A kind of surfactant-free graphene composite conductive ink
A graphene composite, surfactant technology, applied in inks, household appliances, applications, etc., can solve the problems of expensive metal consumables, brittleness of rGO film, poor windability, etc., to achieve high conductivity, excellent flexible conductive film, The effect of excellent printing adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
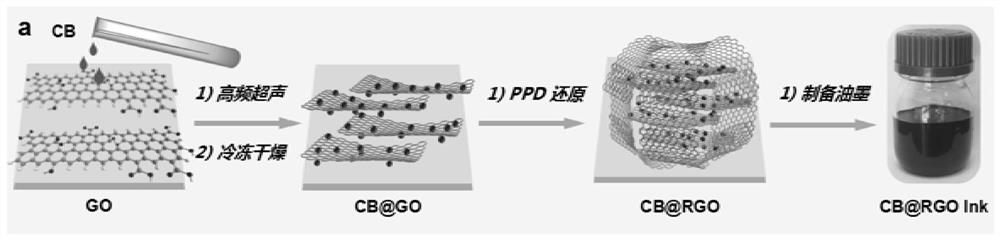
[0036](1) Accurately weigh the following raw materials by mass: 1 part of graphene oxide, 1 part of acetylene carbon black, disperse and exfoliate graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets and intercalate carbon black particles (CB) through high-frequency ultrasonic treatment Graphene oxide nanosheets to obtain a stable graphene oxide / carbon black (GO / CB) dispersion;
[0037] (2) Freeze-drying the resulting GO / CB dispersion to obtain a CB interlayer GO conductive precursor;
[0038] (3) Accurately weigh the following raw materials by mass: p-phenylenediamine (PPD) 0.5 / 5 parts, precursor material 1 part, ethylene glycol 100 parts, mix with high-frequency ultrasound for 1 min, and then keep the temperature of the obtained dispersion The CB@rGO coated structural material was obtained by water bath treatment at 80°C. The excess p-phenylenediamine and free carbon black particles are removed by filtration, water washing, and centrifugation to obtain conductive fillers with low degree of reduc...
Embodiment 2
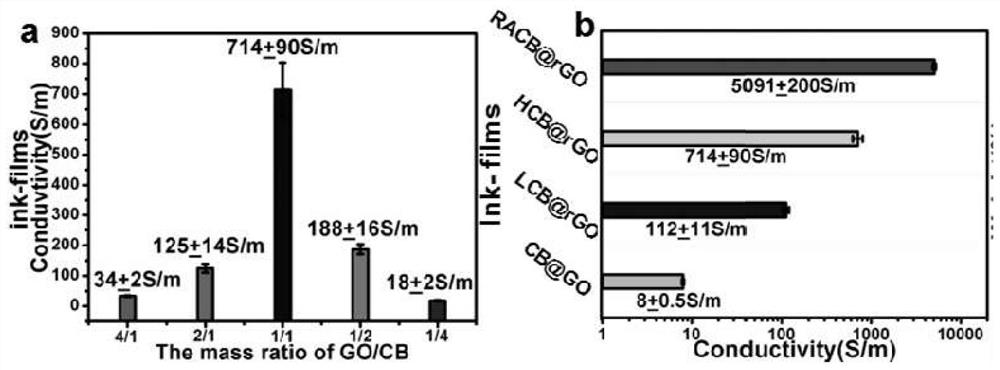
[0043] (1) Accurately weigh the following raw materials by mass: 1 part of graphene oxide, 4 parts / 2 parts / 1 part / 0.5 part / 0.25 part of acetylene carbon black (M GO / M CB =4 / 1, 2 / 1, 1 / 1, 1 / 2, 1 / 4), through high-frequency ultrasonic treatment, disperse and exfoliate graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets and intercalate carbon black particles (CB) into graphite oxide ene nanosheets to obtain a stable graphene oxide / carbon black (GO / CB) dispersion;
[0044] (2) Freeze-drying the resulting GO / CB dispersion to obtain a CB interlayer GO conductive precursor;
[0045] (3) Accurately weigh the following raw materials by mass: 5 parts of p-phenylenediamine (PPD), precursor material (M GO / M CB =4 / 1, 2 / 1, 1 / 1, 1 / 2, 1 / 4) 1 part each, 100 parts of ethylene glycol, after mixing, high-frequency ultrasonication for 1 min, and then treat the obtained dispersion in a water bath at a constant temperature of 80°C to obtain CB @rGO wraps structural materials. Remove excess p-phenylenediamine and fr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com