Magnetic super-hydrophobic polystyrene-based porous material and preparation method thereof
A polystyrene, super-hydrophobic technology, applied in the field of composite materials, to achieve the effect of high contact angle, easy batch preparation, and long-lasting oil-water separation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
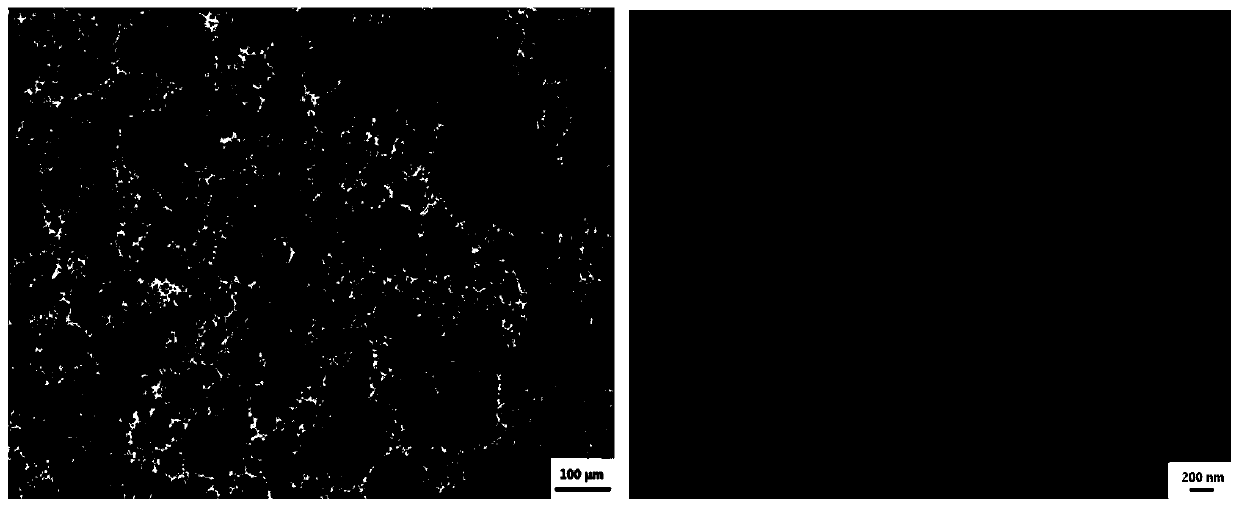
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A method for preparing a magnetic superhydrophobic polystyrene-based porous material, the steps are as follows:
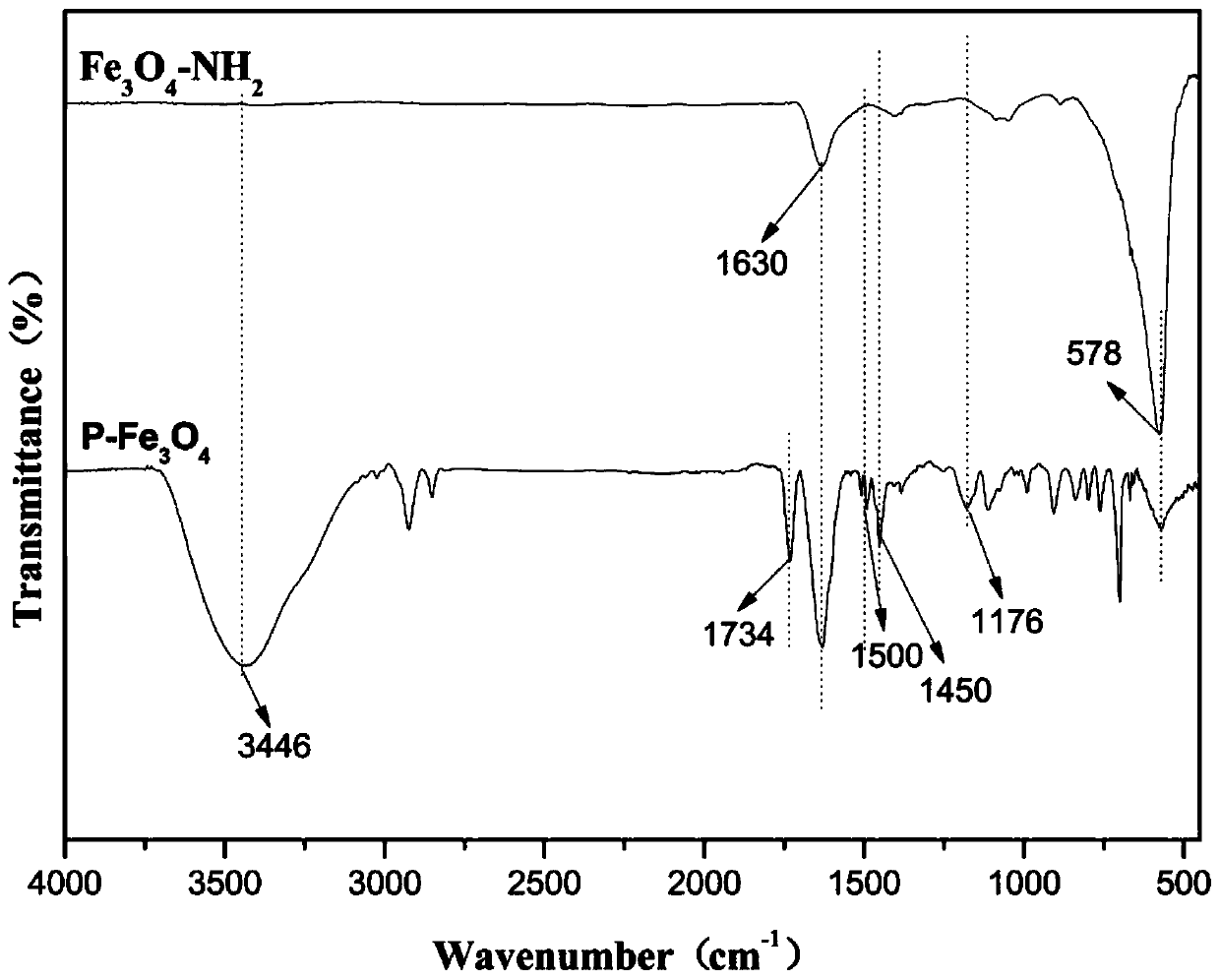
[0037] S1. Disperse 8 parts by weight of ferric chloride hexahydrate in 82 parts by weight of ethylene glycol to form a transparent solution A; then disperse 7 parts by weight of anhydrous sodium acetate and 3 parts by weight of polyethyleneimine in solution A. 400rpm mechanical stirring for 30min to form a uniform mixed solution B. Add the mixed solution B into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, react at 200°C for 8 hours to form a black product, and then wash it several times with absolute ethanol and deionized water under the action of a magnetic field to prepare amino-modified ferric oxide.
[0038] S2, adding 2000 parts by weight of deionized water to 15 parts by weight of styrene, 10 parts by weight of glycidyl methacrylate, 25 parts by weight of divinylbenzene, 5 parts by weight of amino-modified ferric oxide, 15 parts by weight of Span80 , 5 parts b...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for preparing a magnetic superhydrophobic polystyrene-based porous material, the steps are as follows:
[0042] S1. Disperse 5 parts by weight of ferric chloride hexahydrate in 50 parts by weight of glycerol to form a transparent solution A; then disperse 4 parts by weight of anhydrous sodium acetate and 10 parts by weight of polyether amine in solution A, at 200rpm Stir mechanically for 60 min to form a homogeneously mixed solution B. Add the mixed solution B into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, react at 100°C for 24 hours to form a black product, and then wash it several times with absolute ethanol and deionized water under the action of a magnetic field to prepare amino-modified ferric oxide.
[0043] S2, adding 100 parts by weight of deionized water to 10 parts by weight of styrene, 50 parts by weight of glycidyl methacrylate, 10 parts by weight of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, 20 parts by weight of amino-modified ferric oxide, In a mixed system of 50...
Embodiment 3
[0046] S1. Disperse 20 parts by weight of ferric chloride hexahydrate in 90 parts by weight of ethanol to form a transparent solution A; then disperse 20 parts by weight of anhydrous sodium acetate and 1 part by weight of polyacrylamide in solution A, and mechanically stir at 200rpm 5min to form a homogeneous mixed solution B. Add the mixed solution B into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, react at 300°C for 4 hours to form a black product, and then wash it several times with absolute ethanol and deionized water under the action of a magnetic field to prepare amino-modified ferric oxide.
[0047]S2, adding 3000 parts by weight of deionized water to 50 parts by weight of styrene, 50 parts by weight of glycidyl stearate, 50 parts by weight of pentaerythritol triacrylate, 50 parts by weight of amino-modified ferric oxide, 50 parts by weight of Tween80 and 10 parts by weight of benzoyl peroxide in a mixed system, and mechanically emulsified for 60 minutes under the action of an e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com