High-adsorption porous carbon supported zero-valent iron catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
A catalyst, zero-valent iron technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the reduction of oxidation efficiency, sulfate radical removal, secondary pollution and other problems, to achieve the effect of preventing iron agglomeration, facilitating recovery and separation, and stable physical and chemical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Add 1.0g of F127 surfactant (polyethylene oxide-polypropylene oxide triblock copolymer) into 11g of ethanol solution, then add 0.8g of phenolic resin (50wt%), stir for 10min to make it evenly mixed;
[0056] 1.0g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O was dissolved in 3g ethanol solution and added to the above mixed solution, then added 0.28g citric acid, stirred for 30min to evaporate the solvent in the mixed solution;
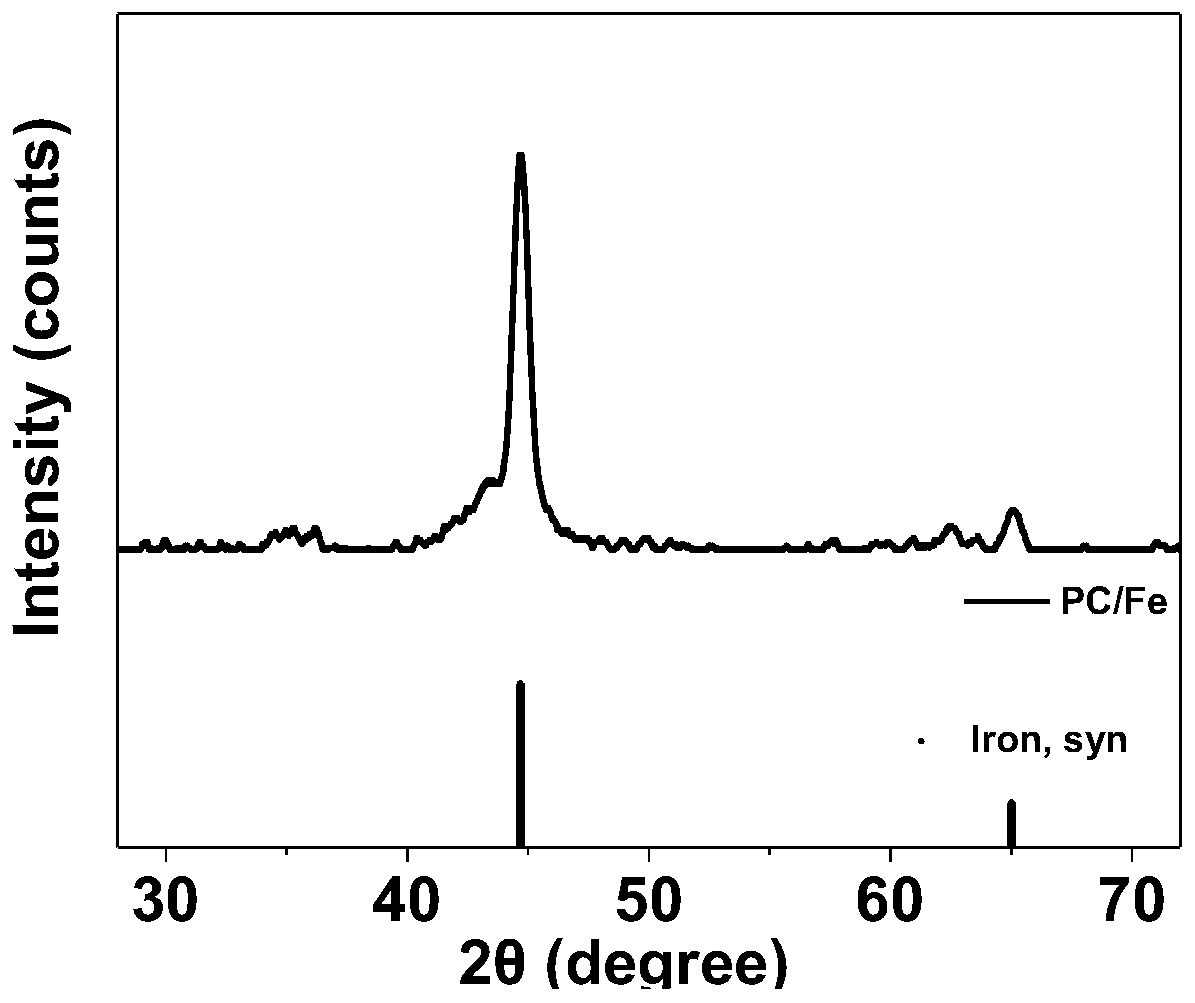
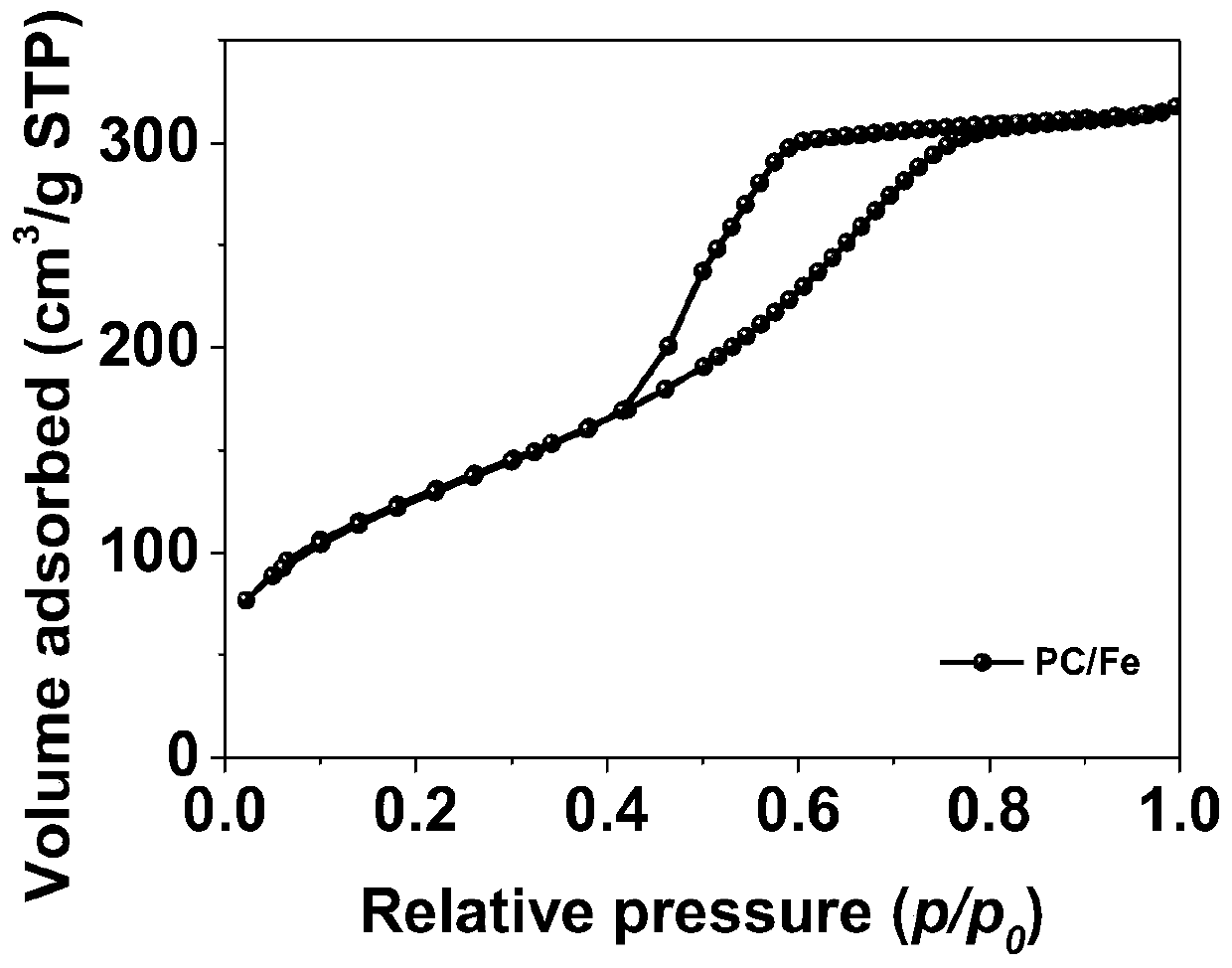
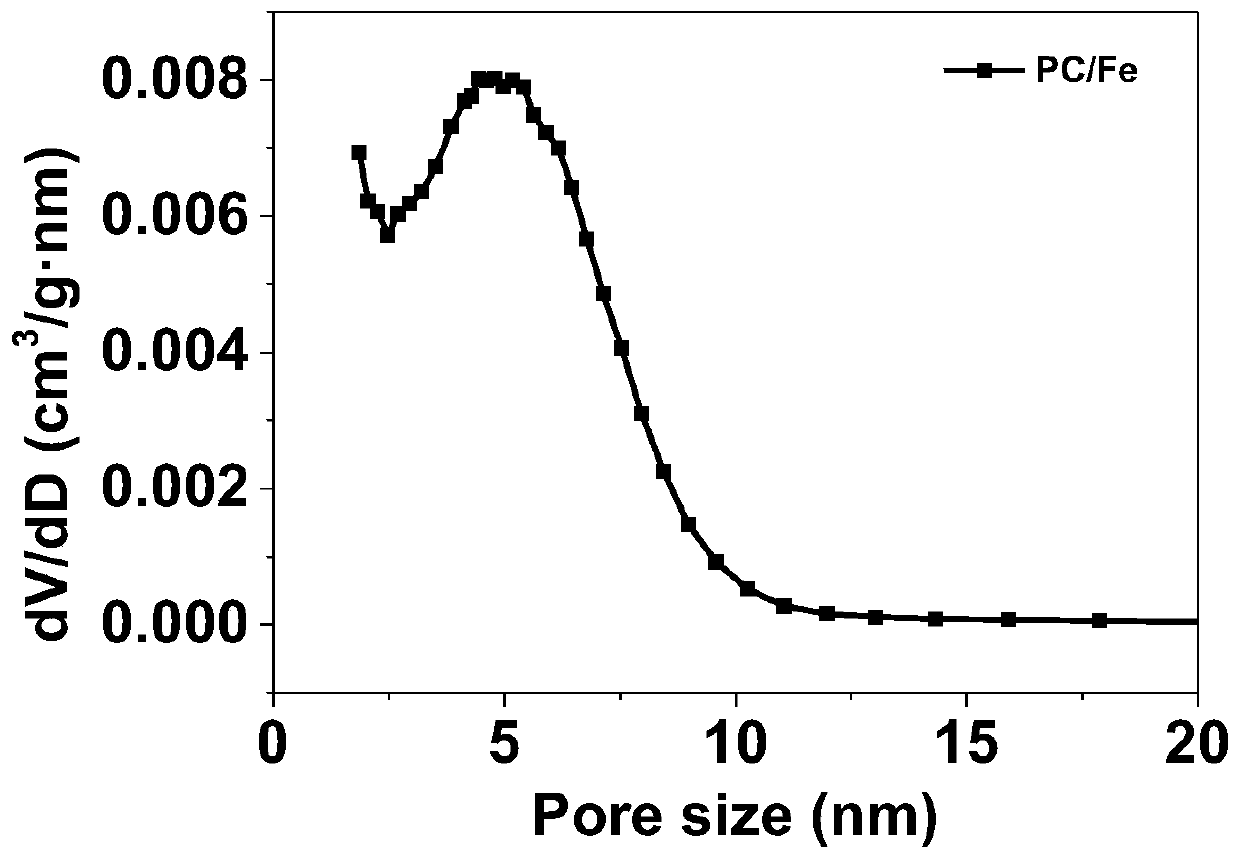
[0057] After the volatilization is complete, thermally polymerize at 100°C for 24h, and the obtained product is heated to 600°C under a nitrogen atmosphere and kept for 3h, then naturally cooled to room temperature; after grinding, a porous carbon-supported zero-valent iron catalyst PC / Fe( Figure 7 ).
[0058] figure 1 The XRD pattern of the porous carbon-supported zero-valent iron catalyst prepared for the present embodiment 1 is obtained by figure 1 It can be seen that the characteristic peaks of the prepared catalyst are consistent with the zero-valent iron, indi...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Add 1.0g of surfactant (polyoxyethylene / polyoxypropylene / polyoxyethylene amphiphilic block copolymer) into 11g of ether solution, then add 0.4g of chitosan, stir for 10min to make it evenly mixed;
[0063] 0.2g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O was dissolved in ether solution and added to the above mixed solution, then added 0.43g of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, stirred for 90min to volatilize the solvent in the mixed solution; then added 1g of peanut shells and stirred evenly;
[0064] After the volatilization is complete, thermally polymerize at 110°C for 24h, and the obtained product is heated to 800°C under an argon atmosphere for 2h, and then naturally cooled to room temperature; after grinding, the porous carbon-supported zero-valent iron catalyst PC / Fe can be obtained.
[0065] The obtained catalyst comprises a carbon-based carrier with a high specific surface area and a zero-valent iron catalyst loaded on the skeleton of the carbon-based carrier, the mass content of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com