A method and additive for reducing oxygen content of sintered NdFeB material
An additive, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inductor/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic objects, etc., can solve problems such as cracking, magnet performance degradation, and easy agglomeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
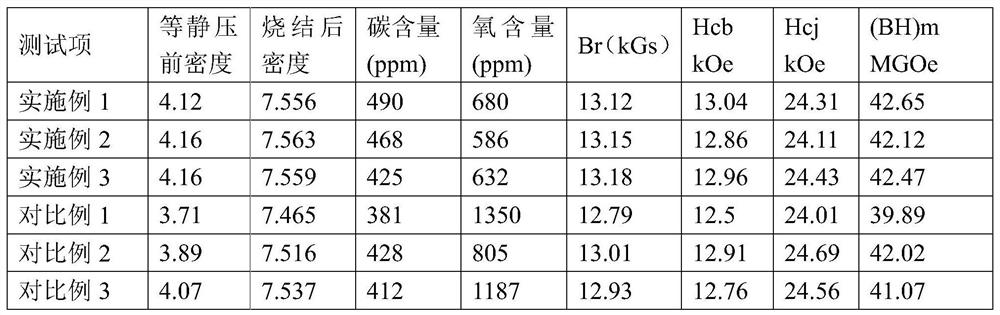
Embodiment 1
[0033] Sintering NdFeB method of this embodiment comprises the following process steps:
[0034] (1) weight ratio Ⅰ and Ⅱ formulation additives:
[0035] Ⅰ type additive formulation: BTA (1%), 200 # solvent oil (60%), isopropanol (25%), cyclohexanone (14%);
[0036] Ⅱ type formulation additives: zinc stearate (5%), 120 # solvent oil (60%), oleic acid amide (10%), terpineol (10%), petroleum ether (10%), stadis (R) 450 (5%);
[0037] (2) the additives Ⅰ, automatic pulse added atomizer feeder hydrogen pulverization furnace at the outlet of the control additive amount of the powder of NdFeB weight of 1.0 ‰, at room temperature, was added a spray manner neodymium iron boron powder, can be mixed in the pipeline, without additional mixing tank for mixing process;
[0038] (3) The mixed powder fed to the jet mill feed tank, a jet mill to adjust the particle size to control the speed of 2.8 ~ 3.0μm, adding automatic pulse feeder atomizer discharge opening at the lower jet mill apparatus ⅱ ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Sintering NdFeB method of this embodiment comprises the following process steps:
[0044] (1) weight ratio Ⅰ and Ⅱ formulation additives:
[0045] Ⅰ type additive formulation: BTA (3%), 200 # solvent oil (40%), isopropanol (35%), cyclohexanone, (22%);
[0046] Ⅱ type formulation additives: zinc stearate (8%), 120 # solvent oil (40%), oleic acid amide (8%), terpineol (20%), petroleum ether (21%), stadis (R) 450 (3%);
[0047] (2) the additives Ⅰ, automatic pulse added atomizer feeder hydrogen pulverization furnace at the outlet of the control additive amount of the powder of NdFeB weight 1.5 ‰; at room temperature, was added a spray manner neodymium iron boron powder, can be mixed in the pipeline, without additional mixing tank for mixing process;
[0048] (3) The mixed powder delivered to the jet mill feed tank, a jet mill to adjust the particle size to control the speed of 2.8 ~ 3.0μm; add automatic pulse feeder atomizer discharge opening at the lower jet mill apparatus ⅱ ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Sintering NdFeB method of this embodiment comprises the following process steps:
[0054] (1) weight ratio Ⅰ and Ⅱ formulation additives:
[0055] Ⅰ type additive formulation: BTA (5%), 200 # solvent oil (20%), isopropanol (45%), cyclohexanone (20%);
[0056] Ⅱ type formulation additives: aluminum stearate (10%), 120 # solvent oil (20%), oleic acid amide (30%), terpineol (30%), petroleum ether (32%), stadis (R) 450 (2%);
[0057] (2) the additives Ⅰ, automatic pulse added atomizer feeder hydrogen pulverization furnace at the outlet of the control additive amount of the powder of NdFeB weight 1.0 ‰; at room temperature, was added a spray manner neodymium iron boron powder, can be mixed in the pipeline, without additional mixing tank for mixing process;
[0058] (3) The mixed powder delivered to the jet mill feed tank, a jet mill to adjust the particle size to control the speed of 2.8 ~ 3.0μm; add automatic pulse feeder atomizer discharge opening at the lower jet mill apparat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com