Pyrolytic carbon loaded zero-valent iron composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and pyrolytic carbon technology, which is applied in the field of pyrolytic carbon-loaded zero-valent iron composite materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of lack of composite material characterization data, inaccurate judgment, and long time required to improve the removal of heavy metals Ability, electrochemical performance advantage, time-consuming effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The preparation method of the pyrolytic carbon loaded zero-valent iron composite material prepared by the one-step method in this embodiment, the steps are:
[0052] Step 1: Mix pine wood biomass and natural hematite powder according to the mass ratio of 1:5 (1:6—1:4), add an appropriate volume of water to immerse the mixed raw materials, and perform ultrasonic treatment for 30 minutes. The material is put into the drying box, 60 o Dry under C conditions;
[0053] The second step: the dried material obtained in the first step is placed in a tube furnace, and pyrolyzed with limited oxygen under a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere, with 5 o C / min heating rate at target temperature 1000 o Pyrolysis at C for 1 h;
[0054] The third step: collect the solid material obtained in the second step, wash it alternately with ethanol and deionized water for three to five times, and place it in a vacuum drying oven for 60 o C collected after drying for 24 h, marked as composite...
example 1
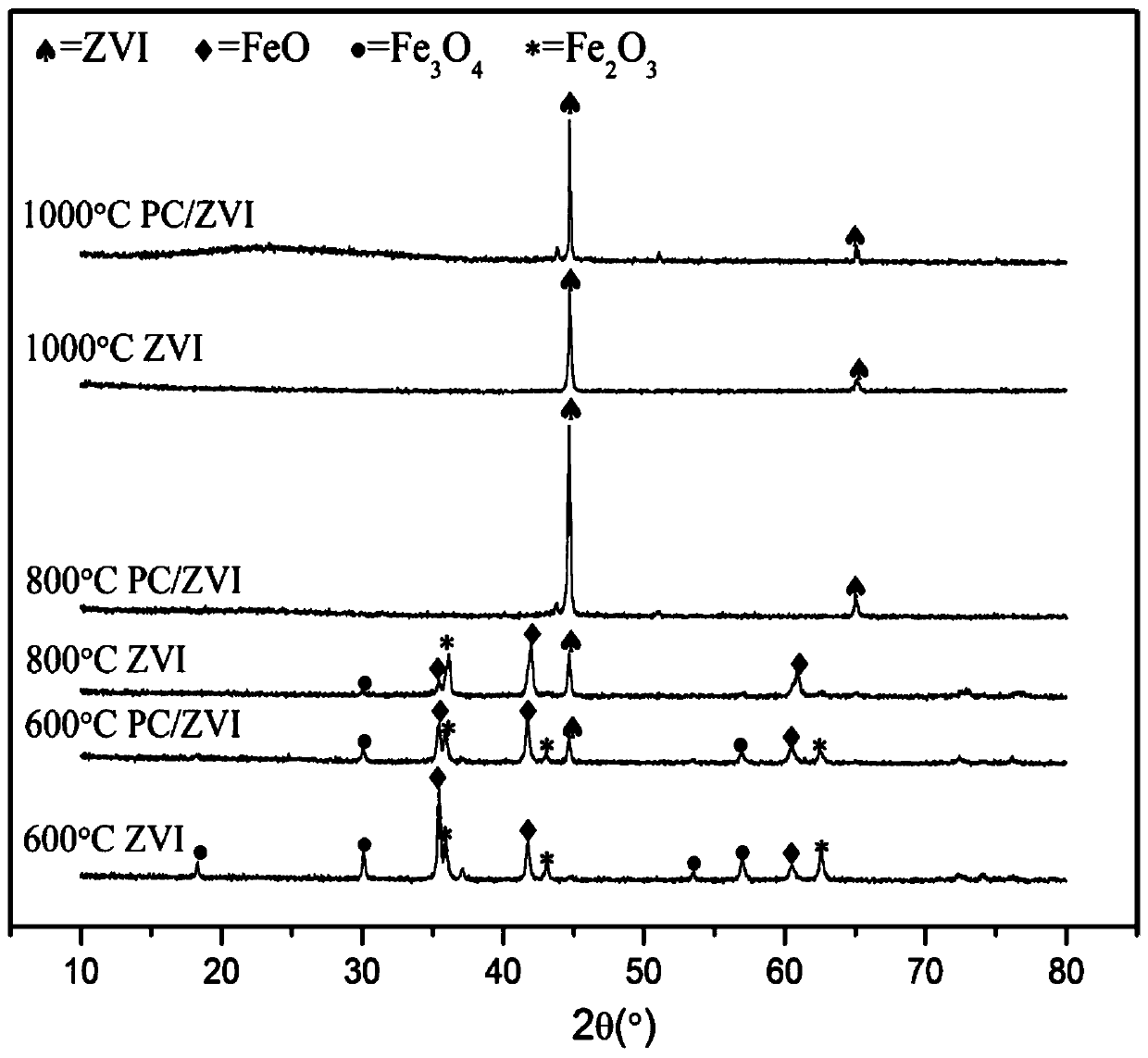
[0067] The natural hematite powder and the crushed pine biomass are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:5, and an appropriate volume of water is added to ultrasonically mix evenly, and then put into an oven for drying. Then the dried material was placed in a tube furnace, under a hydrogen-argon gas mixture atmosphere, at 600 o Pyrolyze at 0°C, collect the resulting solid material, wash, dry, grind, and collect. Pure hematite powder was also prepared under the same pyrolysis conditions. X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) such as figure 1 Shown, 600 o The C composite material has a weaker zero-valent iron characteristic peak, while the 600 o C hematite still exists in the form of iron oxide after pyrolysis, and no zero-valent iron is generated.
example 2
[0069] The natural hematite powder and the crushed pine biomass are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:5, and an appropriate volume of water is added to ultrasonically mix evenly, and then put into an oven for drying. Then the dried material was placed in a tube furnace, under a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere, at 800 o Pyrolyze at 0°C, collect the resulting solid material, wash, dry, grind, and collect. Pure hematite powder was also prepared under the same conditions. X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) such as figure 1 Shown, 800 o The characteristic peak of zero-valent iron in C composite material is obvious (2θ=44.8 o ) and high purity, while 800 o Although C hematite produces a small amount of zero-valent iron, other iron oxides still exist.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com