Anti-bacterial peptide, anti-bacterial peptide hydrogel and preparation method of anti-bacterial peptide hydrogel
An antimicrobial peptide and hydrogel technology, applied in the field of biopharmaceuticals, can solve the problem that mechanical debridement cannot completely remove biofilm, and achieve the effect of promoting rapid healing and promoting growth and proliferation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1 solid-phase synthesis method prepares antimicrobial peptide
[0035] First, the carboxyl group of Fmoc-asparagine is connected with an insoluble polymer resin (as a solid phase carrier) in a covalent bond structure, and then the amino group of asparagine and the carboxyl group of Fmoc-valine are condensed through deprotection Form a peptide bond, repeat the above peptide bond formation reaction, and gradually connect serine, leucine, tyrosine, lysine and isoleucine to the resin, so that the peptide chain grows from the carboxyl terminal to the amino terminal until it reaches The desired length of the peptide chain is finally cut off from the resin with hydrofluoric acid to obtain antimicrobial peptide 1. In a specific embodiment, the insoluble polymer resin is king resin.
[0036] First, the carboxyl group of Fmoc-asparagine is connected with an insoluble polymer resin as a solid phase carrier in a covalent bond structure, and then the amino group of aspar...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity Detection
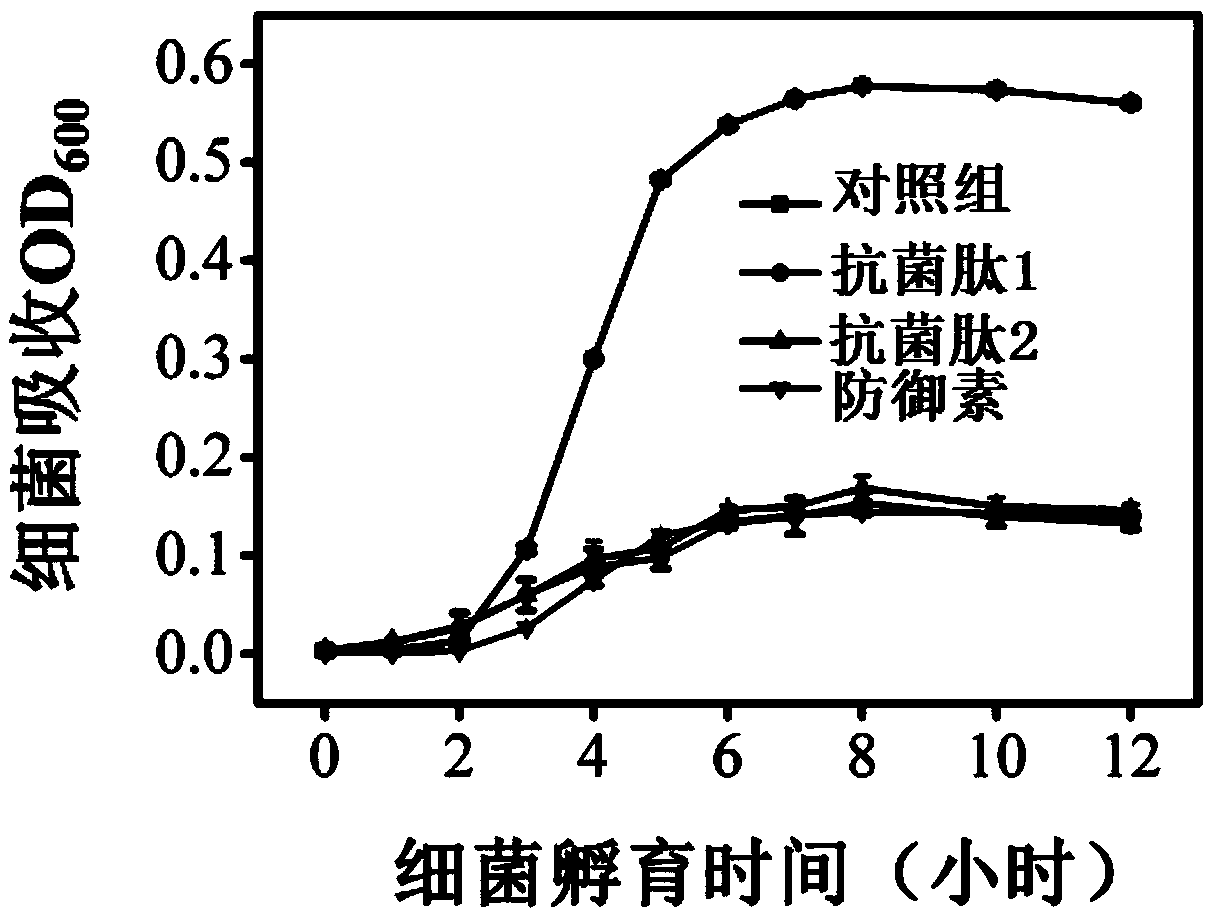
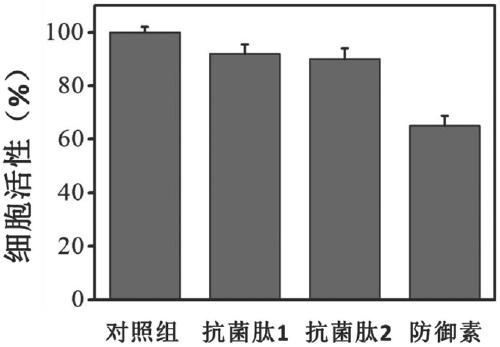
[0040] This embodiment detects the antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of the antimicrobial peptide 1 and antimicrobial peptide 2 prepared in Example 1. The antibacterial activity is taken as an example of Escherichia coli, and the results are shown in Figure 1 ~ Figure 2 .
[0041] The results showed that antimicrobial peptide 1 and antimicrobial peptide 2 had similar antibacterial ability (Escherichia coli) compared with the control group (no polypeptide addition) and the comparative example 1 group (existing antimicrobial peptide defensin). Compared with the control group (no peptide addition), antimicrobial peptide 1 and antimicrobial peptide 2 have basically no effect on the growth of normal cells, showing excellent biocompatibility, while comparative example 1 group (existing antimicrobial peptide defensin) has no effect on Normal cells have certain toxicity and poor biocompatibility.
Embodiment 3
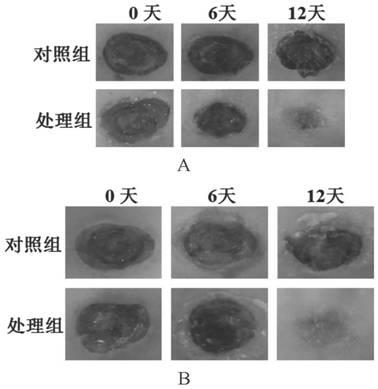
[0042] Example 3 Preparation of Antimicrobial Peptide 1 Hydrogel and Detection of Drug Release Efficiency
[0043] Weigh 4 mg of purified lyophilized antimicrobial peptide 1 powder into a 1.5 mL sample bottle, and then add 400 μL of a solution in which photothermal reagent (20 μg indocyanine green ICG) and wound growth-promoting factor (5 mg of proline) are dissolved , so that the final concentration of antimicrobial peptide 1 was 10 mg / mL, sonicated until the powder of antimicrobial peptide 1 was fully dissolved, and left to stand for 10 minutes to make it self-assemble into a gel. The results of atomic force electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy are shown in image 3 .
[0044] This example further investigated the release efficiency of the photothermal reagent (ICG) and wound growth-promoting factor (proline) loaded in the antimicrobial peptide 1 hydrogel at different pHs. The results are as follows Figure 4~5 shown.
[0045] Depend on Figure 3-5 It can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com