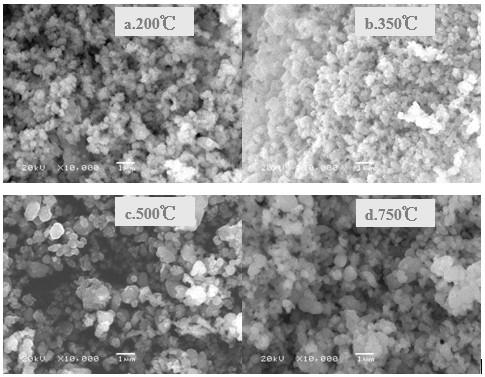
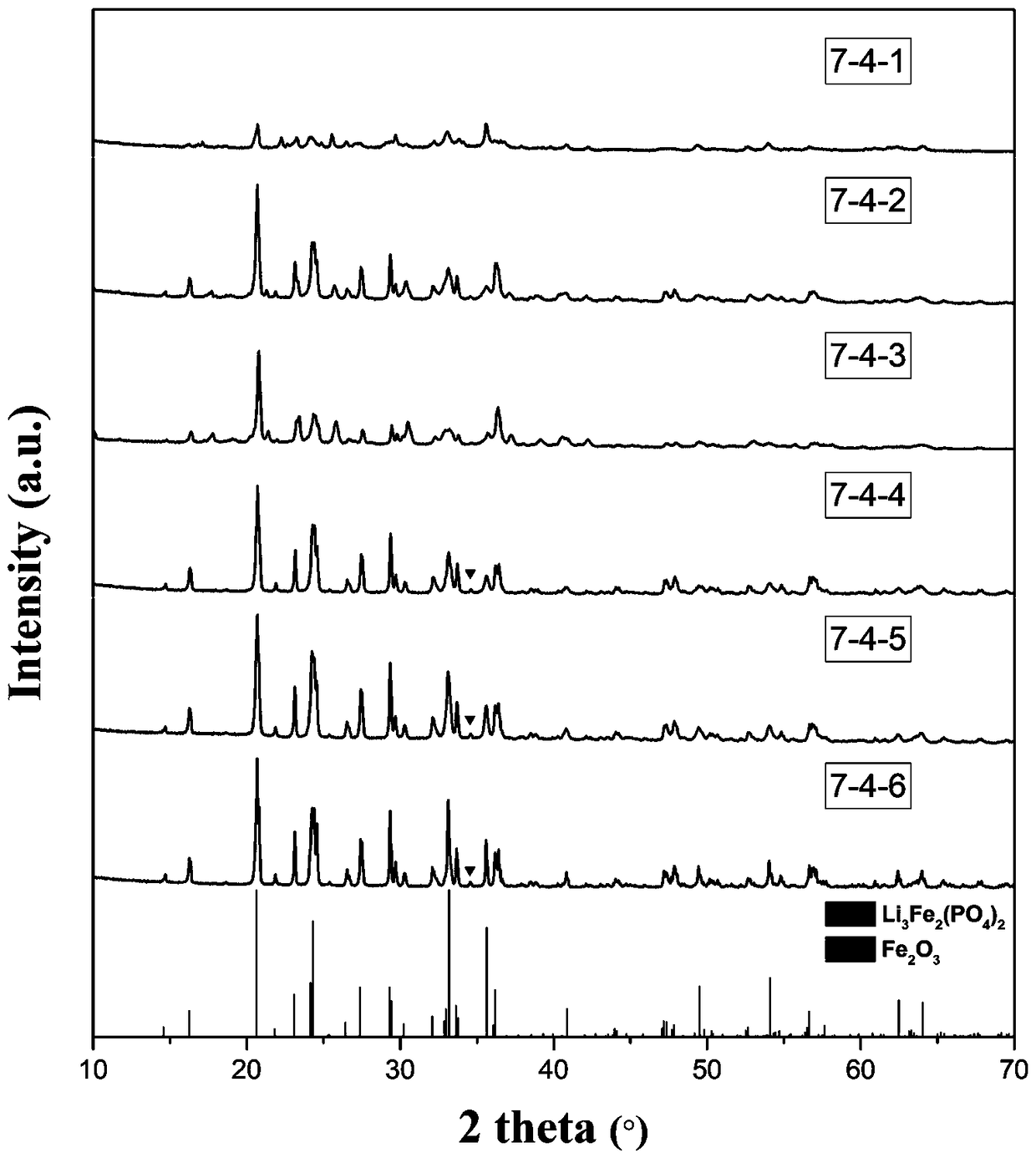
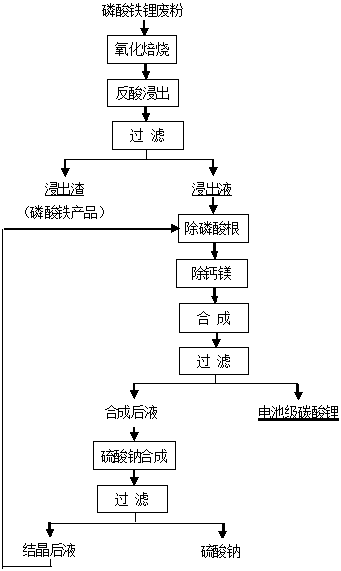
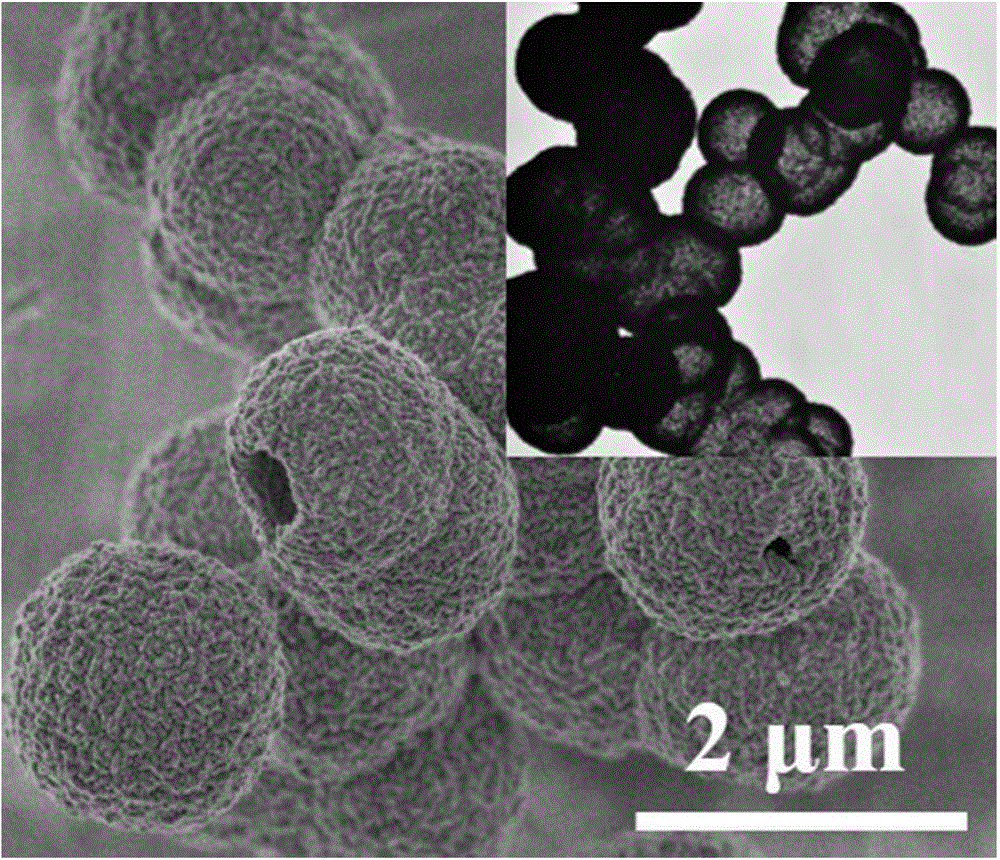
Patents
Literature
137 results about "Calciums magnesium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
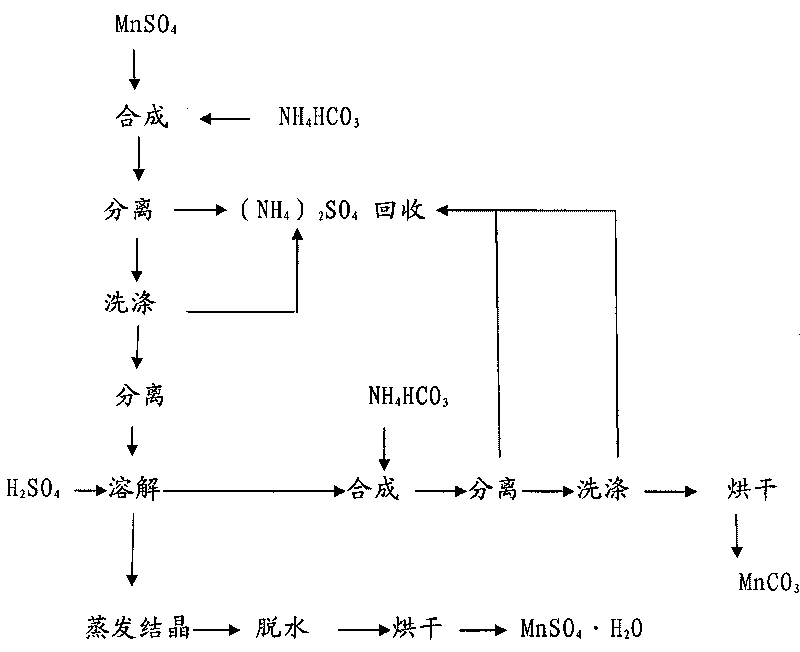
Method for preparing manganese sulfate
ActiveCN101704554AOvercome the Difficulty of SeparationAvoid difficultiesManganese oxides/hydroxidesManganese sulfatesManganeseSulfide
The invention relates to a method for preparing manganese sulfate. The method comprises the following steps: quantitatively adding sulfide with reducibility into a manganese dioxide ore in a reaction molar ratio for sufficient reaction, determining a reaction end point, and separating and washing a solid-phase resultant; reacting the solid-phase resultant with 9 to 12mol / L H2SO4, controlling the reaction end point to the pH of between 3 and 5, controlling the concentration of MnSO4 in the reaction liquid in a range of between 300 and 400g / L, performing solid-liquid separation after the reaction is completed; acidizing the separated solution by H2SO4 until the pH value of the solution is between 2 and 3, adding hydrogen peroxide into the solution and heating the mixture, precisely filtering and removing the part of solid phase; and distilling, concentrating, crystallizing and dehydrating the filtrate to prepare the manganese sulfate. The method can prepare acid soluble manganous oxide and ensure that various heavy metals can generate insoluble sulfides so as to solve the problem of completely separating heavy metals and obtain the manganese sulfate with low calcium magnesium and low heavy metals.
Owner:贵州红星发展大龙锰业有限责任公司
Extraction method for removing calcium and magnesium from copper-cobalt ore leachate
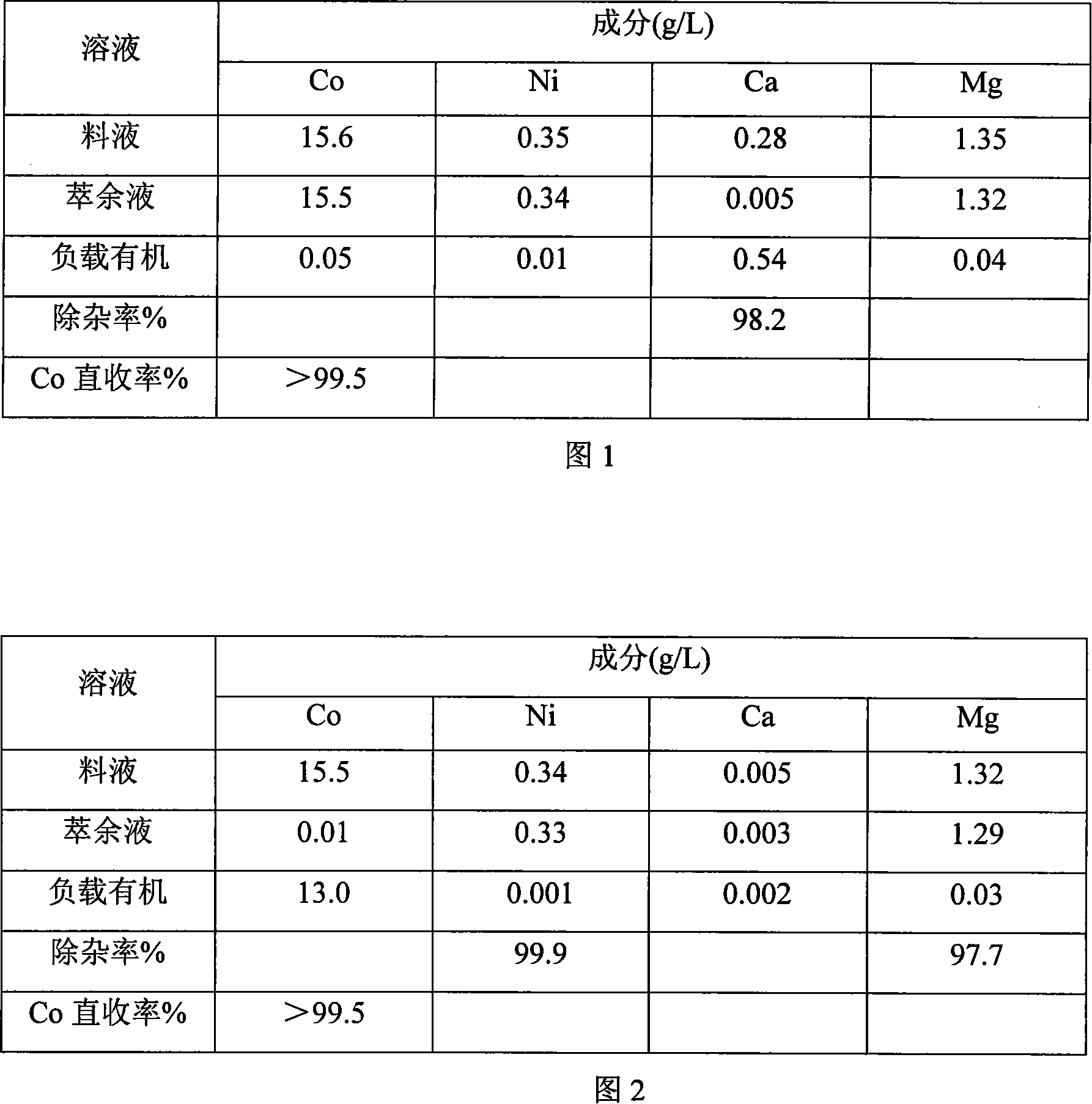
The process of extracting Co and eliminating Ca from copper-cobalt ore includes obtaining mixture leachate with soluble sulfate of Co, Ni, Ca and Mg; and extracting the mixture leachate with organic solvent, which comprises organic matter bis(2-ethyl hexyl) phosphoric acid or ”�2- ethyl hexyl phosphonate ester in 15-25 vol% and kerosene in 75-85 vol%. The organic solvent extracting procedure includes two steps, the first step of transferring Ca into the organic phase while leaving Co, Ni and Mg in the water phase, and the second step of transferring Co to the organic phase while leaving Ni and Mg in the water phase. The process can obtain cobalt sulfate solution with Co content up to 90-100 g / l, Ca ion content lowered to 0.01 g / l, Ni ion content lowered to 0.005 g / l, and Mg ion content lowered to 0.1 g / l and suitable for producing T-cobalt oxide and cobalt salt.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAYOU COBALT
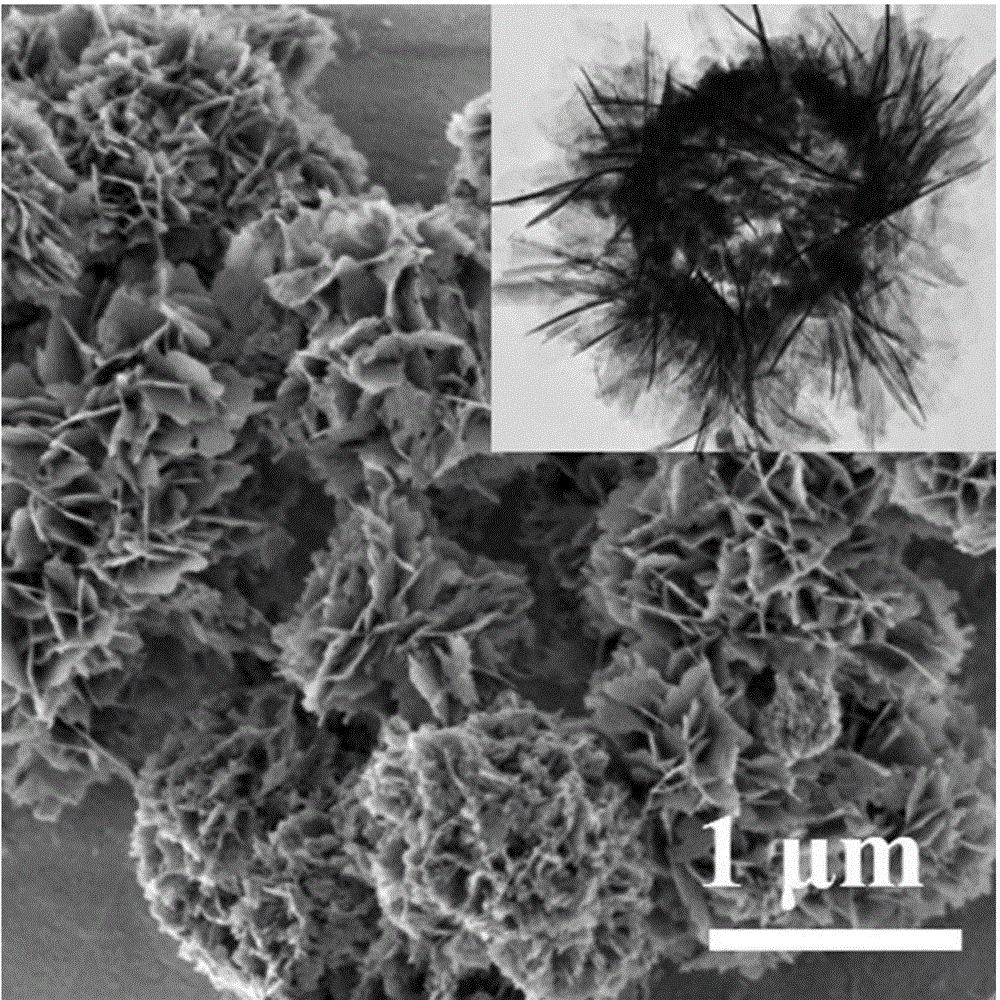
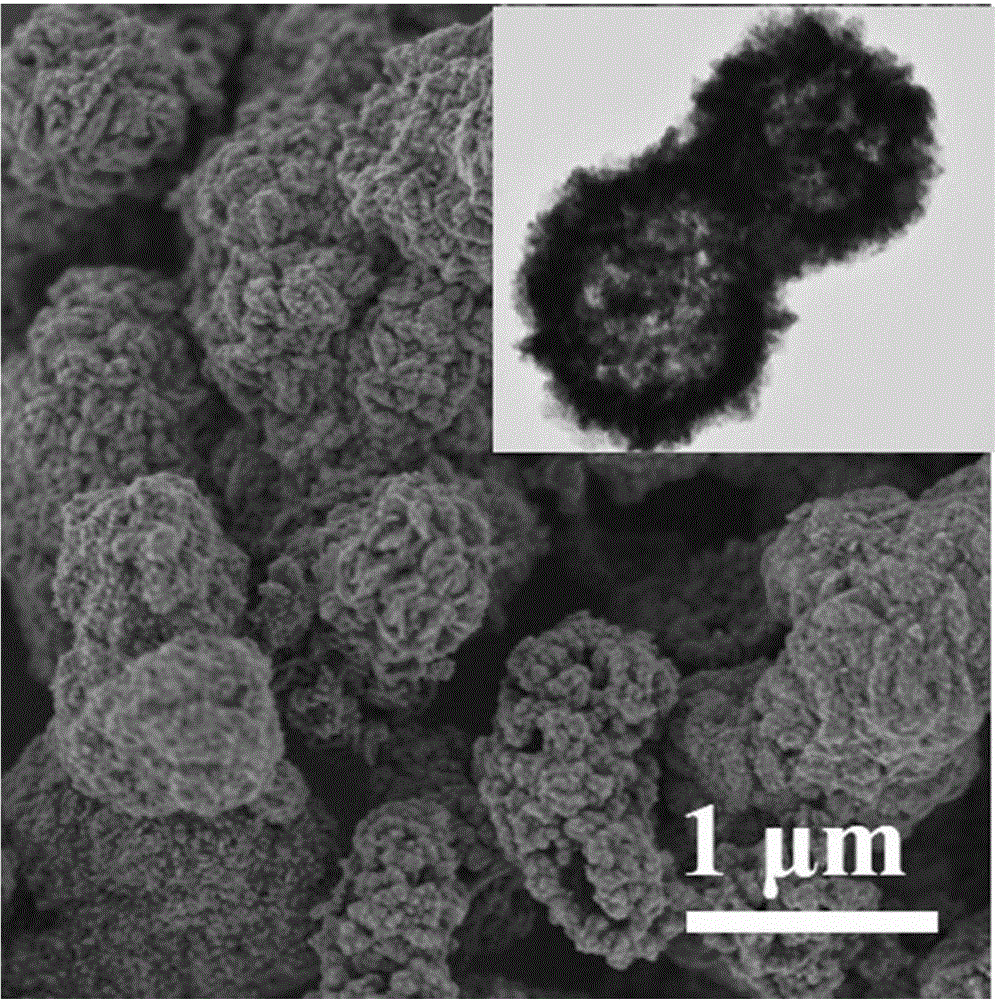
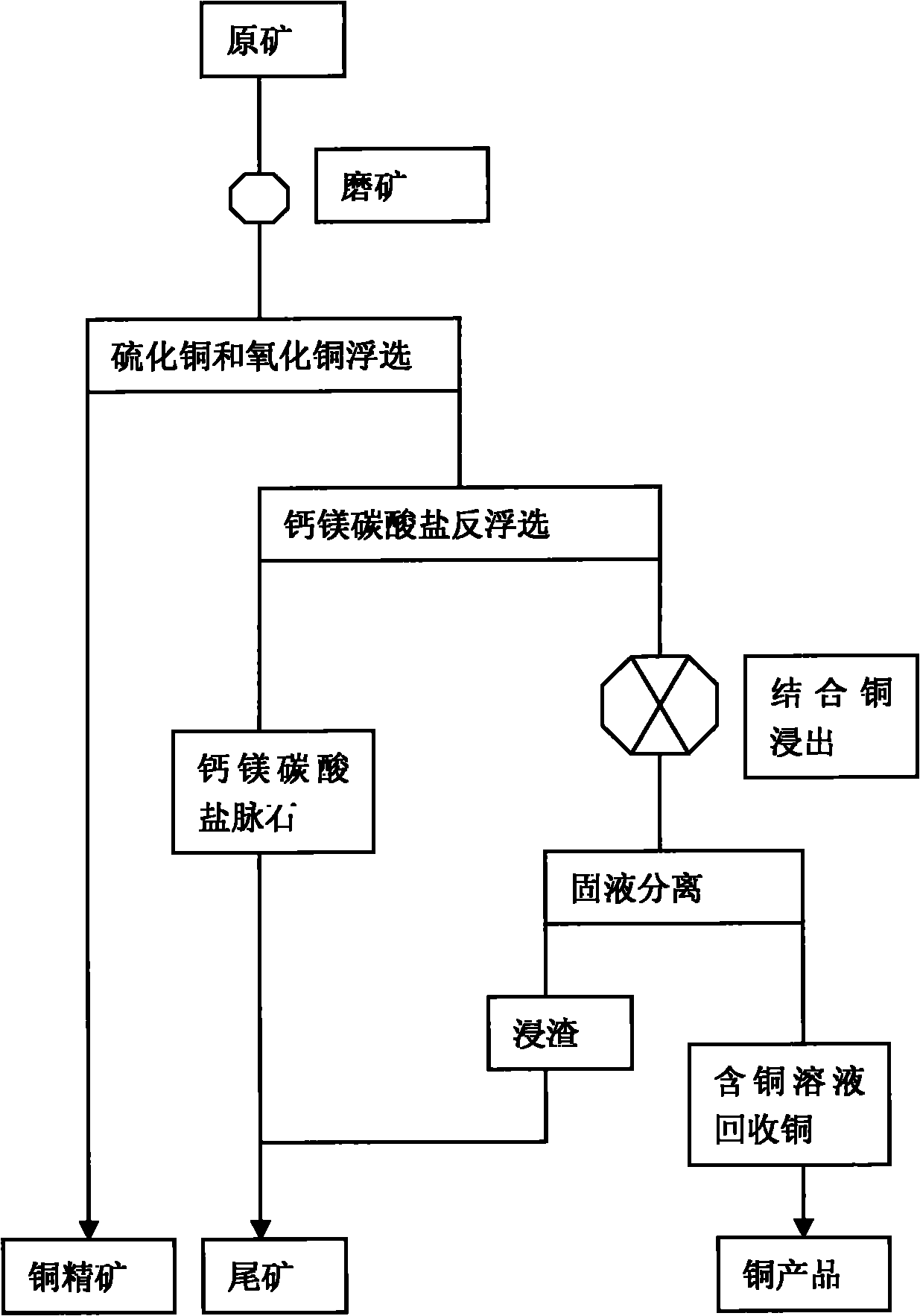
Flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore
ActiveCN101831559AAvoid lostReduce consumptionFlotationProcess efficiency improvementCopper oxideOxygen
The invention relates to a flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore. The flotation and metallurgy method comprises the following steps of: firstly, recovering copper sulfide minerals and free copper oxide minerals in the high-bonding-ratio oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore with high calcium-magnesium carbonate gangue mineral content by flotation; carrying out reverse flotation on calcium-magnesium carbonate ore in tailings obtained after floatation with fatty acid to obtain middlings containing combined copper and less calcium-magnesium carbonate minerals; then, adding sulphuric acid and stirring to leach out combined copper; and processing a copper-contained solution obtained after solid-liquid separation to obtain a copper product by a metallurgy method. The method combines the flotation and the metallurgy for complementary advantages, efficiently recovers and utilizes high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore resources incapable of being processed at present, lessens the emission of castoff, such as carbon dioxide, magnesium calcium sulfate, and the like and has favorable economic benefits and environmental benefits.
Owner:YUNNAN TIEFENG MINING CHEM NEW TECH CO LTD
Balling method using medium- and low-grade phosphate rocks or ground phosphate rocks
ActiveCN103663396AHigh strengthHigh phosphorus contentPhosphorus compoundsPhosphoric acidCalciums magnesium
The invention relates to a balling method using medium- and low-grade phosphate rocks or ground phosphate rocks. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing materials, namely A, 85-100 parts of 60-120-mesh medium-grade and low-grade phosphate rocks or ground phosphate rocks, B, 1-10 parts of water or aqueous liquor of phosphoric acid, C, 2-8 parts of coke powder with the granularity of 60-120 meshes and D, 1-8 parts of one or more of phosphate fire clay, kaolin, sodium silicate, sodium carbonate, calcium carbonate and serpentine; S2, stirring, namely after uniformly mixing the raw materials, pressing the mixture into balls by use of a dry powder ball press machine, after pre-drying, delivering the mixture to a vertical calcining kiln, using purified yellow phosphorus tail gas, heating to 850-950 DEG C; starting roasting to obtain a finished product. The method is free from binders and low in cost, and the medium-grade and low-grade phosphate rocks are not hardened. The value of the medium-grade and low-grade phosphate rocks can be improved, and the ground phosphate rock of a mine can be fully utilized. The phosphate rock balls prepared are suitable for production of yellow phosphorus or calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizers.
Owner:刘静忠 +1
Method for selectively removing calcium ions from concentrated water byproduct of sea water desalination process and other high-calcium-magnesium-content concentrated brines
InactiveCN102936067AHigh removal rateQuick responseGeneral water supply conservationMultistage water/sewage treatmentLoss rateWater desalination
The invention relates to a method for selectively removing calcium ions from a concentrated water byproduct of a sea water desalination process and other high-calcium-magnesium-content concentrated brines, which comprises the following steps: regulating the pH value of the concentrated water to 7.0-8.5, and then heating to a certain temperature; introducing the concentrated water into a heat-insulating apparatus capable of realizing sealed stirring, adding a sodium sulfite or sodium carbonate solution having a certain concentration while stirring, reacting for 1-40 minutes while sufficiently stirring, standing for 5-10 minutes, and then filtering to remove calcium sulfite or calcium carbonate precipitate; and adding hydrochloric acid into the filtrate to regulate the pH value back to 6. According to the invention, the problems of low calcium removal rate, high magnesium loss rate, long stirring time and the like during the concentrated water treatment based on the traditional normal-temperature sodium carbonate precipitation method are overcome, the operation is convenient, the investment is low, and the operation cost is low; and the concentrated water liquid subjected to decalcification treatment can be further deeply concentrated through a membrane method or hot method, thereby improving the fresh water recovery rate and realizing the reutilization and zero discharge of the resources. The method provided by the invention is suitable for selectively removing calcium ions from sea water, sea water or brackish water subjected to other treatment processes such as reverse osmosis or multiple-effect evaporation and concentration, underground salt brines and concentrated water of industrial waste water subjected to reverse osmosis treatment.
Owner:天津凯铂能膜工程技术有限公司
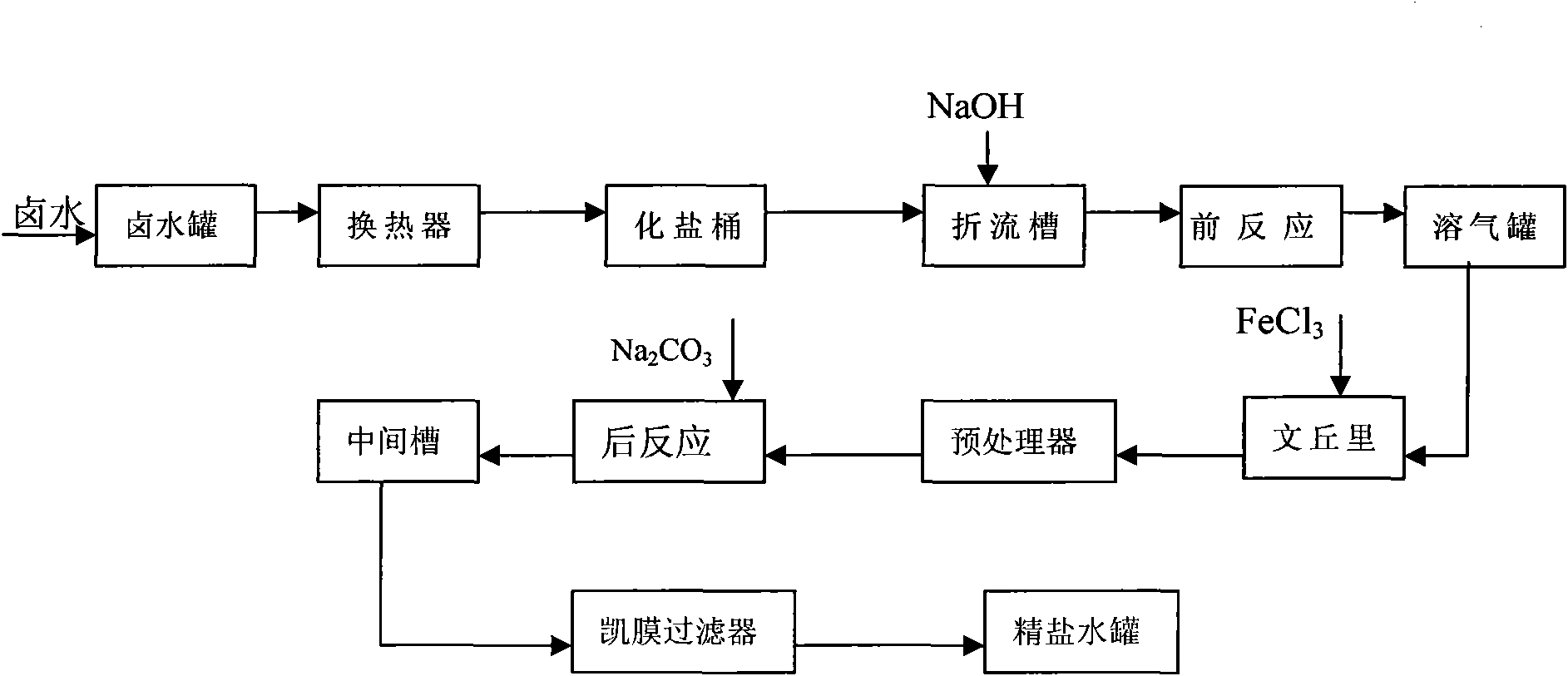
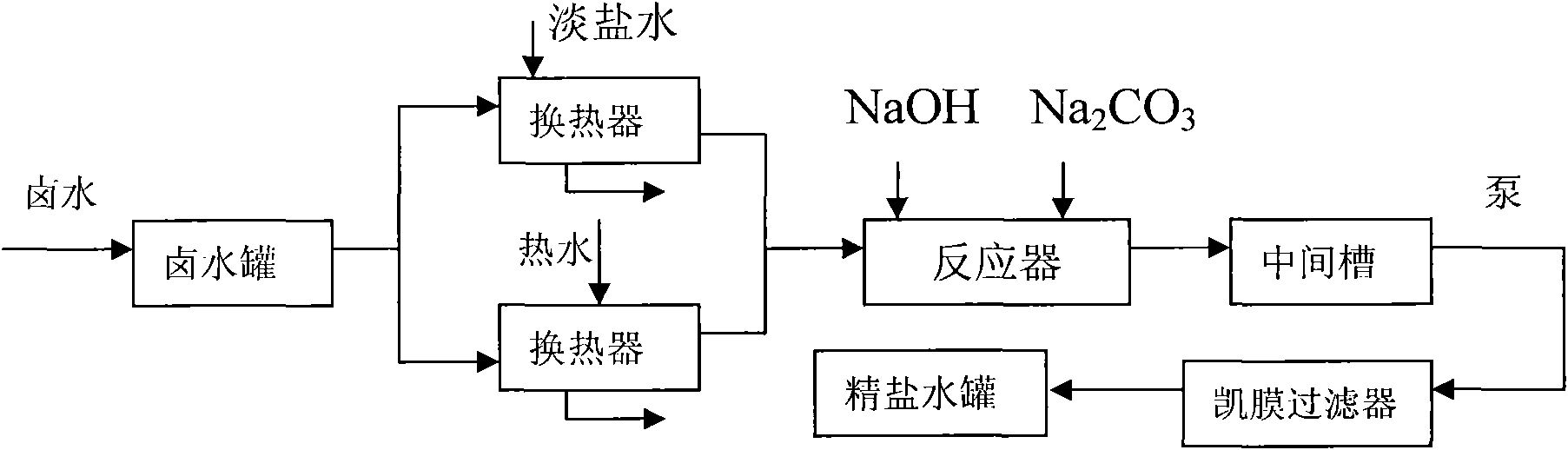
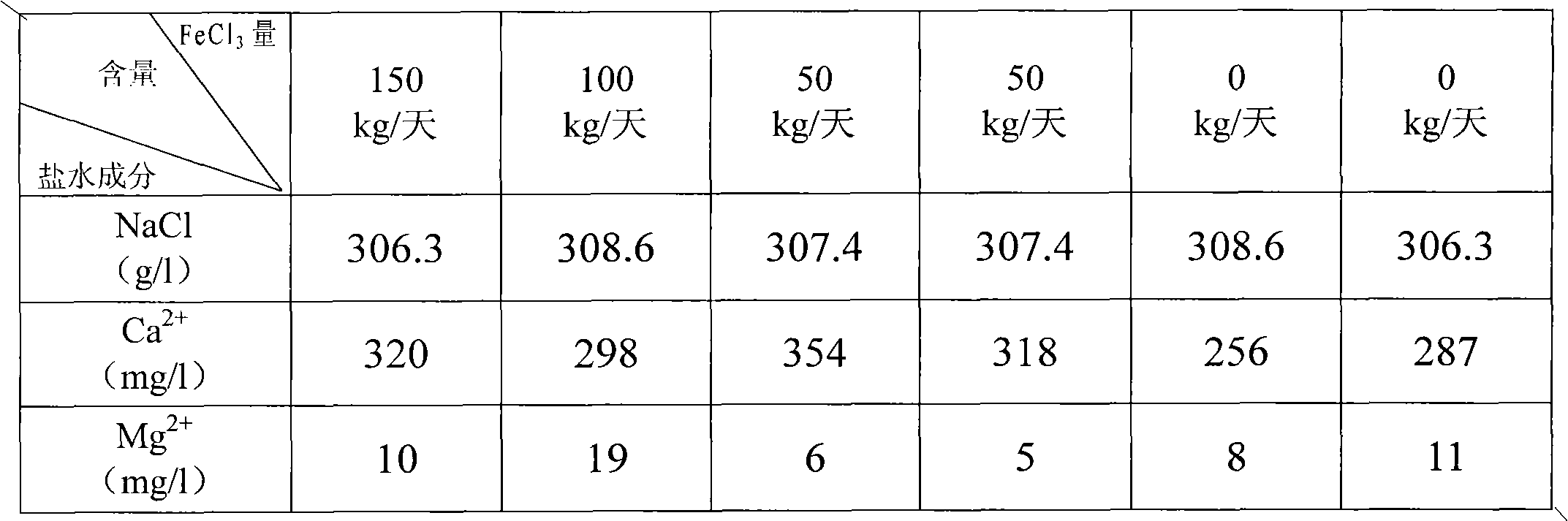
Brine refining process for removing calcium and magnesium by one step
InactiveCN102009987AReduce usageSimple processAlkali metal halide purificationSulfite saltFiltration
The invention provides a brine refining process for removing calcium and magnesium by one step, which comprises the following steps of: pumping saturated brine out of a brine tank by using a pump, dividing the saturated brine into two paths for heat exchange to preheat the brine to 45 to 60 DEG C, and causing the preheated brine to enter a reactor; adding NaOH and Na2CO3 into the reactor, wherein the NaOH and the Na2CO3 partially come from chlor-alkali production process wastewater; performing refining reaction to completely remove Mg<2+> and Ca<2+> from the brine to make 0.2 to 0.5 g / L the concentration of the NaOH and 0.3 to 0.5 g / L the concentration of the Na2CO3 in the brine, and causing the brine to automatically flow into an intermediate tank; and pumping the treated brine into an HVMTM membrane filter for filtration, adjusting a pH value to 8.5 to 10.5 by using hydrochloric acids, adding sodium sulfite to completely remove free chlorine, detecting that suspended solid (SS) content is 0.1 to 0.2 mg / l, and causing the brine to automatically flow into a refined brine tank to prepare fresh brine. The calcium and magnesium impurities are removed simultaneously so as to simplify the process; and the use of ferric chlorides is avoided so as to reduce material consumption and the emission of pollutants.
Owner:河南神马氯碱化工股份有限公司
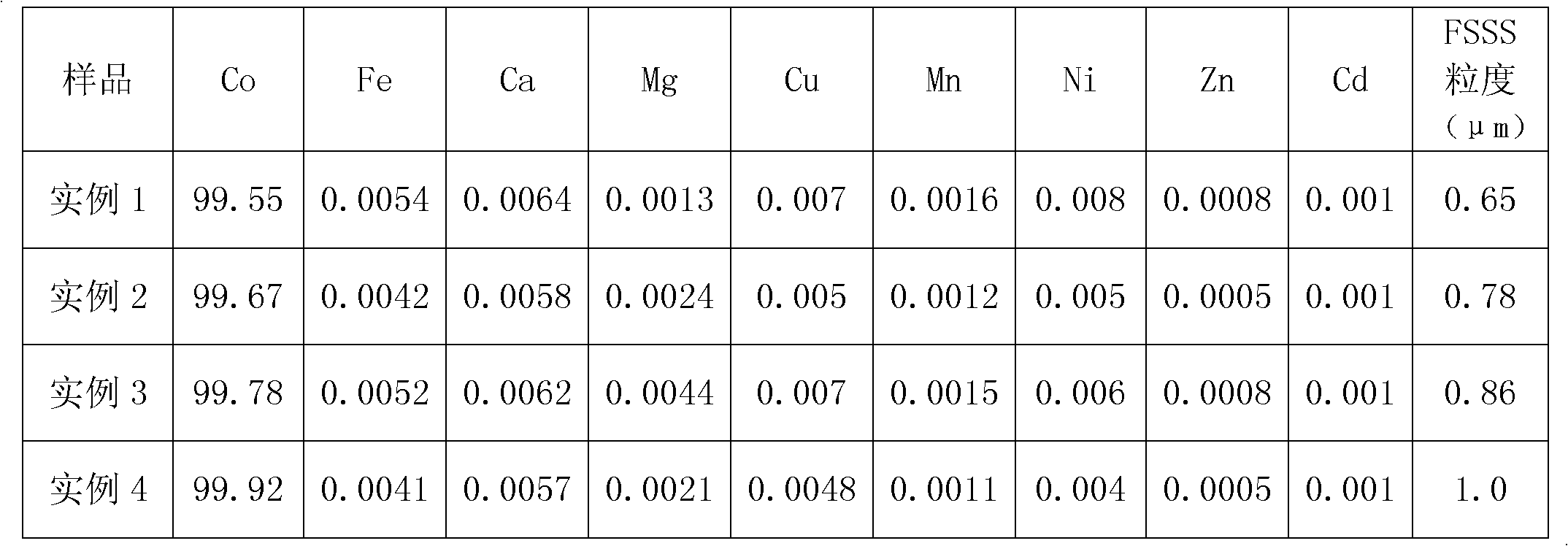
Process for preparing high-purity superfine cobalt powder from copper-cobalt-iron alloy
The invention discloses process for preparing high-purity superfine cobalt powder from copper-cobalt-iron alloy, which is characterized in that the process comprises the following steps: (1) pulverizing the copper-cobalt-iron alloy into alloy powders; (2) pressurizing the alloy powders with inorganic acid for leaching; (3) adjusting the pH value with carbonate to extract impurities to remove ironand fluoride purified calcium and magnesium; (4) extracting, deeply purifying and cleaning to remove copper, manganese and zinc, to separate cobalt from nickel, and to return cobalt to the extractingsolution to precipitate cobalt for preparation of cobalt carbonate; (5) calcining high-purity cobalt carbonate at a high temperature to produce cobalt oxide; and (6) reducing cobalt oxide with hydrogen to high-purity superfine cobalt powders. The beneficial effects of the process disclosed by the invention are as follows: the process is simple and easy to operate, the cost is low, the technical conditions are easy to control, the cobalt loss is small and the leaching rate is high. After several times of purification, the impurities can be completely removed to obtain high-purity superfine cobalt powders.
Owner:HAINAN JINYI NEW MATERIALS
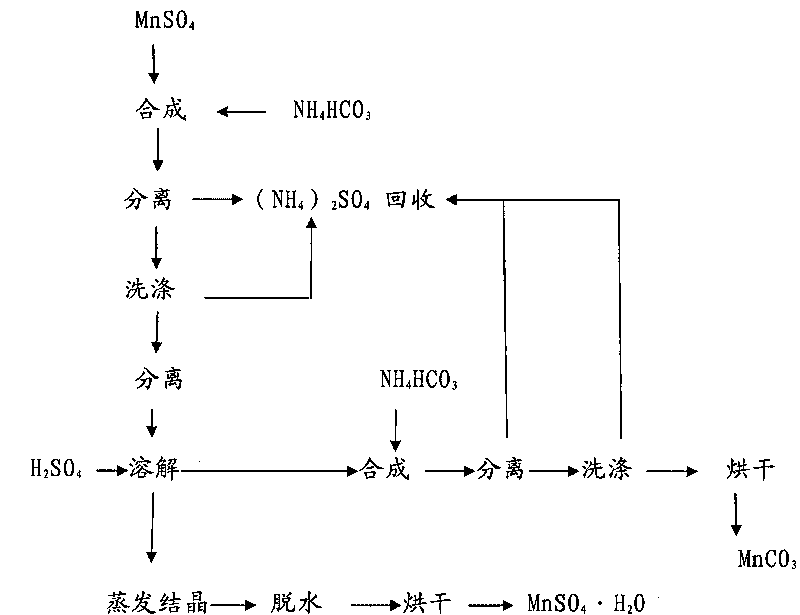
Method for circularly purifying manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate
The invention relates to a method for circularly purifying manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate. The method comprises the following steps: A, stirring manganese sulfate solution at the temperature of between 40 and 80 DEG C, and adding ammonium bicarbonate into the solution for synthesis, controlling the synthesis end point to be an equimolar reaction, separating solid, and washing the solid with hot water to prepare manganese carbonate; B, adding the prepared manganese carbonate into 6 to 12mol / L H2SO4 for reaction, controlling the pH value of the reaction solution to be between 1 and 2, and heating and boiling the solution; C, adding the manganese carbonate prepared in the step A into the reaction solution in the step B, and adjusting the pH value of the solution back to be 4 to 5; and D, performing solid-liquid separation on the reaction solution, distilling and crystallizing the prepared filtrate, and drying the crystal to prepare the manganese sulfate. The circularly purifying method can prepare high-purity manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate with low calcium magnesium and low potassium and sodium.
Owner:GUIZHOU REDSTAR DEVING +1
Method for preparing light calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from dolomite
ActiveCN104016393AHigh puritySimple processCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMagnesiaAtherion elymusCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for preparing light calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from dolomite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calcining and slaking the dolomite to obtain a slaking liquid, converting calcium hydroxide in the slaking liquid to a soluble calcium ion solution through a phase-transfer reaction, meanwhile filtering out magnesium hydrate filter cakes containing impurities, feeding CO2 into the soluble calcium ion solution, precipitating and separating to obtain calcium carbonate and a filter liquor, pulping and carbonizing the magnesium hydrate filter cakes containing impurities to obtain a magnesium bicarbonate solution, then performing a pyrolytic reaction to obtain basic magnesium carbonate, and calcining to obtain light magnesium oxide. The method is simple in technical process and low in energy consumption without strong acid to leach and addition of an impurity removing precipitator, the calcium and magnesium separation effect is good, a common carbonization liquid-solid-gas three-phase reaction is avoided, the reaction condition is easily controlled, and prepared light calcium carbonate accords with demands of national corresponding product standard and lays research basis for industrial scale production.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
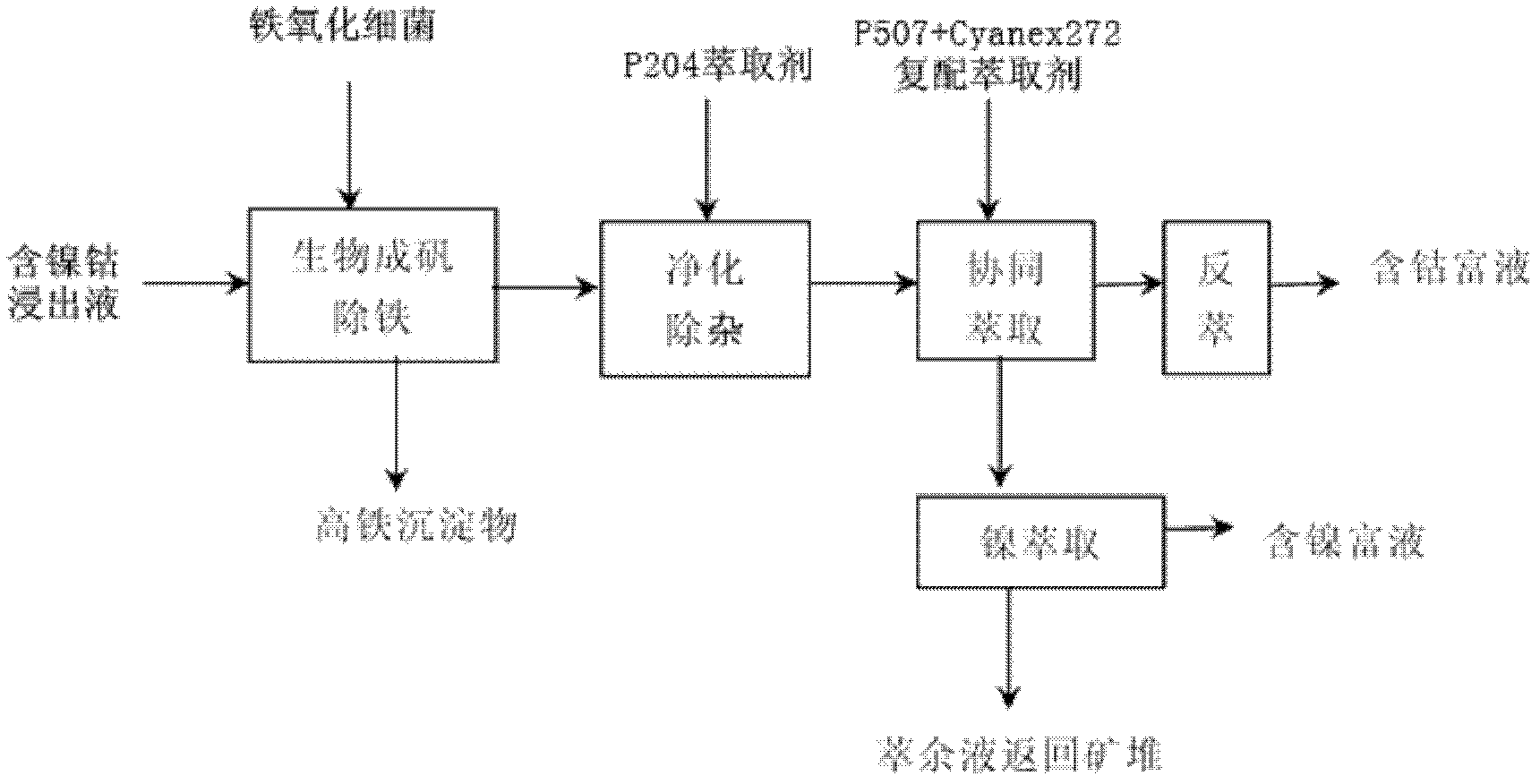
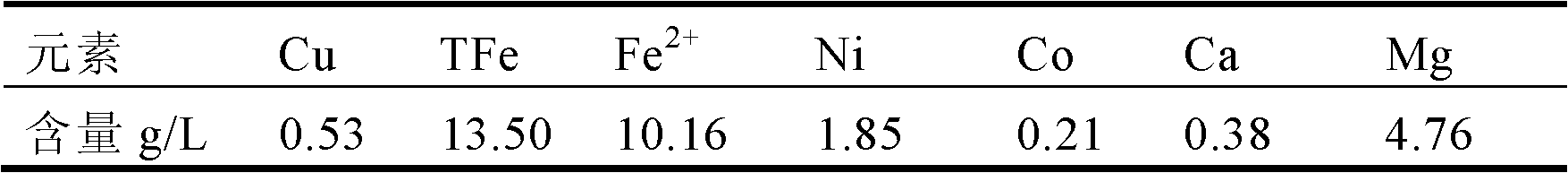
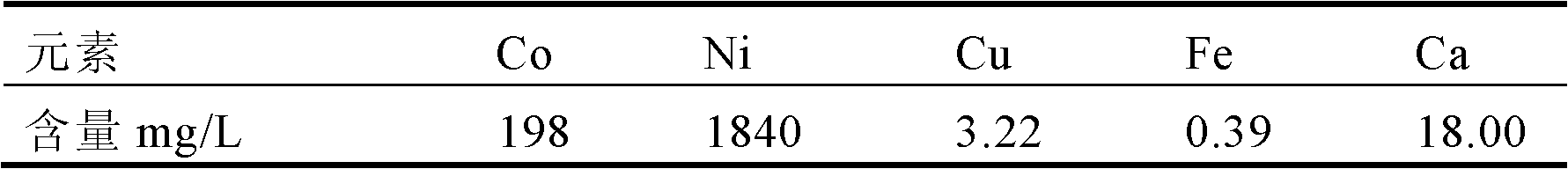
Separation and extraction method for nickel and cobalt in low-grade sulfide mineral bioleaching agent through synergistic extraction
InactiveCN103184337ARealization of iron removalReduce entrainment lossProcess efficiency improvementSulfide mineralsCobalt
The invention provides a separation and extraction method for nickel and cobalt in a low-grade sulfide mineral bioleaching agent through synergistic extraction. The separation and extraction method comprises the following steps: adopting a biological alum precipitation method to perform iron removing on the nickel-cobalt-containing leaching agent, adding iron-oxidizing bacteria under the condition that the pH is 1.8 to 2.0, utilizing oxidation of the bacteria to oxidize ferrous ions in the leaching agent into ferric ions, and enabling the ferric iron to form jarosite-class precipitation; adopting the extraction agent P204 to perform impurity removing on the residual impurities in the leaching agent after iron removing to remove impurities including calcium, magnesium and the like; and using the compound extraction agent containing extraction agent P507 and Cynaex 272 to perform synergistic extraction on the leaching agent after impurity removing, standing for phase splitting for 30 min after extraction, and adding sulfuric acid into the organic phase and performing reverse extraction to extract out cobalt, so as to realize separation of nickel and cobalt through synergistic extraction. The method provided by the invention can reduce neutralization cost of pH value adjustment before extraction of the leaching agent, and omits the pH adjusting procedure when subsequent extraction raffinate returns back to the mineral pile, so as to simplify the technological process, and reduce the neutralization cost and nickel and cobalt entrainment losses caused in the neutralization process.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
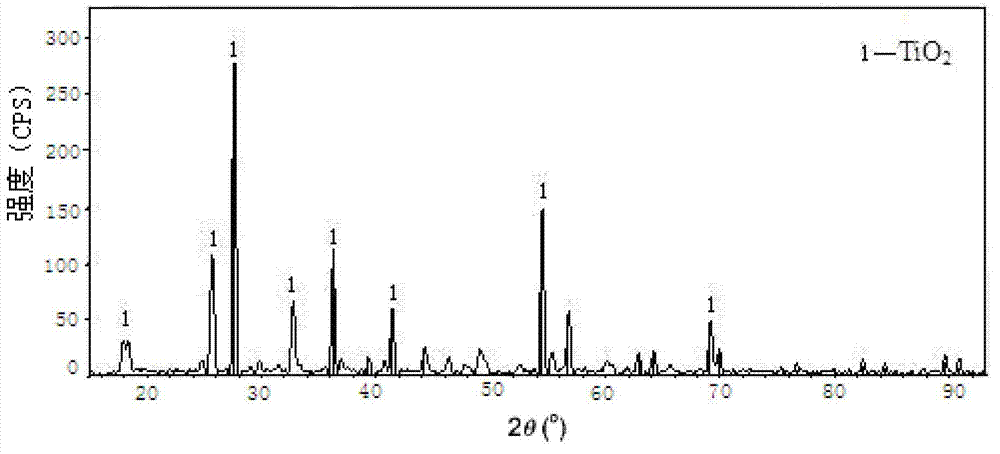
Method for preparing rutile type titanium-rich material from primary titanium-rich material
InactiveCN1710122AIncrease collisionGood for liquid-solid reactionProcess efficiency improvementMicrowave burnRutile
The invention relates to a method refining rutile titanium-rich material with junior titanium-rich material. Heat the junior material with microwave radiation, while add in extractor HCl and addition ammonium hydrofluoride performing a microwave acid dip, the HCl density is controlled between 5 to 10 percent by weight, the adopted amount of ammonium hydrofluoride is 0.5 to 1 percent by weight, the liquor solid ratio V : W = 8 to 12 : 1, producing extraction material containing TiO2 and extraction liquor containing chloride of calcium, magnesium, and ferric. The extraction material is made into rutile titanium-rich material of purity greater than 96 percent, the amount of CaO plus MgO lager lesser than 0.4 percent after processes of filtering, washing, and microwave burning. The titanium recycle is of high rate and purity due to that extraction and burning are adopted microwave. The product can be applied as raw material of boiling chloridization or spongy titanium electrolyse.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing magnesium hydroxide and calcium carbonate in manners of burning dolomite and dissolving into water to separate calcium and magnesium
ActiveCN103738986ASimple processLow costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMagnesium hydroxideCalcium hydroxideCalcium carbonate precipitation
The invention provides a method for separating calcium and magnesium and preparing magnesium hydroxide by water dissolving and leaching of burnt dolomite. The method comprises the following operation steps: crushing the dolomite and burning into dolomite ashes; slaking the dolomite ashes by water to generate calcium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide; filtering and separating an insoluble substance magnesium hydroxide; introducing carbon dioxide to leaching liquid to separate out calcium carbonate precipitate; separating again to obtain a calcium carbonate product, adding a purifying agent to filter residue to remove impurities such as iron, aluminum and the like, centrifuging and separating, and baking, so as to obtain the magnesium hydroxide product. The method has the characteristics of being low in cost, simple in process, and good in product quality, and a new production way is provided for preparation of magnesium hydroxide from dolomite.
Owner:贵州胜威化工新材料研究院有限公司
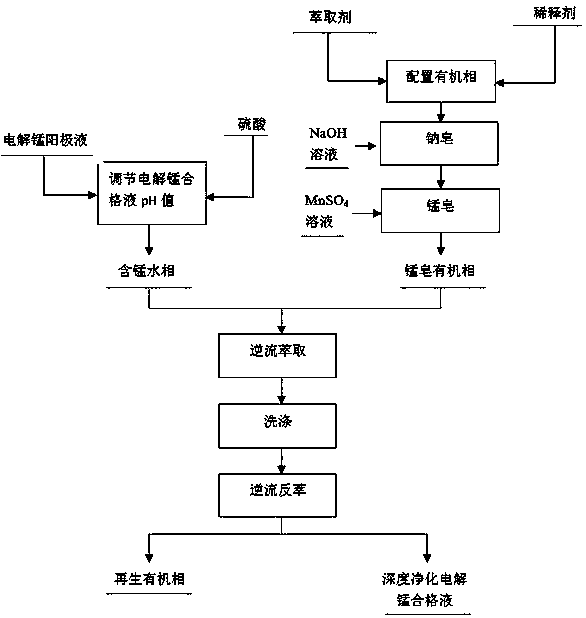
Method for reducing calcium ions and magnesium ions in electrolytic manganese qualified solution
ActiveCN108517425AEasy to realize lossNo lossElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for reducing calcium ions and magnesium ions in an electrolytic manganese qualified solution, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy through an electrolyticmanganese metal wet method. The pH value of the electrolytic manganese qualified solution is adjusted, and an extraction organic phase is prepared; the extraction organic phase is subjected to saponification through alkalin liquor to obtain a sodium soap organic phase, and the sodium soap organic phase is subjected to manganese soaping through a manganese sulfate solution to obtain a manganese soap organic phase; the obtained manganese soap organic phase is used as an extraction agent, and the electrolytic manganese qualified solution subjected to pH adjustment is used as extraction liquid for extraction to obtain an organic phase loaded with the metal ions of the calcium ions and the magnesium ions and a deeply-purified electrolytic manganese qualified solution; the obtained organic phase loaded with the metal ions of the calcium ions and the magnesium ions is subjected to manganese washing through a dilute manganese sulfate solution, and then sulfate reverse extraction is adopted toobtain a regenerative extraction organic phase and a water phase loaded with the metal ions of the calcium ions and the magnesium ions, wherein the regenerative extraction organic phase can be recycled. By means of the method, removing of the calcium ions and the magnesium ions with high concentrations in the electrolytic manganese qualified solution can be effectively achieved, meanwhile, loss of manganese ions is avoided, and moreover, impurity ions such as F<-> are not introduced.
Owner:贵州武陵锰业有限公司 +1
Comprehensive recovery method of lithium iron phosphate waste powder
ActiveCN109095481AEasy to recycleAvoid pollutionProcess efficiency improvementPhosphorus compoundsCalciums magnesiumMagnesium
A comprehensive recovery method of lithium iron phosphate waste powder comprises the following steps that A, lithium iron phosphate waste powder is oxidized and roasted to obtain activated roasted sand; B, acid regurgitation and leaching are performed, wherein the Li in the activated roasted sand is leached out as much as possible, so that valuable elements phosphorus and iron form iron phosphate;C, a certain amount of precipitator is added, and impurities phosphate anions are removed; D, by means of regulation of a neutralizer and sodium carbonate, impurities such as calcium and magnesium inthe solution are removed; E, sodium carbonate is added under the high-temperature condition to obtain battery grade lithium carbonate; F, sodium sulfate is synthesized. The valuable elements phosphorus, iron and lithium in the lithium iron phosphate waste powder are recovered to the most degree, and the method has the advantages of being reasonable in process, low in manufacturing cost, free of pollution, nonhazardous and the like.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Method for preparing lithium carbonate with high-lithium salt lake bittern
InactiveCN105036159AReduce contentHigh purityLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesInorganic saltsLithium chloride
The invention relates to the field of inorganic salt chemical engineering and discloses a method for preparing lithium carbonate with high-lithium salt lake bittern. The method comprises the steps of adding inorganic salt into the salt lake bittern for removing impurities, extracting lithium chloride, and then adding addition agents, complexing agents and precipitating agents into a lithium chloride solution for preparing the lithium carbonate. By means of the added complexing agents, micro calcium and magnesium ions remaining in the bittern can be effectively removed, and the content of the calcium and magnesium ions in a lithium carbonate product is reduced; by means of the addition agents, the lithium carbonate purity is effectively raised.
Owner:韦海棉
Method for making pellet by fine-grinded steel slag instead of bentonite
The method to use fine-grinding steel sludge instead of bentonite to prepare the pellet ore comprises: a. fine grinding the steel sludge into power with 200items content more than 90%; b. adding 1-10m% former steel sludge into refined iron powder instead of bentonite; c. adding 6-10% water into the mixture; generating 8-20mm raw roll; d. sending former balls into shaft furnace or chain-pellet for drying and baking. The experiments show the product has up to the standard, increases grade 2.2% and reduces SiO2 1.7%, and realizes sludge recovery.
Owner:TANGSHAN GUOFENG IRON & STEEL
Method for preparing ultra-fine calcium oxide with dolostone
InactiveCN101318681AImprove protectionUniform particlesCalcium/strontium/barium oxides/hydroxidesDolostoneCalcium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing superfine calcium oxide from dolostone. The dolostone has very rich reserves in China, and the main composition of the dolostone is dolomite with a chemical formula MgCa(CO3)2. The method comprises the following simple steps: firstly, separation of calcium and magnesium is realized through reaction between dolostone calcined powder and dolostone acidizing fluid; and secondly, an alkaline solution is dripped into a calcium chloride solution obtained after separation of the calcium and the magnesium, and activated superfine calcium oxide powder is obtained after calcination of obtained calcium hydroxide granules. The superfine calcium oxide is widely applied in the fields such as fire retardant, absorbent, filler and so on. The method for preparing the superfine calcium oxide provided by the invention has a simple technological flow, small equipment investment, and low operating cost; the purity of the prepared calcium oxide is over 90 percent, and superfine magnesium hydrate powder with economic value is simultaneously obtained; and the method is an economic and effective method for preparing the superfine calcium oxide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Calcium magnesium phosphate nanometer structure material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104961114ASimple preparation processEasy to operatePhosphorus compoundsPhosphateMagnesium salt
The invention relates to a calcium magnesium phosphate nanometer structure material and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the following steps of using water soluble calcium salt as a calcium source, water soluble magnesium salt as a magnesium source and phosphorus biological molecules as a phosphorus source; performing hydrothermal reaction on mixed water solution containing the calcium source, the magnesium source and the phosphorus source to obtain the calcium magnesium phosphate nanometer structure material. The phase and the morphology of the calcium magnesium phosphate nanometer structure material are regulated and controlled by means of regulating the molar ratio of the calcium source to the magnesium source.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing basic magnesium chloride whisker from dolomite and bittern
InactiveCN101353815AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePolycrystalline material growthMagnesium chloridesCalciums magnesiumDolomite
The invention discloses a method for preparing basic magnesium chloride crystal whiskers taking dolomite and bittern as raw materials. The method mainly comprises the following steps: roasting and acidization treatment are carried out to natural dolomite firstly to respectively obtain dolomite roasted powder and dolomite solution; the dolomite solution is mixed and reacts with the bittern to remove sulfate ions from the bittern and obtain a mixed solution; the mixed solution reacts with the dolomite roasted powder by a certain ration, and the basic magnesium chloride crystal whiskers are obtained after aging, and waste liquid produced in the preparation process can be recycled and reused. The method for preparing basic magnesium chloride crystal whiskers provided by the invention takes dolomite and bittern as raw materials which are widely available and cheap, the production technology is simple, recycle of resource is realized, calcium and magnesium resource of the dolomite and the bittern is fully used, the basic magnesium chloride crystal whiskers obtained are a filling agent and flame retardant with wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
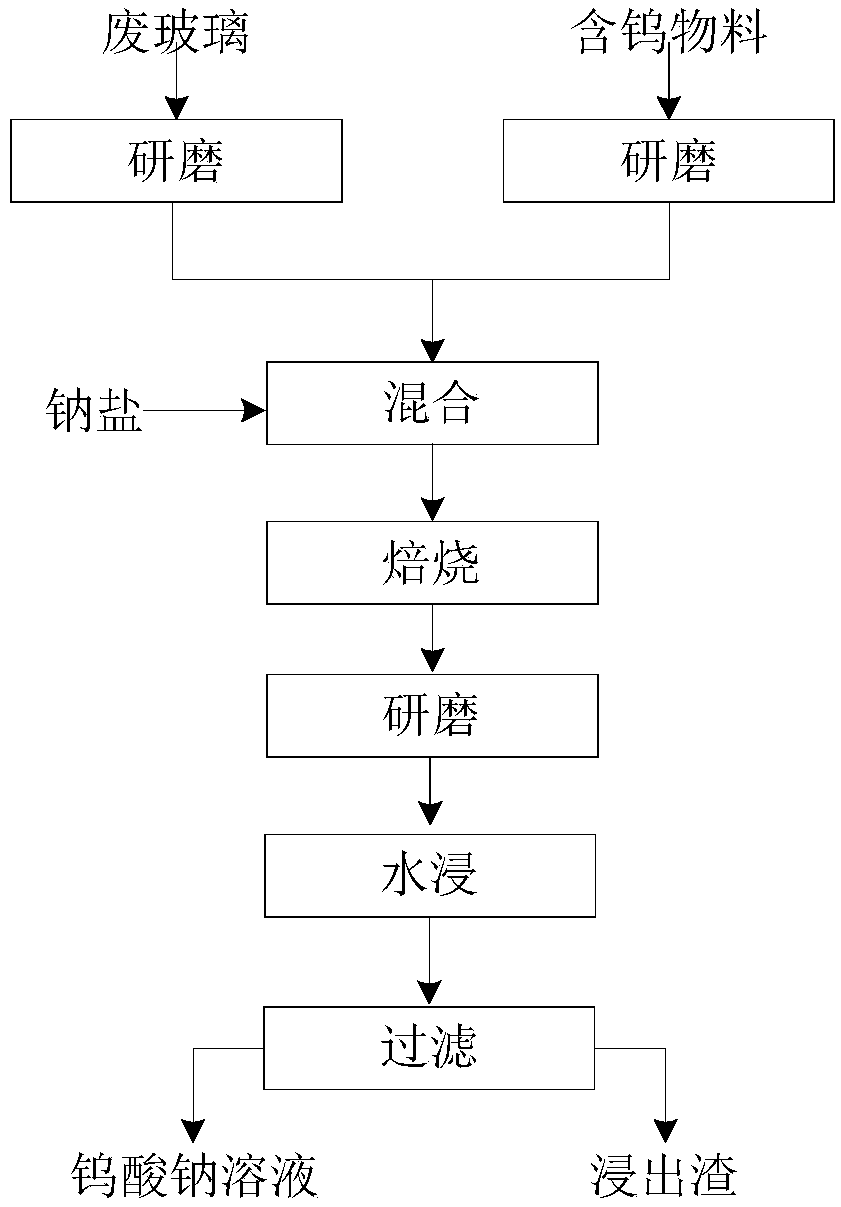
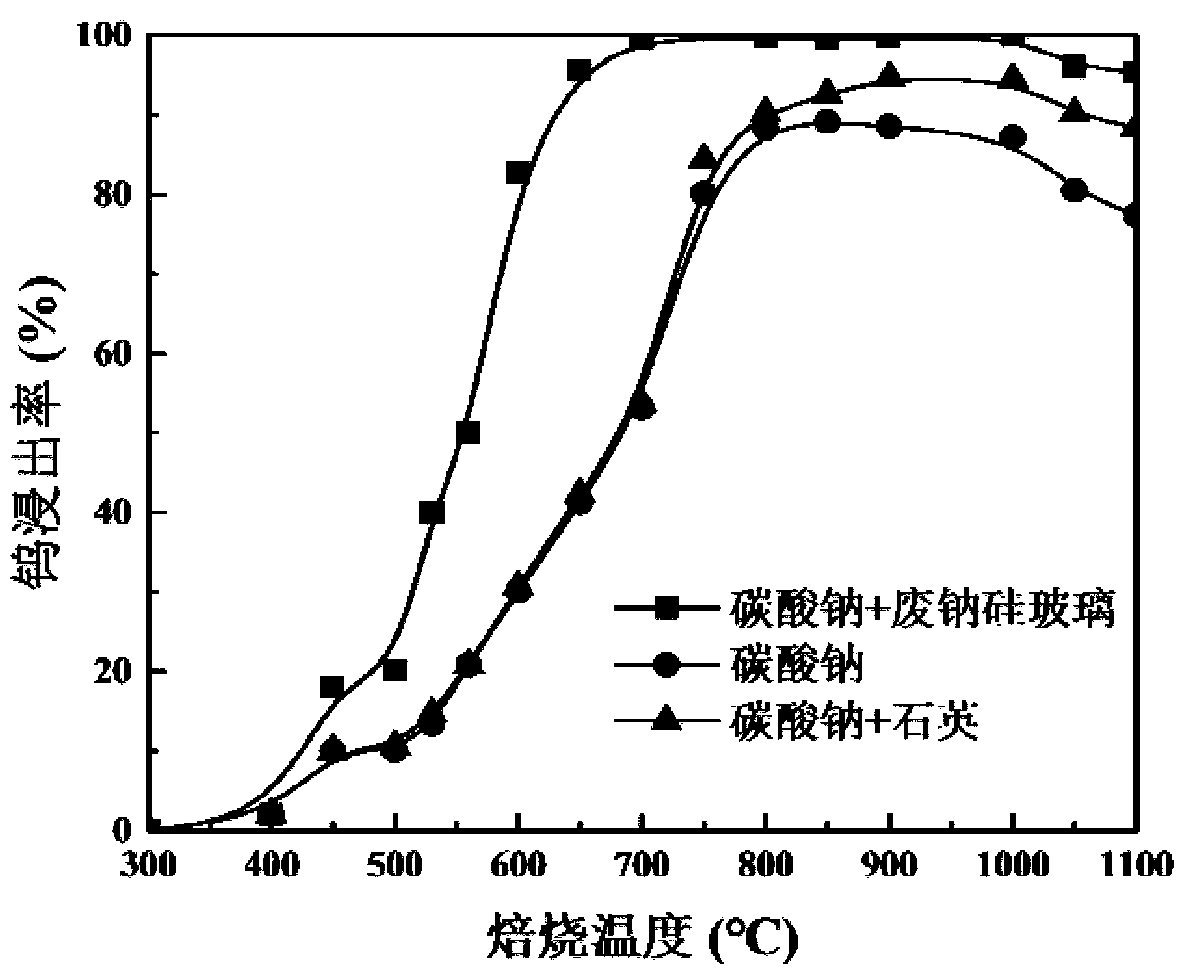
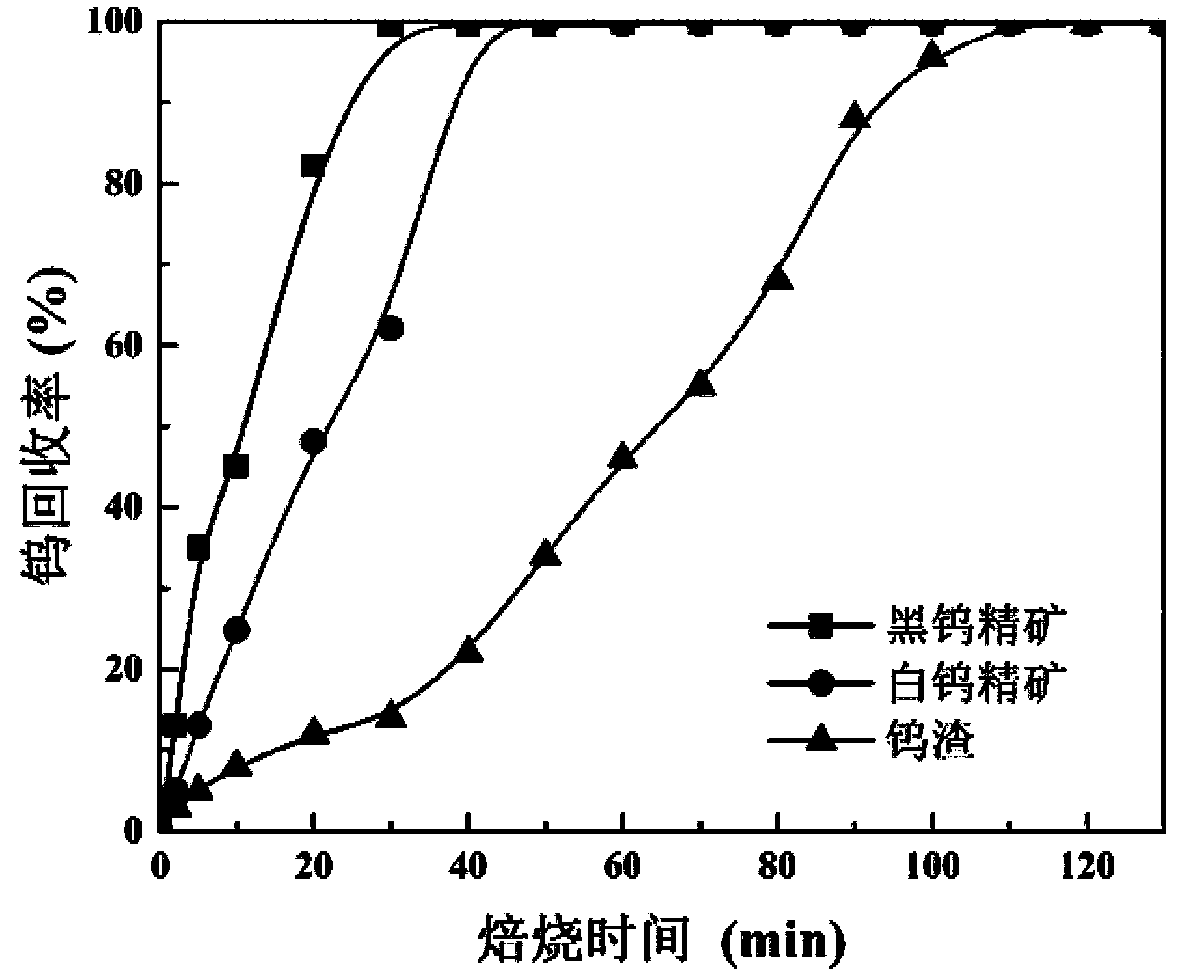
Method for extracting tungsten from tungsten-containing raw material through waste glass
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten from a tungsten-containing raw material through waste glass. The method includes the steps that the tungsten-containing material and the wasteglass are ground and smashed and then mixed with sodium salt, the mixture is roasted, and a sintered material is obtained; and after being ore-ground, the sintered material is leached with water, andtungsten-containing extract is obtained. According to the method, quartz used in the traditional tungsten ore thermometallurgy process is replaced with the waste glass, the tungsten leaching rate canbe increased, the operation is easy, the requirements on the raw material are low, the operating cost is low, the problem of low efficiency of fixing of calcium and magnesium by the quartz in the traditional sodium salt roasting process is solved, and the method is also an effective means for consuming the waste glass on a large scale.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
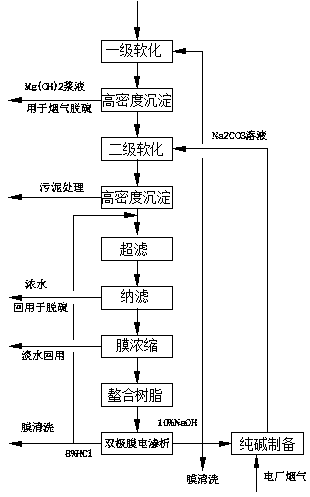
Method for magnesium oxide method power plant desulfurization wastewater zero discharging treatment
PendingCN110104851AReduce usageReduce processing costsChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideDispersed particle separationSlurryChelation
The invention discloses a method for magnesium oxide method power plant desulfurization wastewater zero discharging treatment. The method comprises the steps that wastewater is subjected to primary softening to remove Mg2+ and heavy metal ions, a primarily softened mud and water mixture enters a first high density precipitation unit, an obtained supernate enters a secondary softening unit to remove Ca2+, a secondarily softened mud and water mixture enters a second high density precipitation unit for precipitation, a supernate is treated through a film system, obtained fresh water is recycled,produced concentrated water enters a chelation resin unit, calcium, magnesium and heavy metal ions are removed deep, outflow water enters a bi-polar membrane electrodialysis unit, and a sodium hydroxide solution with the concentration being 10% and a hydrochloric acid with the concentration being 8% are obtained through treatment; the method achieves recycling of magnesium hydroxide slurry, the consumption of flue gas desulfurization magnesium oxide is greatly lowered, the bi-polar membrane electrodialysis acid-alkali producing technology is adopted, meanwhile, carbon dioxide in flue gas of apower plant is used for preparing sodium carbonate, recycling of salt in wastewater is achieved, and no softening medicament needs to be purchased additionally.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Method for producing potassium chloride and co-producing calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and silicon composite fertilizer by potassium feldspar
ActiveCN103183364ASignificant progressLower firing temperatureAlkali metal chloridesFertilizer mixturesPhosphateDolomite
The invention relates to a method for producing potassium chloride and co-producing a calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and silicon composite fertilizer by potassium feldspar. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing materials, crushing and mixing the materials to form raw materials, homogenizing and calcining, and finally preparing potassium chloride and calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and silicon composite fertilizer, wherein the raw materials comprise the components in percentage by weight as follows: 40-46% of potassium feldspar, 30-38% of phosphate ore, 12-16% of dolomite and 9-11% of industrial salt; calcining at 850-950 DEG C, and if a rotary kiln is selected, calcining at 850-900 DEG C; water-quenching red hot clinkers obtained, separating liquid from dregs and concentrating the liquid to obtain potassium chloride; drying, dehydrating and crushing residual solid dregs to 150-200 meshes, and packaging to obtain the calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and silicon composite fertilizer. Compared with the prior art, not only is the sintering temperature reduced by 40 DEG G, but also the calcining cost is reduced by 50% and the yield is improved by 5-6 times.
Owner:江苏纳鼎材料科技有限公司
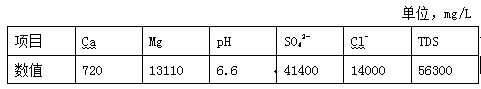
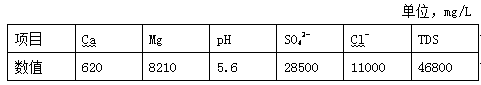
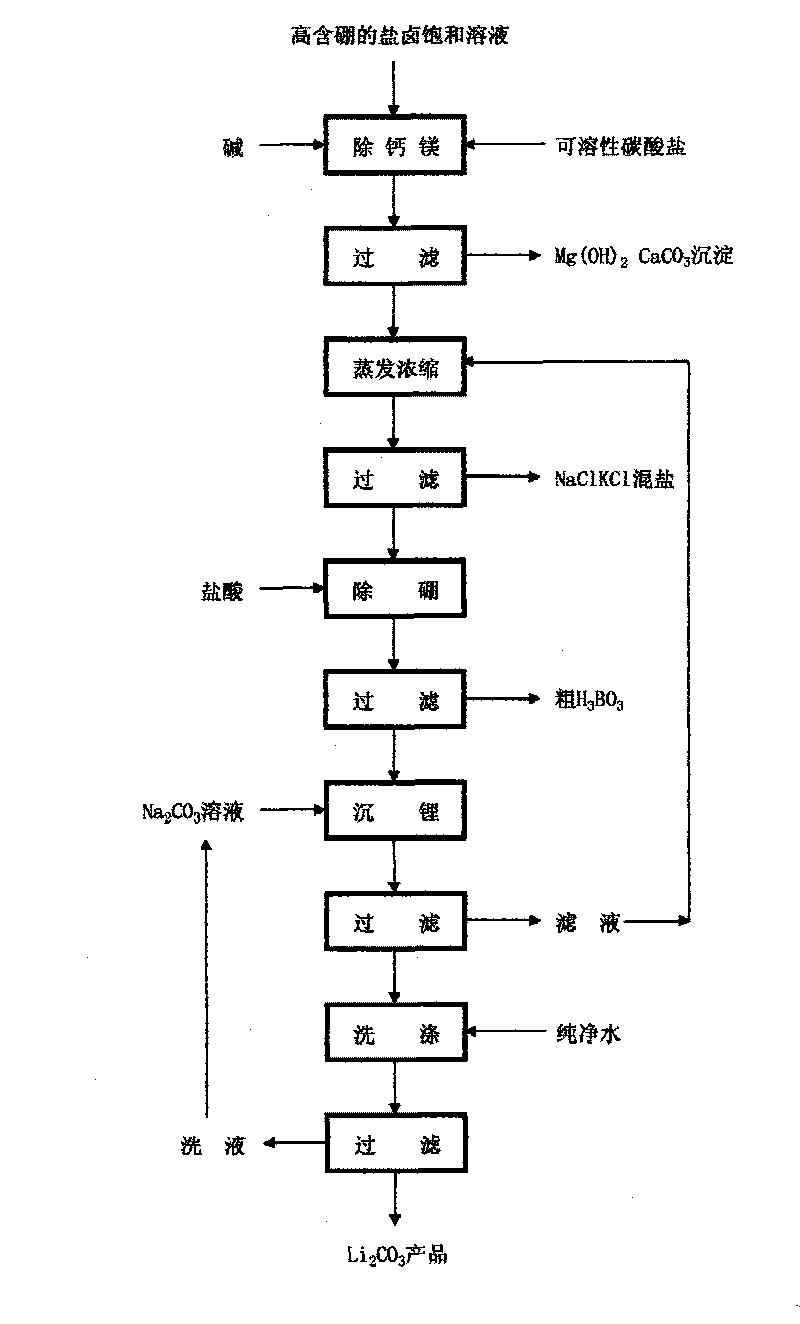
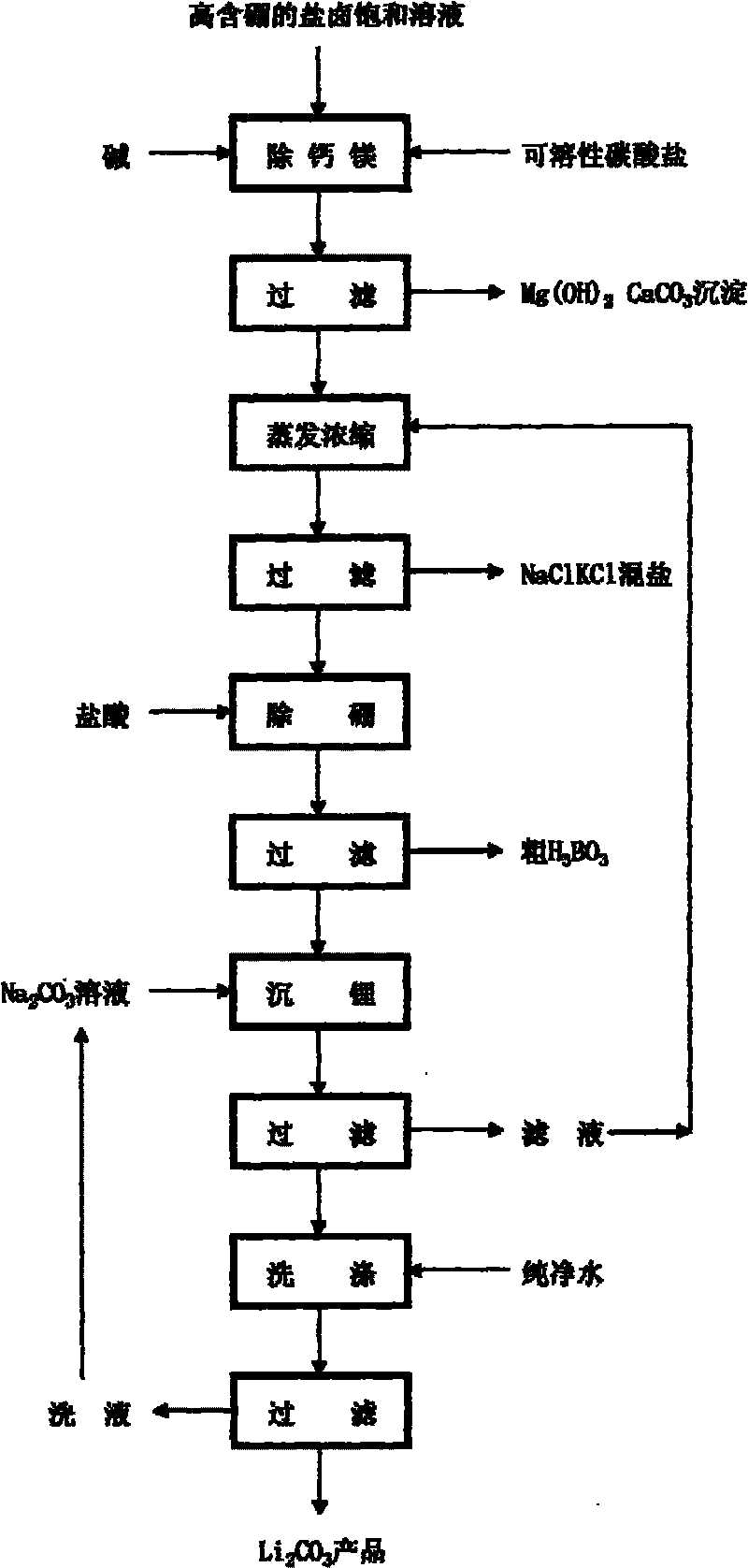
Method for preparing lithium carbonate by using high boric bittern saturated solution
InactiveCN101691231ADoes not affect extractionNo dischargeLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSocial benefitsLithium carbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing lithium carbonate by using high boric bittern saturated solution, which is mainly used in the production of lithium carbonate prepared by using deep marine bittern rich in potassium and comprises the process flow that the high boric bittern saturated solution is prepared into a lithium carbonate product through calcium and magnesium removal, evaporation and concentration, boron removal, lithium settlement and washing. The method has the advantages of simple and feasible process, low equipment investment, low production cost, high yield, better economic and social benefits and the like, and can reclaim boron at the same time; and the high-content boron does not influence the extraction of lithium.
Owner:DAZHOU HENGCHENG ENERGY GROUP
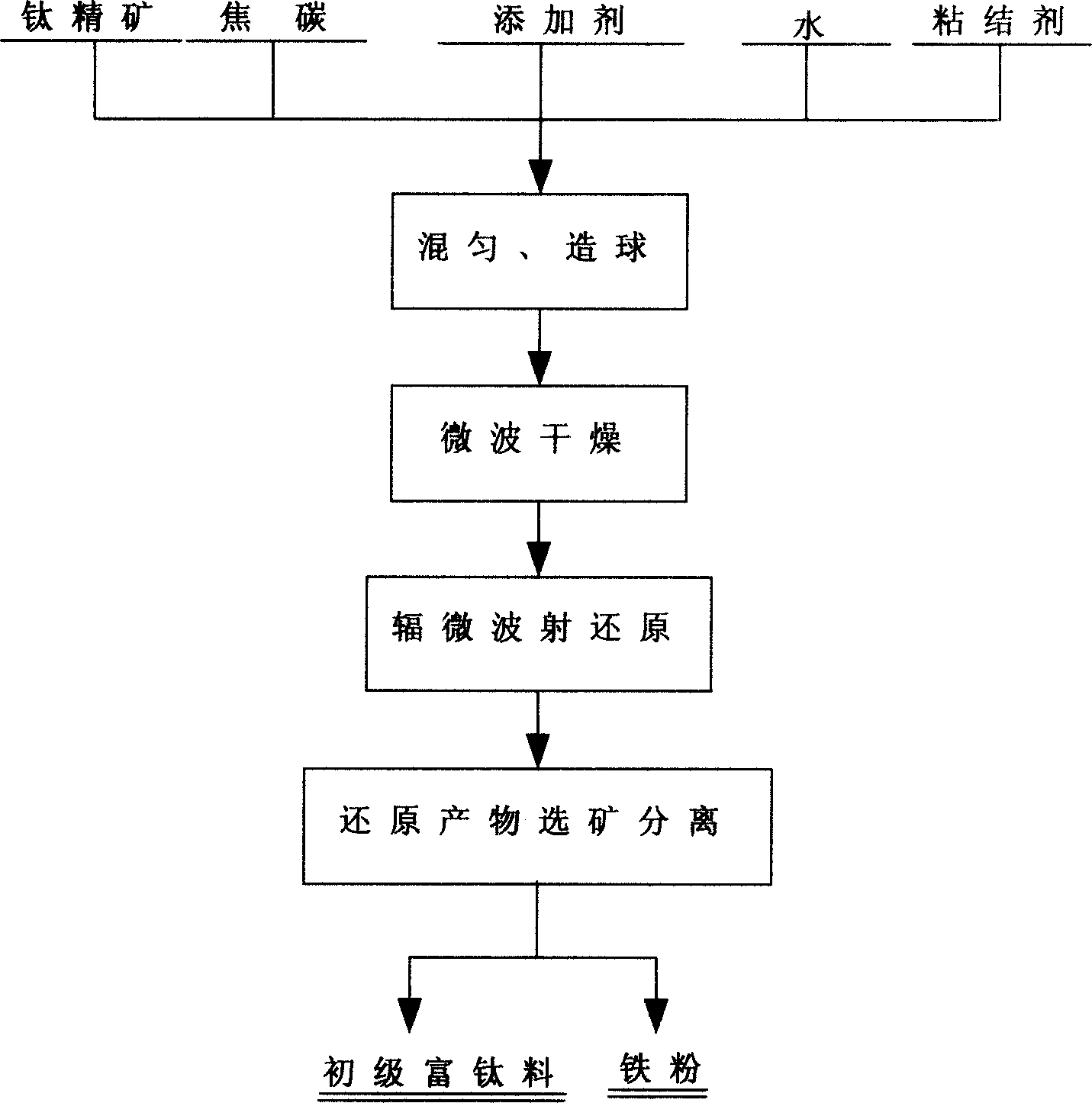
Method for preparing primary titanium-rich material from high calcium-magnesium-titanium headings
The invention relates to a technique refining junior titanium-rich material with high calcium magnesium titanium fine ore. Crash titanium ore of purity 45.00 to 50.00 percent till particles of which the size is smaller than 0.074mm taking 60 to 80 percent weight, then add in with water 8 to 20 percent weight of the ore, adherent sodium silicate 3 to 5 percent, chark 10 to 20 percent, 1 to 5 percent addition sodium sulfate, 1 to 3 percent addition iron powder, 3 to 5 percent addition potassium chloride, making complex balls sized 10 to 15 mm, and acquire junior titanium-rich material after microwave drying, microwave heating and restoring, ore selecting and separating. As the titanium ore is highly wave absorptive, the heating speed is high, and the restore temperature is lowered by 80-120 deg.C, extraneous material calcium and magnesium are of good acid dissolvability which ensures the high purity of the junior titanium-rich material.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Purification and impurity removal method for lithium chloride mixed solution
InactiveCN106048218AHigh acceptanceReduce calcium and magnesium contentSemi-permeable membranesProcess efficiency improvementLow salinityLithium chloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium production, and particularly relates to a purification and impurity removal method for a lithium chloride mixed solution. The method includes the step that impurity removal is conducted on the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution through a nanometer filter to obtain a low-salinity lithium chloride solution, wherein the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution is a mixed solution of lithium chloride, magnesium chloride and calcium chloride; in the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution, the content of lithium ranges from 0 g / L to 55.0 g / L, and the content of calcium and magnesium ranges from 0 g / L to 30 g / L; in the low-salinity lithium chloride solution, the content of lithium ranges from 0 g / L to 55.0 g / L, and the content of calcium and magnesium is smaller than or equal to 5 mg / L; and a nanometer filter membrane in the nanometer filter is a monovalent ion selective nanometer filter membrane. The content of calcium and magnesium in discharged water subjected to impurity removal through the purification and impurity removal method of a salt chlorine-containing system is extremely low, the content of lithium reaches up to saturation, and possibility is provided for obtaining low-calcium and low-magnesium lithium production intermediate fine products by directly processing lithium production intermediate rough products.
Owner:SICHUAN SIDANENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing titanium-rich material by directly reducing molten slag from vanadium-titanium-ferrum concentrate
ActiveCN102787194AQuality improvementImprove utilizationProcess efficiency improvementMolten saltMolten slag
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium-rich material by directly reducing the molten slag from the vanadium-titanium-ferrum concentrate, belonging to the technical field of the comprehensive utilization of the vanadium-titanium-magent ore. The method comprises the following steps: (a) grinding the molten slag directly reduced from the vanadium-titanium-ferrum concentrate, and modifying by oxidizing to prepare the modified slag; (b) adding hydrochloric acid solution into the modified slag prepared in the step (a) for acid leaching, and filtering to obtain the acid-leached slag and the acid-leached liquid; (c) adding sodium hydroxide solution into the acid-leached slag obtain in the step (b) for alkali leaching, and filtering to obtain the alkali-leached slag and the alkali-leached liquid; and (d) washing and calcinating the alkali-leached slag obtained in the step (c) to obtain the titanium-rich material. The invention discloses the novel application of the vanadium-titanium-ferrum concentrate to the direct reduction of the molten slag, and the application effect of the vanadium-titanium-ferrum concentrate is improved greatly. The titanium-rich material prepared by adopting the method has high quality, contains more than 90% of TiO2 and less calcium and magnesium and is suitable for producing chloride process titanium dioxide and titanium sponge.
Owner:盐城捷晶科技有限公司
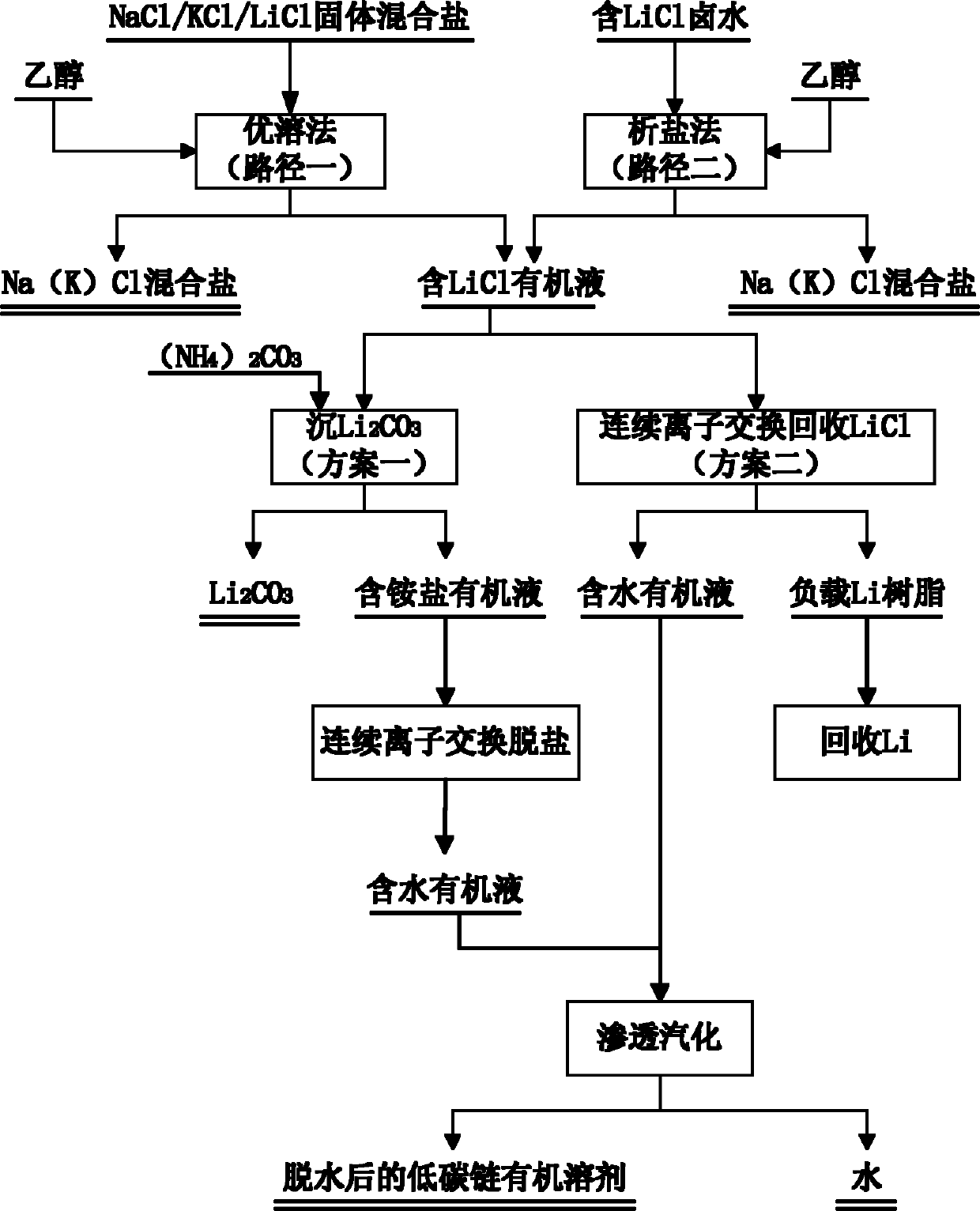
Process for extracting lithium from salt lake water subjected to calcium and magnesium preseparation
InactiveCN102168183AHigh purityHigh lithium yieldProcess efficiency improvementLithium chlorideIon exchange
The invention relates to a process for extracting lithium from salt lake water subjected to calcium and magnesium preseparation. A low-carbon chain organic compound, such as ethanol, propanol or acetone as a solvent for extracting lithium is fully mixed with solid mixed salts obtained after salt lake water is subjected to calcium and magnesium removal or a saturated solution of the solid mixed salts so that LiCl enters an organic solvent, other salts are retained in a solid phase, and the aims of separating, extracting and purifying lithium are achieved. According to the obtained lithium-contained organic solution, lithium carbonate is precipitated by ammonium carbonate, and desalinization is carried out by a continuous ion exchange system consisting of hydrogenous and oxyhydrogen resin, or lithium chloride is directly removed from the lithium-chloride-containing organic solution by the continuous ion exchange system consisting of hydrogenous and oxyhydrogen resin. The organic solvent obtained after desalination treatment only contains water without salt, and the process is used for water separation recycling and organic solvent return process by adopting a pervaporation method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
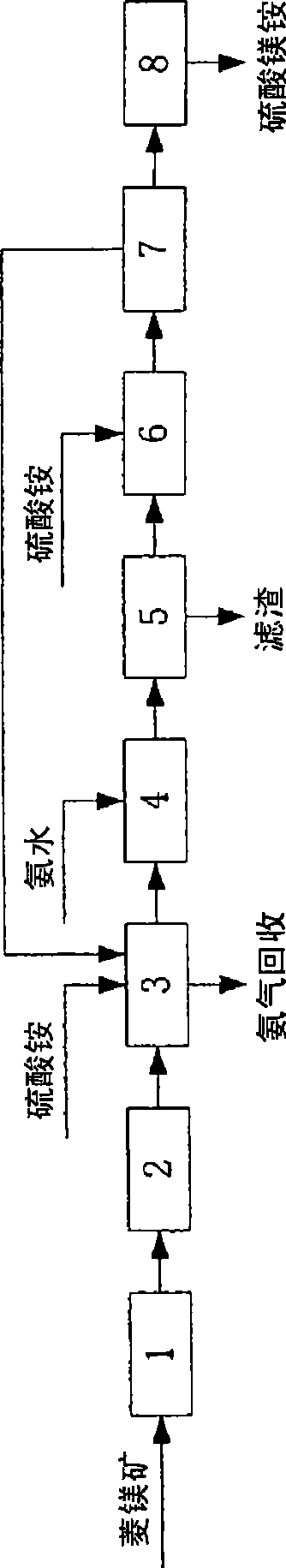
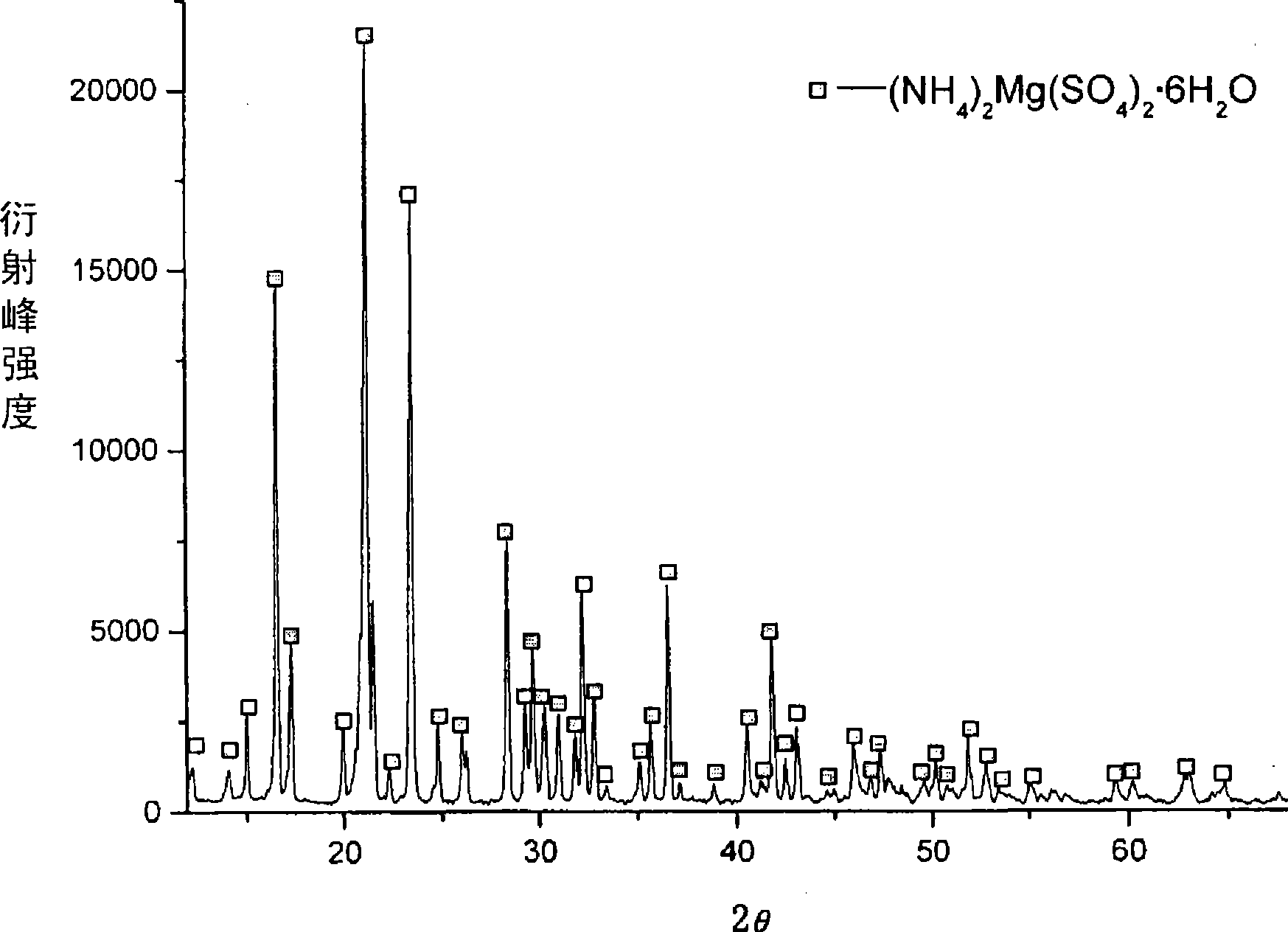
Method for preparing ammonium magnesium sulfate hexahydrate from giobertite
InactiveCN101497453AHigh reactivityEfficient removalSulfate preparationMagnesium sulfatesMagnesiteCalciums magnesium
The invention discloses a method for preparing ammonium magnesium sulfate hexahydrate from magnesite, which comprises the following steps: A) performing activated roasting on the magnesite; B) preparing a magnesium sulfate solution by leaching roasted powder of the magnesite by ammonium sulfate, and removing iron ions by regulating the pH value; and C) mixing and crystallizing the magnesium sulfate solution prepared in the step B and an ammonium sulfate solution, and filtering and drying the obtained product to obtain ammonium magnesium sulfate hexahydrate crystals. A washing liquid and a filtrate during the production can be circularly used. The method is characterized in that the method utilizes the ammonium sulfate to ensure that magnesium is quickly dissolved out from the roasted magnesite and calcium is not dissolved out, realizes the separation of the calcium and the magnesium, improves the overall production efficiency, and reduces the production cost for ammonium magnesium sulfate.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
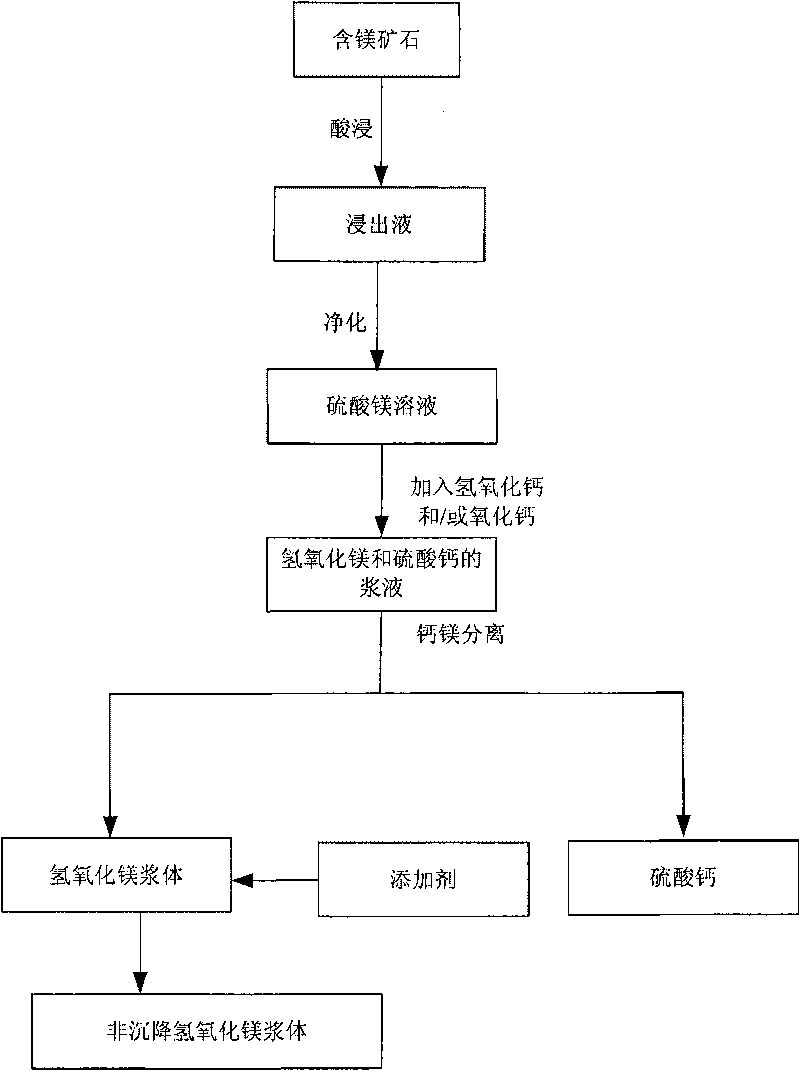
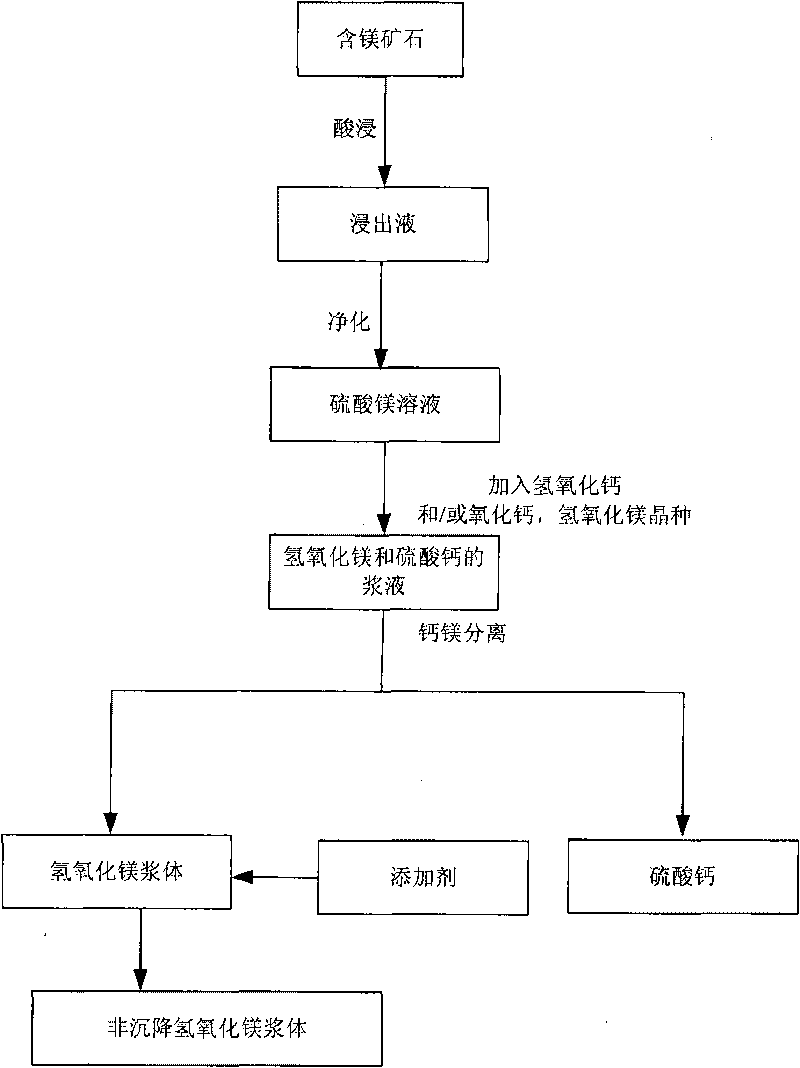
Improved method for leaching magnesium-containing ore
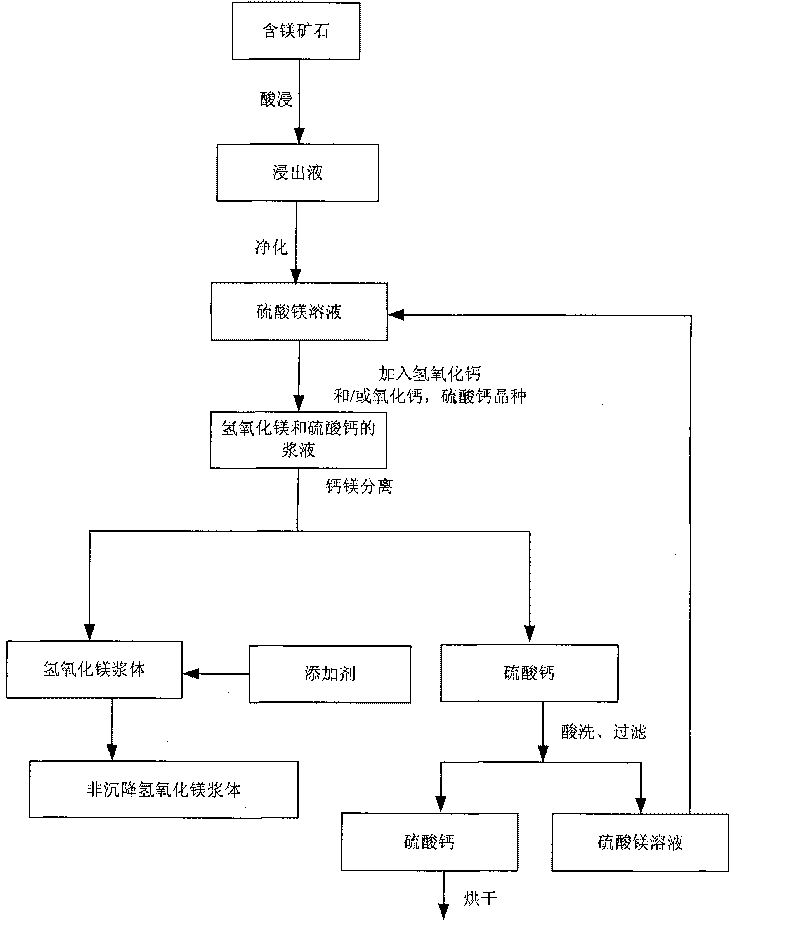
InactiveCN101760617AReduce pollutionRecycle resourcesProcess efficiency improvementMagnesium hydroxideSlurryCalciums magnesium
The invention discloses a method for leaching magnesium-containing ore, which comprises the steps of: mixing magnesium-containing ore with vitriol solution to carry out acid leaching to obtain magnesium sulfate-containing lixivium; purifying the lixivium to obtain magnesium sulfate solution; mixing the magnesium sulfate solution with calcium hydroxide and / or calcium oxide to obtain serous fluid containing magnesium hydroxide and calcium sulfate; separating calcium from magnesium in the serous fluid to obtain the magnesium hydroxide serous fluid and the calcium sulfate; and adding additive into the magnesium hydroxide serous fluid to flocculate into non-deposited magnesium hydroxide. The technology can recover the magnesium with high efficiency and low cost from the purified magnesium sulfate solution, wherein the recovered magnesium can be used for desulphurization in electricity generating stations; recycles the magnesium in the magnesium sulfate solution; and saves the resources.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Al-Ca-Mg-Fe alloy for final deoxidisation of molten steel and its preparation
An AlGaMgFe alloy for final deoxidization of molten steel contains Al (30-60%), Ca (2-15%), Mg (2-15%), Si (0-3%) and Fe (rest) and is prepared through proportionally mixing silica rock, lime, coke and iron filings, smelting to obtain low-Si ferrocalcium, adding Al, Mg and Fe, and smelting. It can improve the mechanical performance of steel and prevent the sprute from being blocked, and has desulfurizing effect.
Owner:郭庆成
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com