3D printing composite bio-ink material and preparation method and application thereof
A bio-ink, 3D printing technology, applied in the field of 3D bioprinting, can solve the problems of poor interface bonding between matrix and filler, unfavorable polymer matrix coating, decreased mechanical properties of materials, etc., to improve interface bonding, good application prospects, improve The effect of interface combination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
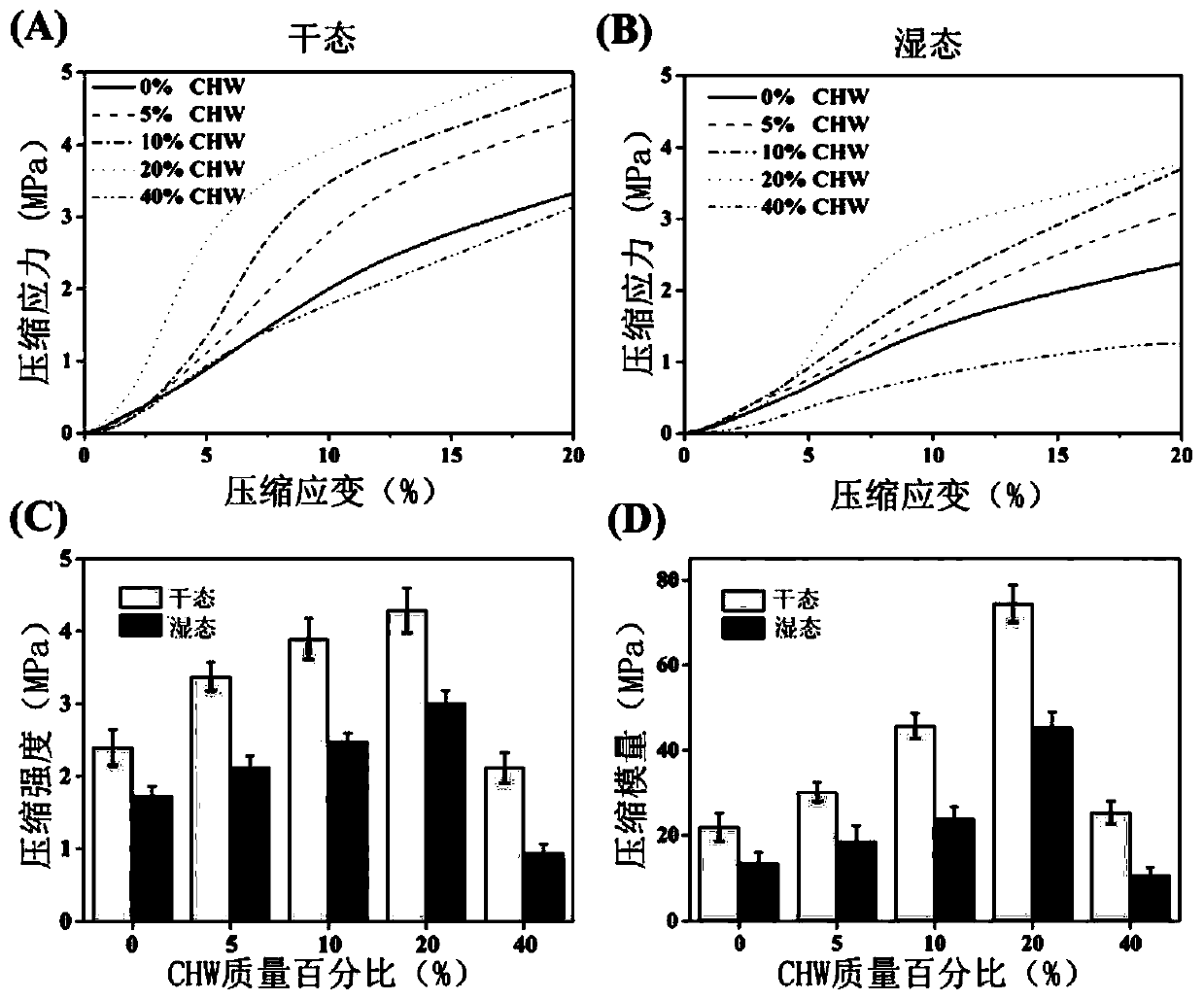
[0047] Example 1 Preparation and 3D printing of ternary solvent composite bio-ink material with added chitin whiskers
[0048] Mix different masses of chitin whiskers (CHW) with 4 mL of dichloromethane, and ultrasonicate for 60 min to form a homogeneous suspension. Add 1 g of poly(L-lactide) (PLLA, Mn=100000) to the above suspension, and magnetically After stirring for 6 hours, 1.3 mL of 2-butoxyethanol and 0.5 mL of dibutyl phthalate were added. After stirring for 4 hours, the air bubbles were removed by ultrasound, and a ternary solvent composite bio-ink material containing CHW was obtained. Then, move it into the syringe and discharge the air bubbles. According to the established digital model, that is, a cylindrical 3D model with a thickness of 10mm and a diameter of 5mm, set the printing speed to 10mm / s and the filling density to 90%, and print it to the receiving platform through the needle at 28°C. Finally, the composite porous scaffold was prepared by layer-by-layer st...
Embodiment 2
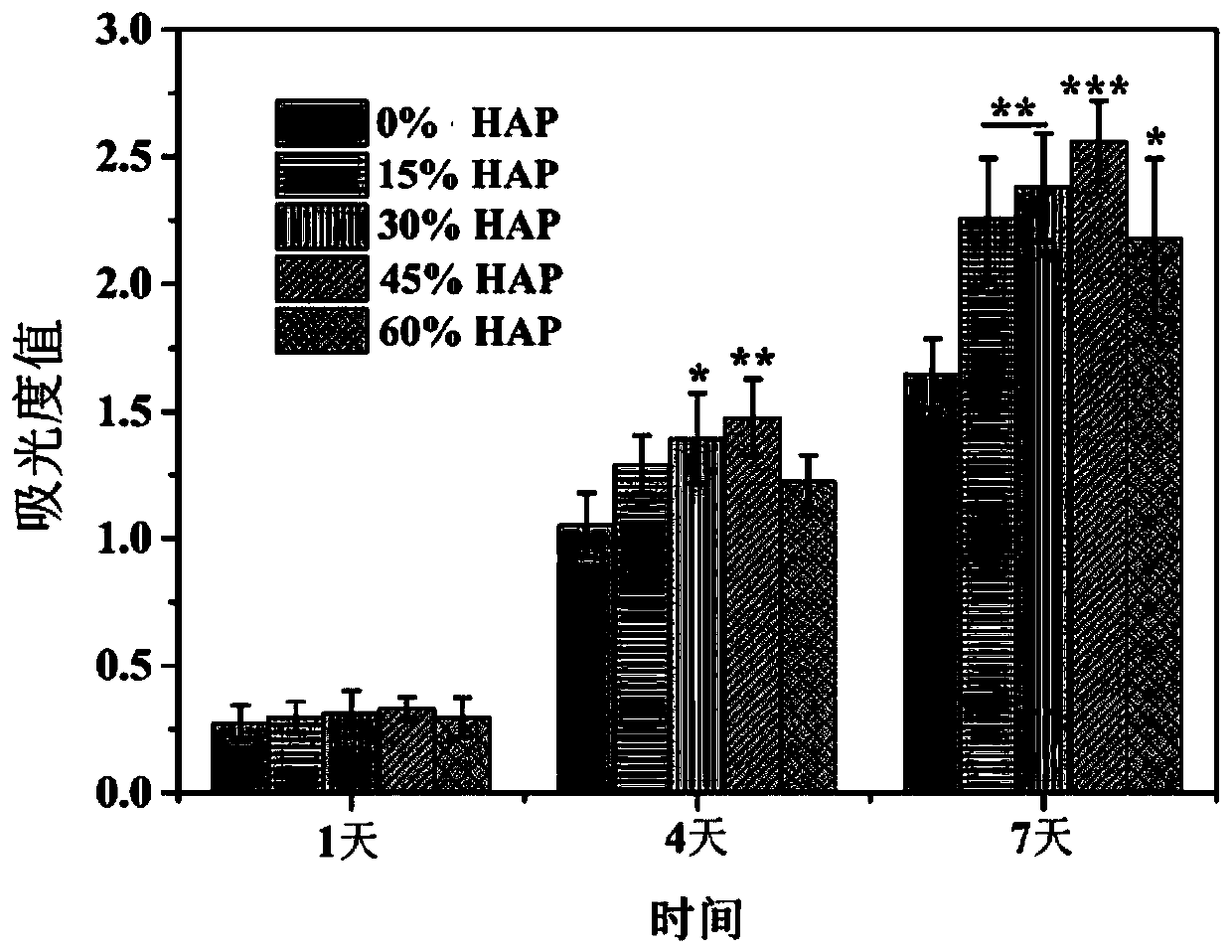
[0051] Example 2 Preparation and 3D printing of ternary solvent composite bio-ink material with added hydroxyapatite whiskers
[0052] Different masses of hydroxyapatite whiskers (HAP) were mixed with 3 mL of chloroform, and ultrasonicated for 35 min to form a homogeneous suspension, and 1.2 g of poly(D,L-lactide) (PDLLA, Mn=200000) was added to The above suspension was magnetically stirred for 5 hours, then 1.5 mL of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 0.5 mL of citrate were added, and after stirring for 10 hours, the air bubbles were removed by ultrasonication at room temperature to obtain a ternary solvent composite bio-ink material with HAP added. Then, move it into the syringe and remove the air bubbles. According to the established digital model, that is, a cylindrical 3D model with a thickness of 5mm and a diameter of 5mm, set the printing speed to 5mm / s and the filling density to 70%, and print it to the receiving platform through the needle at 20°C. Finally, the three-...
Embodiment 3
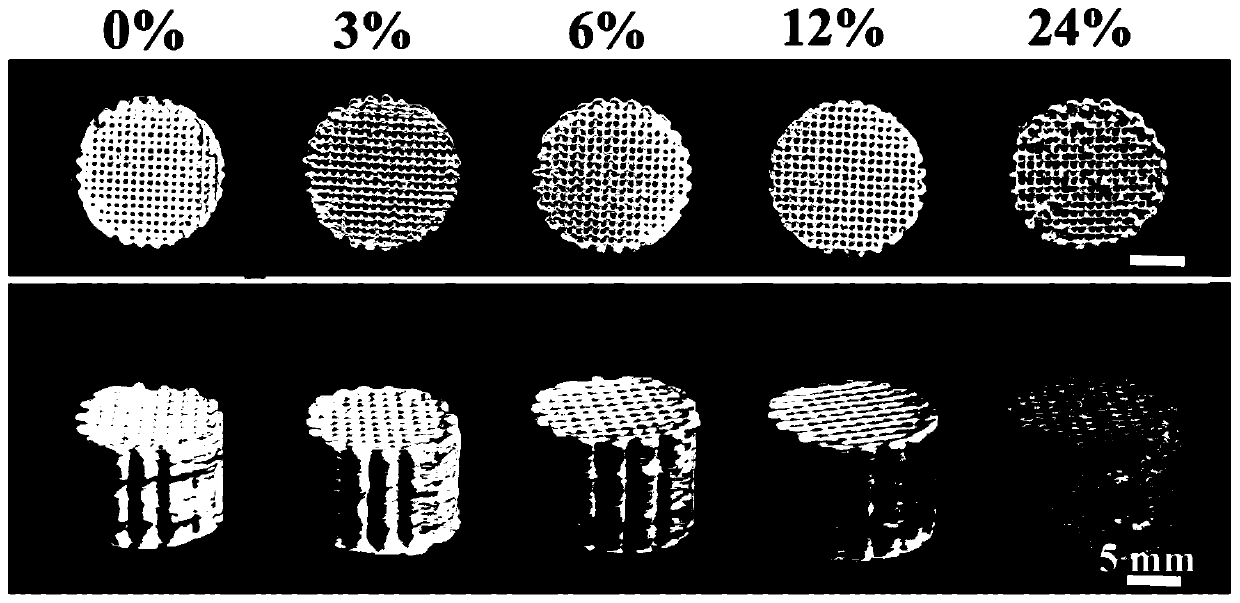
[0061] Example 3 Preparation and 3D printing of ternary solvent composite bio-ink material with added hydroxyapatite whiskers
[0062] Different masses of hydroxyapatite whiskers (HAP) were mixed with 10 mL of hexafluoroisopropanol, and ultrasonicated for 45 min to form a homogeneous suspension, and 1.0 g of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA, Mn =300000) was added to the above suspension, stirred magnetically for 10 hours, then added 1.2mL sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and 0.4mL dibutyl phthalate, stirred for 6 hours, and then ultrasonically discharged the air bubbles at room temperature to obtain the HAP-added three Meta-solvent composite bioink materials. Then, move it into the syringe and remove the air bubbles. According to the established digital model, that is, a long 3D model with a length of 5cm, a width of 1cm, and a thickness of 1.5mm, set the printing speed to 25mm / s and the filling density to 45%. The needles were printed on the receiving platform, and finally the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com