Method for preparing cell-free medical implant material
An implant material and cell-free technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of medical implant materials, can solve the problems of ECM three-dimensional structure damage, harsh and excessive decellularization process, and achieve mild and targeted action mode and good tissue repair function Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
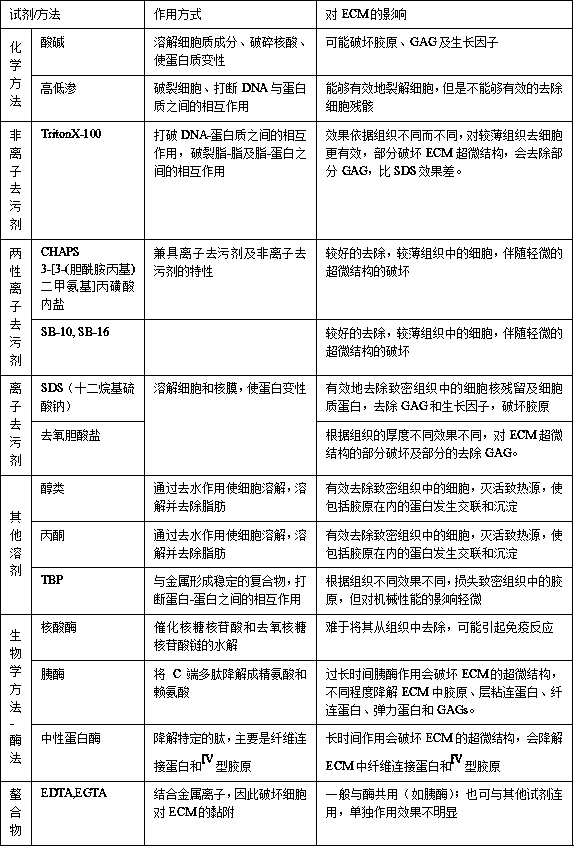
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Example 1 (Commercial pork SIS+0.25%Saponin)
[0097] The preparation of the acellular medical material of porcine small intestine submucosa, the specific steps are as follows:
[0098] 1) Material selection: Fresh small intestines of commercial pork pigs are selected in slaughterhouses as raw materials for decellularization
[0099] 2) Pretreatment: use physical scraping method to remove the mucous membrane layer, muscular layer, serosa layer and lymph nodes of the pig small intestine, separate the submucosa, soak in 0.5% acetic acid solution for 30 minutes, the ratio of pig small intestine to acetic acid solution is 1 :5, then soaked in water to obtain the decellularized raw material, i.e. small intestinal submucosa, hereinafter referred to as SIS material
[0100] 3) Disinfection: use a mixed solution containing 1.0% peracetic acid and 15% ethanol, the ratio of the SIS material to the mixed aqueous solution is 1:10, and immerse at room temperature for 100 minutes un...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2 (commodity pig SIS+0.25%SDS)
[0106] In this example, the decellularized raw material is the small intestine tissue of commercial pork pigs. In the preparation method, the steps of pretreatment of the pig small intestine tissue, disinfection, degreasing, decellularization, DNA and α-Gal antigen removal, freeze-drying, and sterilization are completely complete. Same as Example 1; the difference is only in the choice of decellularization reagent, in this example, 0.25% SDS was used to replace the 0.25% saponin solution in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3: Optical observation and active ingredient detection of acellular medical materials.
[0108] Method: fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, cut the decellularized material in the example into thin slices, dewaxed with xylene, dehydrated with alcohol, stained with hematoxylin-eosin, observed the residual cells and Matrix fiber structure.
[0109] Results: In all the decellularized medical materials obtained in the two examples, no cells and their fragments were observed; the collagen fibers were continuous and varied in thickness, but there was no obvious fracture.
[0110] For the cell-free medical implant materials prepared in 1-2 examples, the content of the important active ingredient hyaluronic acid (HA) was detected using a commercial ELISA kit; Various decellularized materials were processed, and the test results are as follows:
[0111] group Sources and processing methods of decellularized materials Hyaluronic acid HA (ug / mg) Exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com