Bacterial strain for producing D-arabitol and application thereof
A technology of arabitol and seeds, applied in fungi, methods based on microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as pollution, increased extraction cost, and increased extraction difficulty, and achieve the effect of wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: ARTP mutagenesis treatment of starting strains and screening of high-yield D-arabitol strains
[0031] The starting strain Candida parapsilosis (Candida parapsilosis) SK26.002 was inoculated into the seed medium, and cultured at 200 rpm at 30° C. for 21 h. Take 1 mL of the bacterial solution in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the bacterial cells with 1 mL of 0.9% sterile saline, centrifuge and wash the bacterial cells again to make a bacterial suspension. Then take 10 μL of the bacterial suspension and spread it evenly on the surface of the metal slide, place the slide in the ARTP mutagenesis system, place the slide in the corresponding grooves with sterile tweezers, and set the plasma mutagenesis time as 140s, after the sample processing is completed, use sterile tweezers to move the slide to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube filled with 1mL sterile saline, and shake evenly on the shaker. The new ba...
Embodiment 2
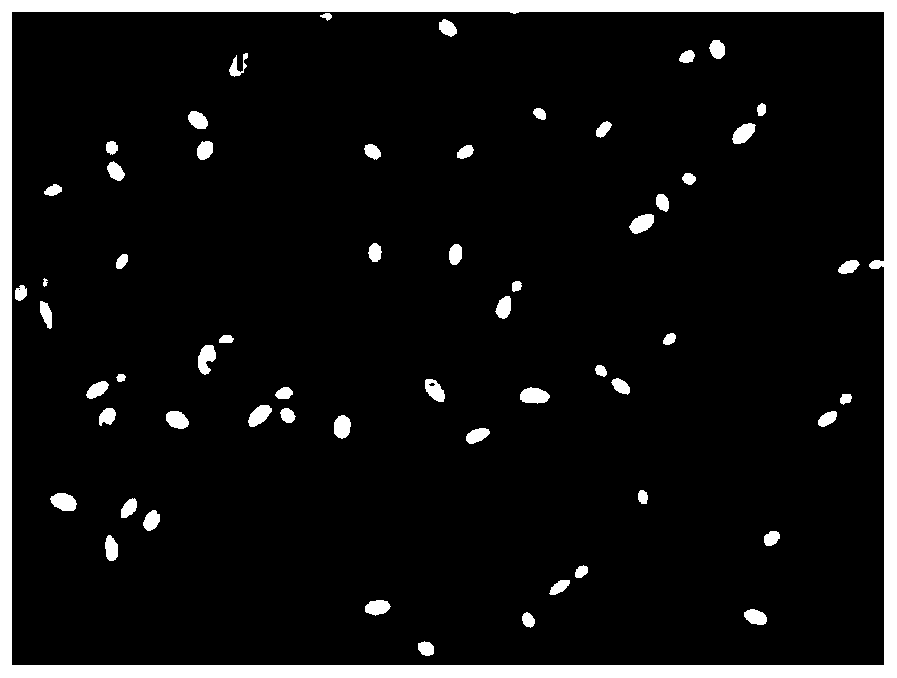
[0033] Example 2: Comparison of strain D-arabitol production before and after mutagenesis
[0034]Use an inoculation loop to dip a ring of bacteria solution of the starting strain SK26.002 and the mutant strain SK26.002A6 from the preserved bacteria solution in the glycerol tube, respectively, streak on the plate medium, and incubate them upside down in a 30°C incubator for 24 hours. Pick a single colony of the starting strain SK26.002 and a single colony of the mutant strain SK26.002 A6 that have grown well, and inoculate them in the seed medium, cultivate them at 30°C and 200rpm for 21 hours, and then inoculate the seed solution with 4% inoculum in the In a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of fermentation medium, culture at 30°C and 200rpm for 72h. After the fermentation, the bacterial liquid was collected and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 min to obtain a supernatant liquid containing D-arabitol. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane, an...
Embodiment 3
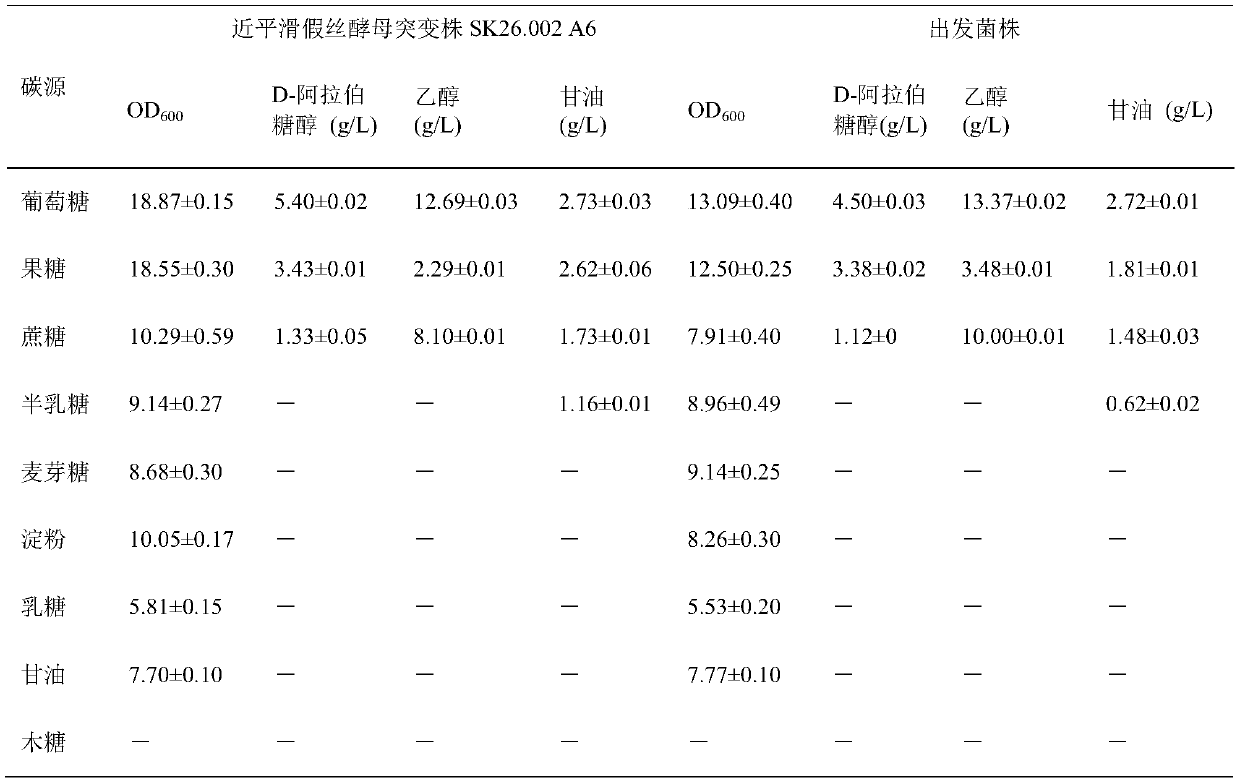
[0036] Example 3: Comparison of carbon source utilization patterns of strains before and after mutagenesis
[0037] Using glucose, fructose, sucrose, galactose, maltose, starch, lactose, glycerol and xylose as carbon sources, the carbon source utilization patterns of the starting strain and the Candida parapsilosis mutant strain SK26.002 A6 were compared.
[0038] Prepare medium containing 100 g / L of the above-mentioned carbon source and 20 g / L of yeast extract respectively, and distribute them in 20×200 mm test tubes with 10 mL aliquots, inoculate the respective seed cultures, and incubate at 30 Cultivate for 48 hours at 200 rpm. The carbon source utilization pattern of the strains before and after mutagenesis was analyzed by measuring cell growth and product formation.
[0039] The results showed that both the mutant strain and the starting strain had the ability to utilize glucose, fructose, sucrose, galactose, maltose, starch, lactose or glycerol for growth, and neither h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com