Method for efficiently and directionally enriching and separating hydrogen producing bacteria
A directional enrichment and high-efficiency technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effects of low energy consumption, high substrate conversion efficiency, and simple synthesis method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Method for efficient directional enrichment and isolation of hydrogen-producing bacteria:
[0047] 1) Anaerobic sludge heat treatment and incubation under oligotrophic induction conditions:
[0048] Wastewater activated sludge was obtained from a full-scale upflow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) reactor for wastewater treatment in a brewery and stored in a 4 °C refrigerator until use. Among them, the pH of activated sludge: 5-7, solid concentration (MLSS) is 50-55mg / L, soluble total organic carbon (STOC) is 2000mg / L;
[0049] (1) Mix 50g of activated sludge with 500mL of inorganic salt basal medium evenly, and add 2g of straw powder as a substrate to obtain a slurry suspension;
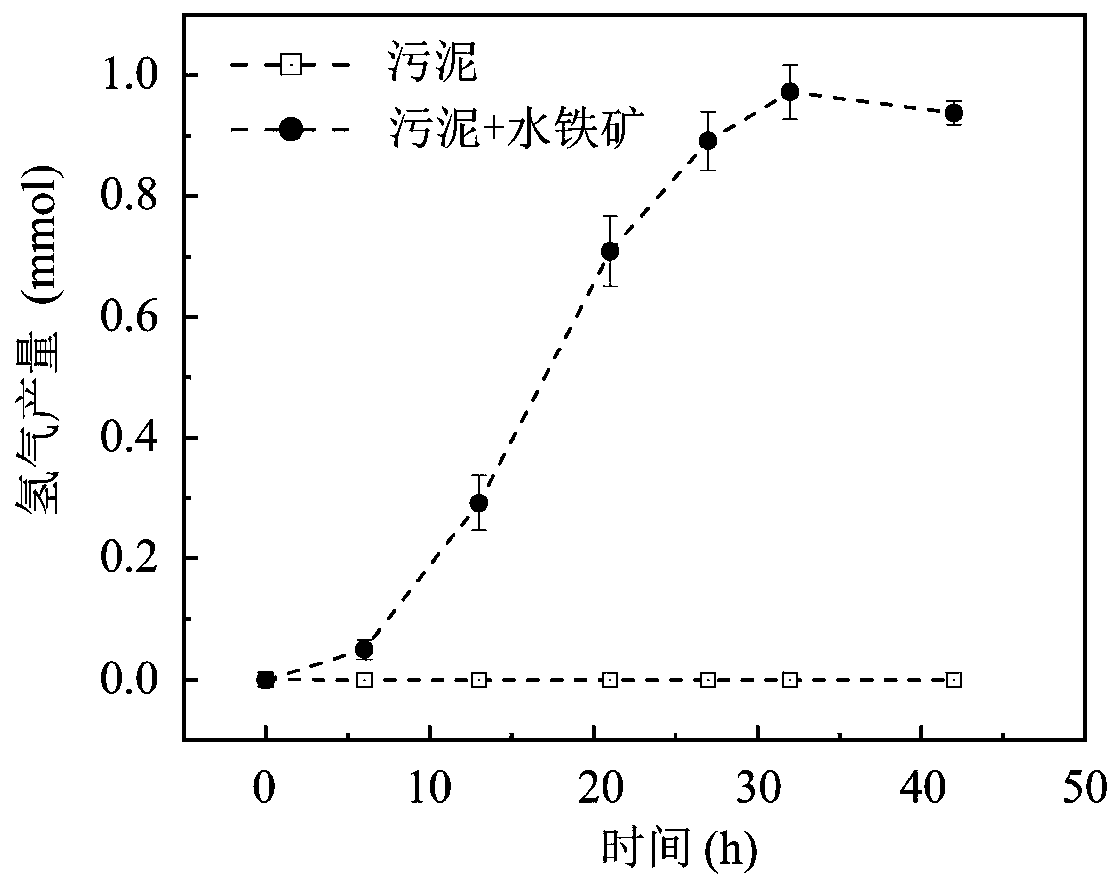
[0050] (2) Pack the mixed mud suspension and divide it into an experimental group and a control group. The experimental group adds amorphous ferrihydrite with a final concentration of 100mg / L, and the control group adds an equal volume of PBS solution without adding ferrihydrite. mine;
[0051] ...
Embodiment 2
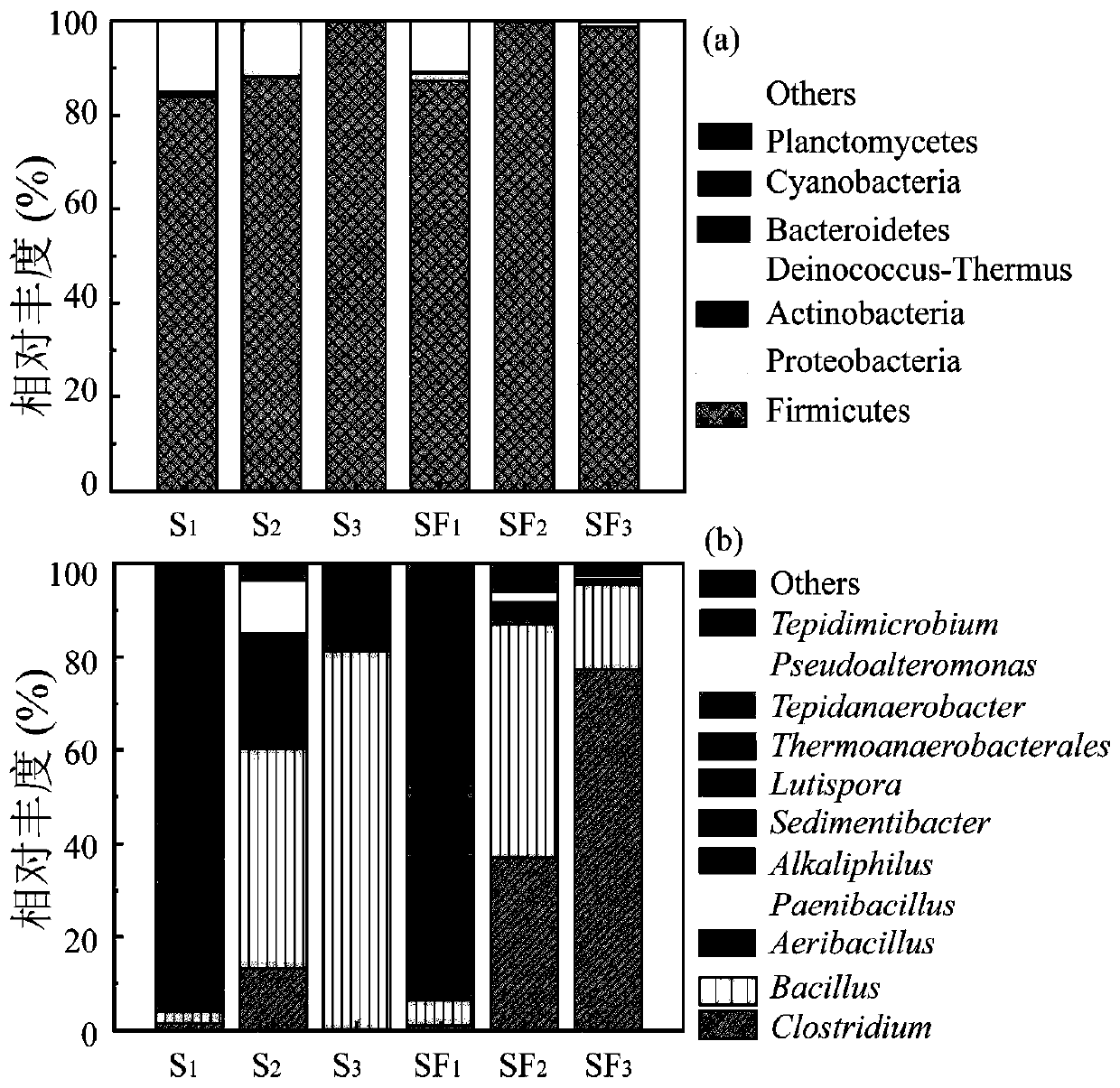
[0062] Based on the high-throughput sequencing analysis of the 16S rRNA gene, the community structure of the above-mentioned high-hydrogen-producing bacteria was obtained:
[0063] In the enrichment products SF1-SF3 of the experimental group and the enrichment products S1-S3 of the control group at the phylum level, Firmicutes are dominant phyla such as figure 2 (a), its abundance is as high as 85%, such as figure 2 (b) shows the results; while the dynamic analysis of the community structure at the genus level shows that the abundance of the main hydrogen-producing bacteria genus Clostridium in the experimental group SF1-SF3 increases from 1% to 27.69% with the enrichment and passage process gradually increased to 77.4%, that is to say, the hydrogen-producing Clostridium gradually changed from a rare species to an absolute dominant genus during the enrichment induction process, and the results were as follows: figure 2 as shown in b. Given that Clostridium is the main gen...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Further purification and separation of the above-mentioned hydrogen-producing colonies:
[0066] After the suspension of the hydrogen-producing enriched bacterial population is serially diluted (in order to obtain a single colony of the hydrogen-producing strain), it is evenly spread on the surface of the MSG solid medium supplemented with 2% agarose, and incubated in the dark at 30-37°C until Monoclonal colonies appear on the surface of the culture medium, which is the high-efficiency hydrogen-producing strain Clostridium pasteurianum YC-1.
[0067]The obtained strains were subjected to colony PCR, and a single colony was selected and inserted into 20 μL sterile water, and 2 μL was used for PCR. PCR reaction system: 2 μL buffer buffer; 2 μL dNTP (2.5mol / L); 0.5 μL Taq enzyme (5U / μL); 0.5 μL Ba907R (20 μmol / L, 5′-AGA GTTTGATCCTGG CTCAG-3′) reverse primer; 0.5 μL Ba27F (20 μmol / L, 5′-CCGTCAATTCCTTTRAGTTT-3′) forward primer; 2 μL single colony suspension template; 2.5 μL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com