Technology for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina
A technology of spirulina and chlorophyll, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problems of reducing yield and biological activity, large solvent consumption, chlorophyll decomposition, etc., to improve food safety, improve yield and purity, and promote the reaction. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
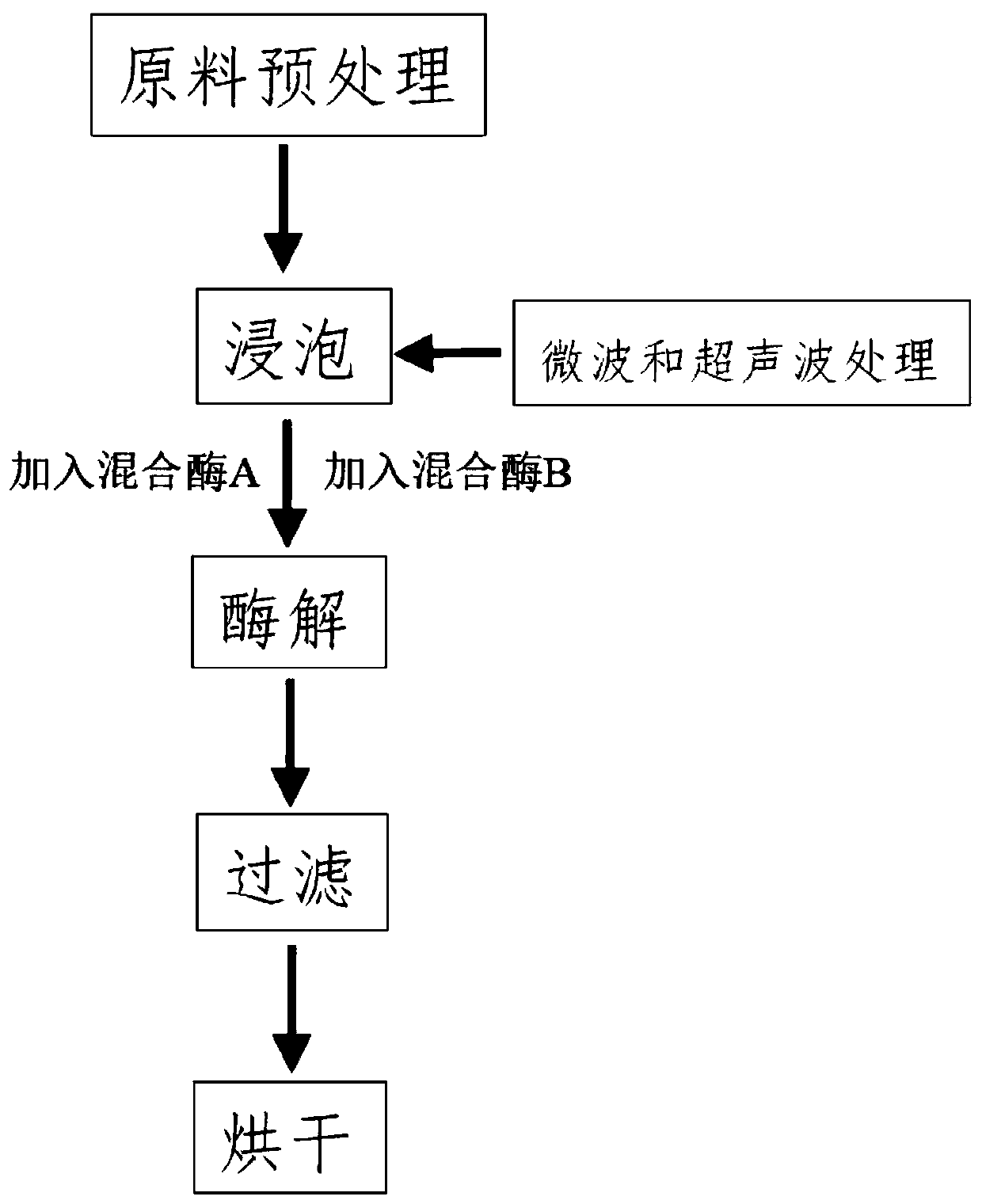
[0040] A process for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Raw material pretreatment: Wash the fresh spirulina, treat it in the dark at 1°C for 80 minutes, then crush it at 8°C until it passes through a 50-mesh sieve, put it into a centrifuge tube with steel balls, pour it into liquid nitrogen, When the liquid nitrogen has just evaporated, cover the centrifuge tube cover and place it on a vortex instrument to vortex until the spirulina powder passes through a 250 mesh sieve; during the vortex process, repeatedly invert the centrifuge tube 3 times;
[0042] (2) Soaking: under the conditions of darkness and argon or nitrogen protection, add deionized water to the above-mentioned spirulina powder for immersion treatment, and use microwave and ultrasonic treatment to assist immersion to obtain an aqueous solution of spirulina;
[0043] The method of microwave and ultrasonic treatment assisted soaking is as follows: firstly conduct micr...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A process for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina, comprising the following steps:
[0050] (1) Raw material pretreatment: Wash the fresh spirulina, treat it in the dark at 9°C for 90 minutes, then crush it at 1°C until it passes through a 100-mesh sieve, put it into a centrifuge tube with steel balls, pour it into liquid nitrogen, When the liquid nitrogen has just evaporated, cover the centrifuge tube cover and place it on a vortex instrument to vortex until the spirulina powder passes through a 350 mesh sieve; during the vortex process, repeatedly invert the centrifuge tube 5 times;
[0051] (2) Soaking: under the conditions of darkness and argon or nitrogen protection, add deionized water to the above-mentioned spirulina powder for immersion treatment, and use microwave and ultrasonic treatment to assist immersion to obtain an aqueous solution of spirulina;
[0052] The microwave and ultrasonic treatment assisted soaking method is as follows: firstly carry out micr...
Embodiment 3
[0058] A process for extracting chlorophyll from spirulina, comprising the following steps:
[0059] (1) Raw material pretreatment: Wash the fresh spirulina, treat it in the dark at 2°C for 82 minutes, then crush it at 7°C until it passes through a 60-mesh sieve, put it into a centrifuge tube with steel balls, pour it into liquid nitrogen, When the liquid nitrogen has just evaporated, cover the centrifuge tube cover and place it on a vortex instrument to vortex until the spirulina powder passes through a 270 mesh sieve; during the vortex process, repeatedly invert the centrifuge tube 5 times;
[0060] (2) Soaking: under the conditions of darkness and argon or nitrogen protection, add deionized water to the above-mentioned spirulina powder for immersion treatment, and use microwave and ultrasonic treatment to assist immersion to obtain an aqueous solution of spirulina;
[0061] The method of microwave and ultrasonic treatment assisted soaking is as follows: firstly carry out mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com