Preparation method of gelatin microspheres and application thereof
A technology of gelatin and microspheres, applied in the field of interventional medicine, can solve the problems of limiting biological applications, lack of cell adhesion sites, and reducing the biological activity of loaded cells, and achieve the effects of cell safety, good cell loading, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
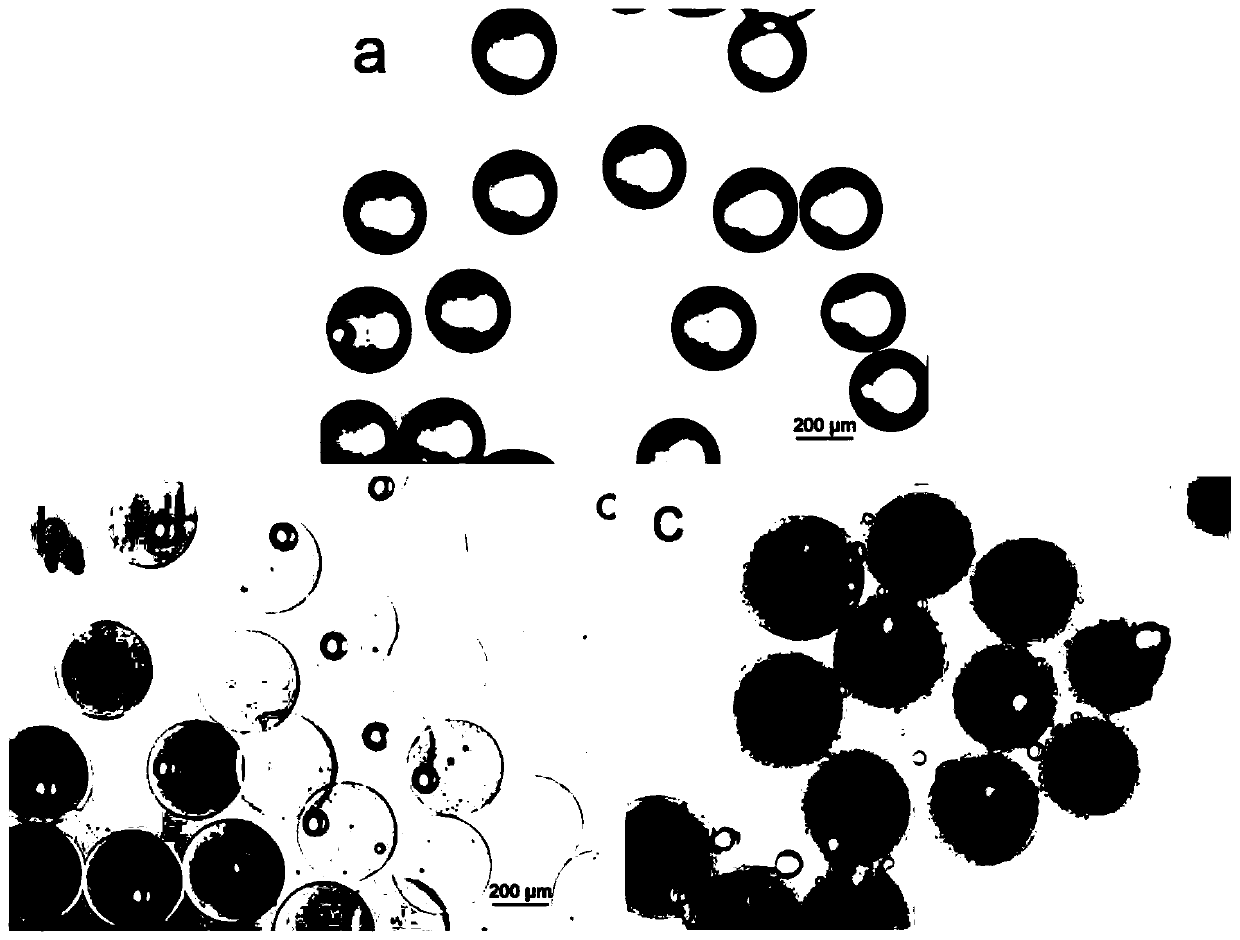
[0033] The preparation of embodiment 1 gelatin microsphere
[0034] 1. Fabrication of microfluidic devices
[0035] Prepare a PTFE tube with a length of about 35cm (inner diameter 0.3mm, outer diameter 0.6mm), insert a 26G needle into one end of the PTFE tube, insert a 31G needle into the PTFE tube in parallel at a distance of 20cm from the needle, and keep the needle tip in the middle of the tube; use AB Fix the needle and PTFE tube at the joint with rubber seal. After the device is completed, first check the connectivity and tightness of the device. Use a 5mL syringe to absorb deionized water, insert a 31G needle, and manually push the syringe. If liquid flows out of the PTFE tube, then Internal connectivity is good. Connect the syringes to the 20G needle at the same time, block the outlet of the PTFE tube, and squeeze the two syringes manually at the same time. If no liquid leaks out, the device is well sealed. Dry the prepared device for later use.
[0036] 2. Preparati...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 Fibroblast adhesion and proliferation characterization on the surface of gelatin microspheres
[0045] To test the adhesion and proliferation of fibroblasts on the surface of gelatin microspheres, the specific process is:
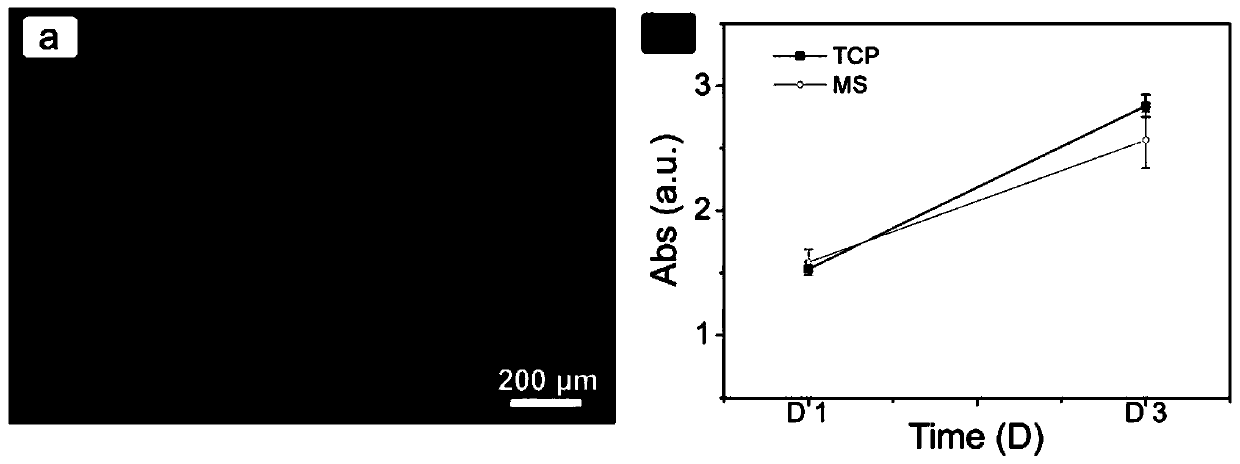
[0046] Spread gelatin microspheres on the bottom of a 48-well plate (non-adhesive plate), and NIH-3T3 cells (mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line) in a 5×10 4The cells / well density was inoculated, and each group had three parallel samples, and the control group was TCP (adhesive type). On days 1 and 3, use CCK-8 solution to detect cell viability;
[0047] The staining result is as figure 2 shown, where figure 2 a is the result of cell death and life staining on the surface of the microspheres 2 days after inoculation, the results show that the cells grow well on the surface of the microspheres, and there are no dead cells in the field of view. Within 3 days, the proliferation rate of the MS group was good, such as figure 2 b, sho...
Embodiment 3
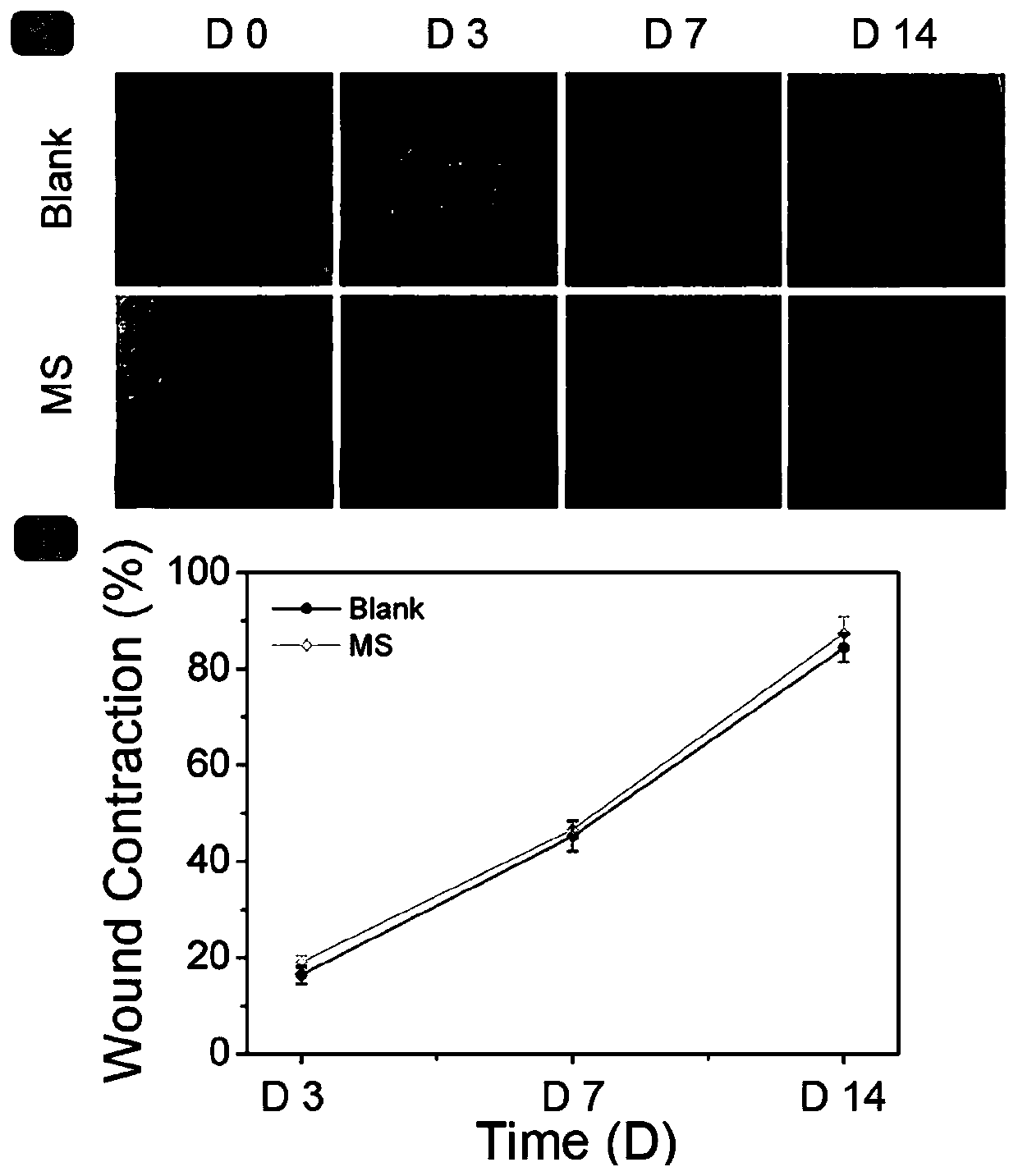
[0048] Example 3 Testing the effect of MS on full-thickness skin excision wounds
[0049] 1. Modeling of Type I Diabetic Rats (TIDM)
[0050] Fifteen SD rats (8 weeks old, weighing 200-250 g, male) were used to induce TIDM to model, and fasted for 24 hours before model making. Weigh each rat's body weight before modeling, and take tail vein blood to measure the fasting blood glucose value of each rat;
[0051] 1% STZ (streptozotocin) solution was injected intraperitoneally at a dose of 50 mg / kg. After the operation was completed, the rats were housed in separate cages. After modeling, blood was collected from the tail vein to measure the blood glucose of the rats. If the blood glucose value before induction was <8.9mmol / L, and the random blood glucose of rats was ≥16.7mmol / L for three consecutive days after induction, the model was considered successful. If the induced TIDM model fails, feed the rats with a normal diet and monitor the blood sugar level. After the blood sug...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com