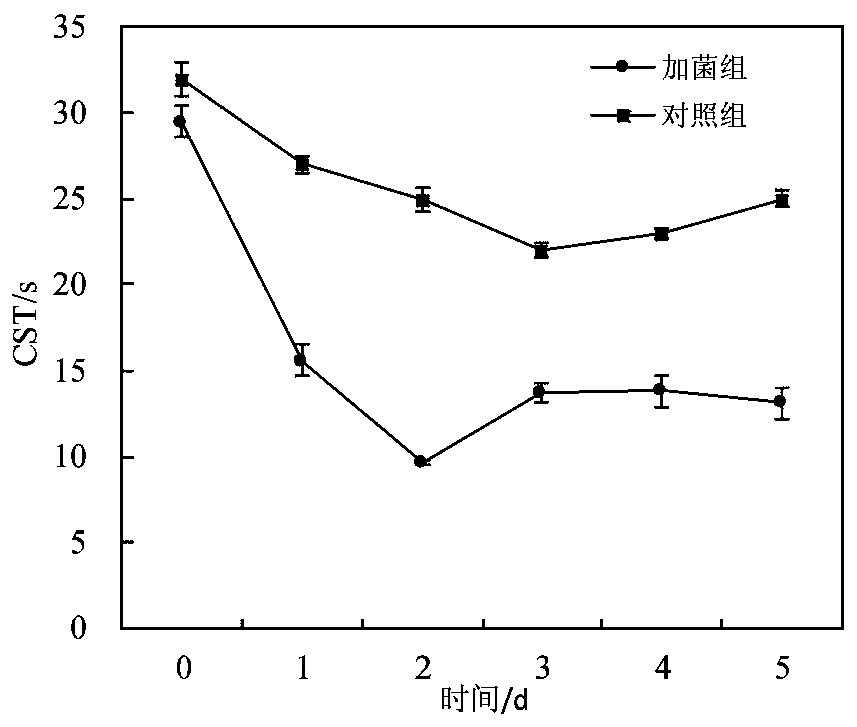
[0038] A method for improving the dehydration performance of citric acid sludge by using Penicillium oxalicum according to the present invention. During the specific implementation and operation, the sludge samples for testing were taken from the secondary sedimentation process of the oxidation ditch treatment process of the sewage treatment workshop of a citric acid production enterprise in Shandong. Pool return sludge. The enterprise produces 60t of absolute dry sludge every day. The sludge treatment method is to add PAM coagulation after concentration. The basic characteristics of the tested sludge are listed in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1 Basic characteristics of the sludge samples tested
[0040] Moisture content (%) Capillary water absorption time (s) Sludge specific resistance (×10 14 m / kg)
Embodiment 2
[0041] The separation and purification of embodiment 2 sludge filamentous fungi
[0042] Dilute the citric acid wastewater sludge sample by 10-10 5 After different concentration gradients, they were inoculated in Sabouraud medium by the coating plate method, cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 25-30°C for 2-3 days, and a variety of fungal colonies were isolated and picked by the three-point inoculation method. Colonies were grown in petri dishes. Repeat the inoculation for 3 to 5 times, isolate and purify the fungi with different colony forms, inoculate the fungi with different colony characteristics on the slant medium, and store them in a refrigerator at 4°C.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Screening and Identification of Filamentous Fungi
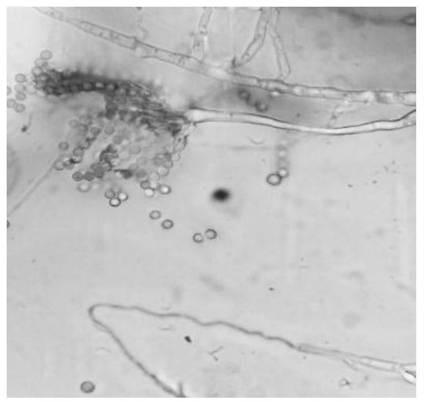
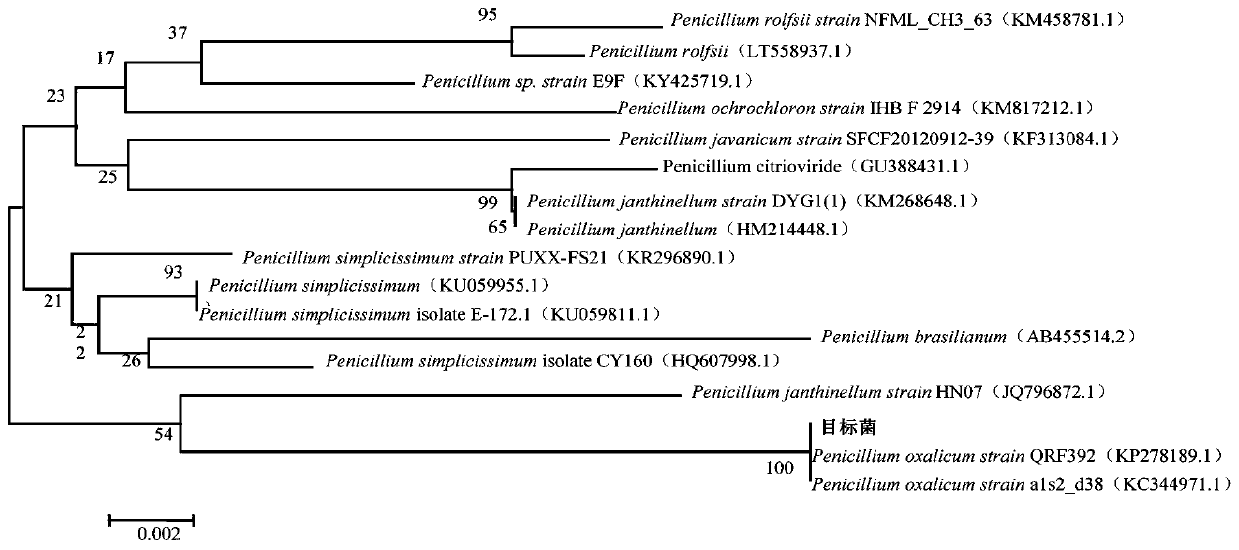
[0044] Analyze the morphology and growth characteristics of the purified fungi, screen out filamentous fungi with fast growth and developed mycelia, and then conduct organic degradation experiments on them, including gelatin liquefaction, cellulose hydrolysis, starch hydrolysis, and screen out characteristics Obvious filamentous fungus, identified by 18SrDNA gene sequence and morphology, the morphology under the microscope is as follows figure 1 As shown, it was identified as Penicillium oxalicum.
[0045] (1) Gelatin liquefaction experiment
[0046] Medium configuration: glucose 20g, peptone 5.0g, gelatin 200g, dissolved in 1000mL distilled water for sterilization, take 10mL sterilized medium solution in a test tube. The fungus was inoculated on the culture medium and cultured at 25°C and 180rpm for several days. Put the blank control group and the fungus-inoculated group into a low-temperature environment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com