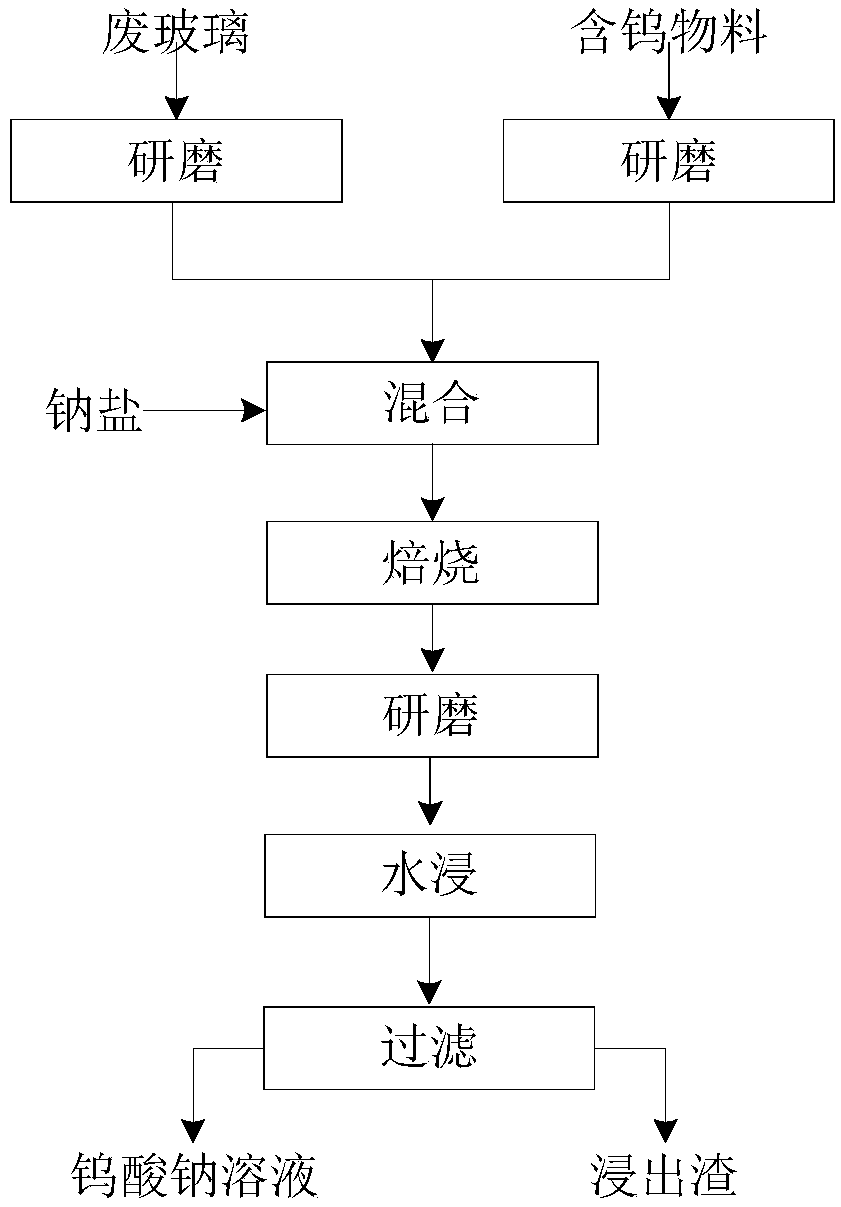
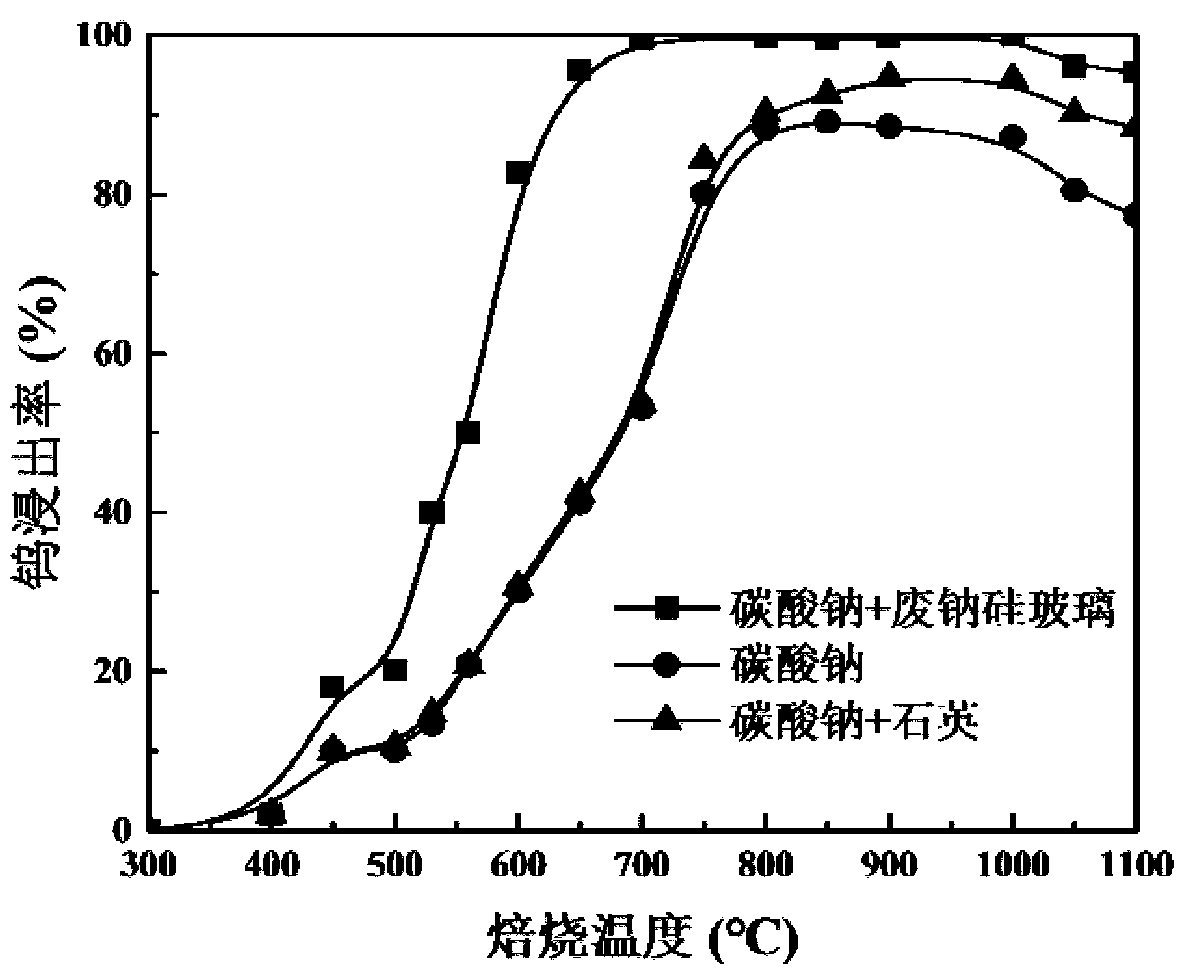
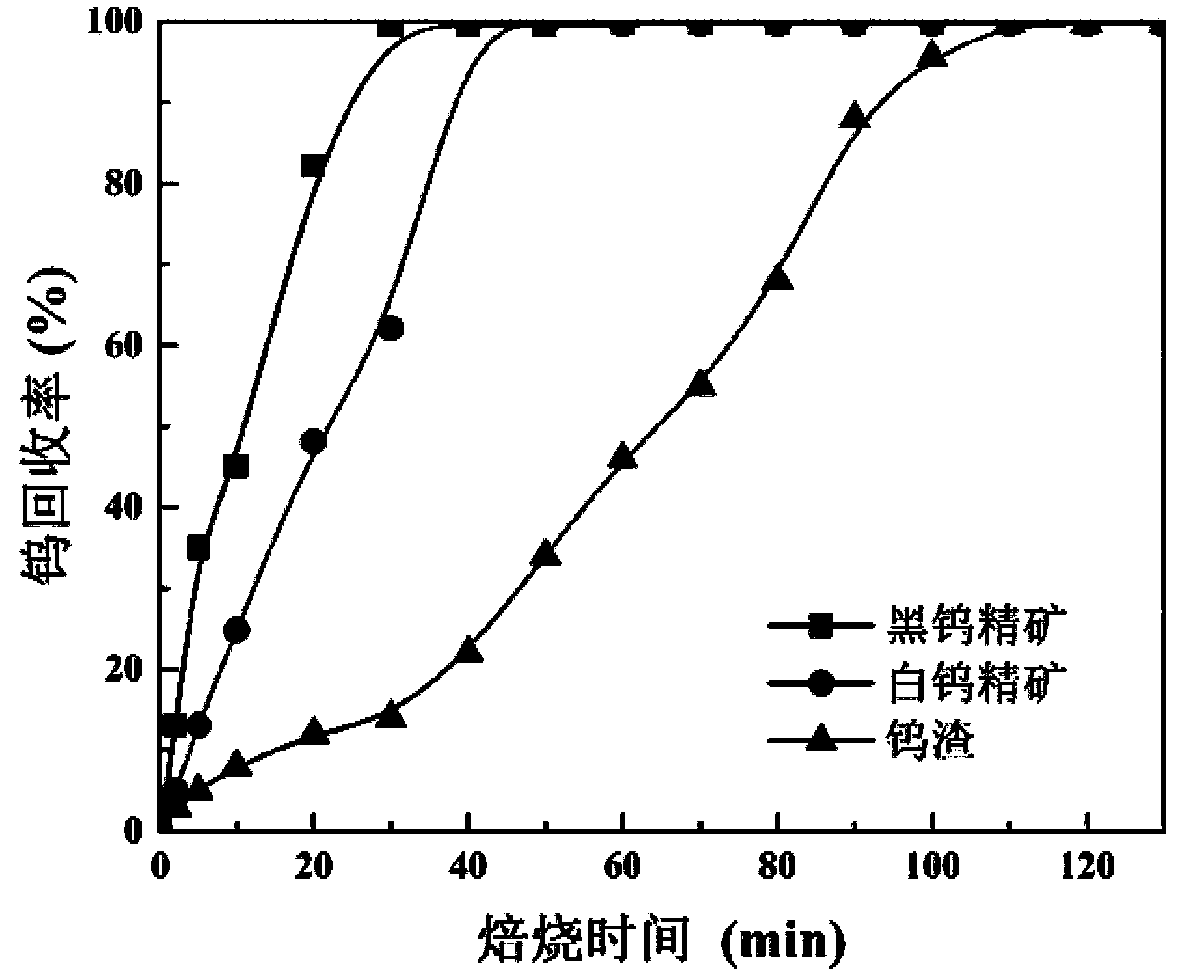
Method for extracting tungsten from tungsten-containing raw material through waste glass
A technology for waste glass and raw materials, applied in the field of tungsten smelting, can solve the problems of difficult to exceed 95% tungsten recovery rate, poor mass and heat transfer effect of quartz, low tungsten leaching rate, etc., achieving low cost, low cost and good treatment effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Take a WO 3 Grind scheelite concentrate with a content of 50.1% to less than 74 μm, and another soda-calcium-silica waste glass to grind it to less than 74 μm, and grind the materials according to the ratio of scheelite concentrate:waste glass:sodium carbonate=1:0.2 The mass ratio of :1 is fully mixed, roasted at 700°C for 30 minutes, and the roasted material is ground to less than 74 μm and put into water for leaching. According to the liquid-solid ratio of 2:1, the leaching temperature is 50°C, and the leaching stirring time is 30 minutes. A tungsten-containing leaching solution with a leaching rate of 99.6% can be obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Take a WO 3 The low-grade wolframite concentrate with a content of 35.8% is ground to less than 74 μm, and another high-silica waste glass is ground to less than 74 μm, and the ground material is ground according to wolframite concentrate: waste glass: sodium hydroxide: The ratio of sodium nitrate=1:0.1:0.6:0.1 is fully mixed. Since wolframite contains divalent iron elements, the oxygen released during the roasting process of sodium nitrate can convert it into ferric iron with higher reactivity, so Sodium nitrate is needed as a combined sodium source, roasted at 450°C for 40 minutes, the roasted material is ground to less than 74μm, and then put into water for leaching. According to the liquid-solid ratio of 4:1, the leaching temperature is 80°C, the leaching stirring time is 40 minutes, and the leaching rate is obtained by filtration. 99.8% of leachate, WO in slag phase 3 The content is 0.17%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Take a WO 3 Grind tungsten slag with a content of 1.2% to less than 74 μm, and another waste quartz glass to grind it to less than 74 μm, and grind the material according to tungsten slag:waste glass:sodium carbonate:sodium sulfate=1:0.1:0.1: Mix it thoroughly at a ratio of 0.1, roast at 950°C for 100 minutes, grind the roasted material to less than 74 μm, and then put it into water for leaching. According to the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, the leaching temperature is 90°C, the leaching stirring time is 40 minutes, and the leaching rate is obtained by filtration. 99.1% of the leachate, WO in the slag phase 3 The content is 0.04%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com