Method and kit for separating extracellular vesicles of tissue specific origin
A technology of cells and vesicles, applied in the field of separating tissue-specific extracellular vesicles, which can solve the problems of low recovery, low purity, and poor dispersion, and achieve stable recovery, simple operation, and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
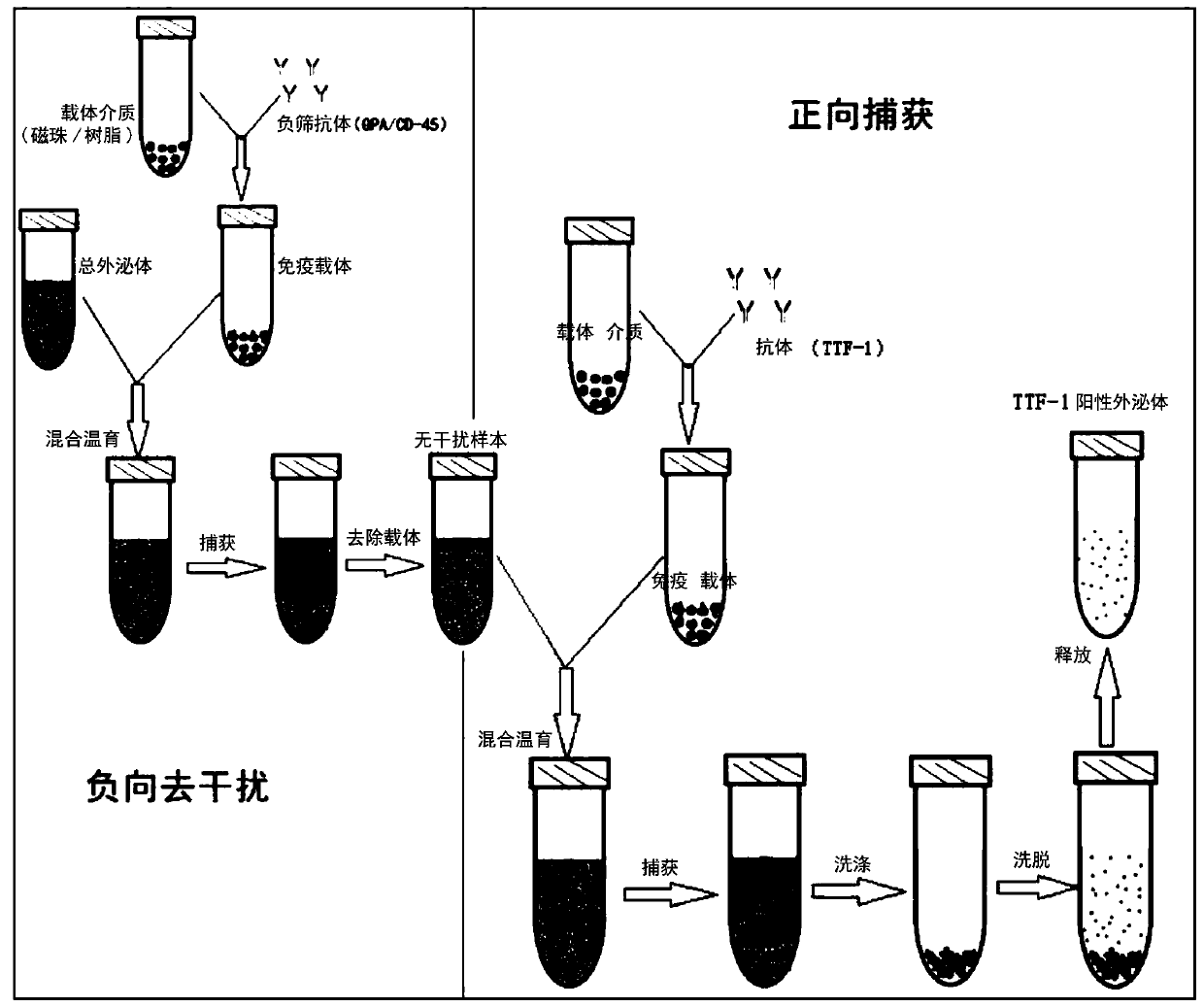
[0103] Example 1 Specific extracellular vesicle / exosome capture and isolation method
[0104] 1.1 Sample pretreatment and obtain total extracellular vesicles or total exosomes without background interference
[0105] 1.1.1 Enrichment of total extracellular vesicles or total exosomes
[0106] Total extracellular vesicles or total exosomes were extracted and purified from samples (blood, urine, pleural effusion, cell supernatant, pleural effusion, alveolar lavage fluid) by PEG precipitation or molecular chromatography exclusion (SEC). Specific steps are as follows:
[0107] 1) Enrichment of total extracellular vesicles by PEG precipitation
[0108] Add 120 μL PEG8000 precipitant to 500 μL serum / plasma, add 60 μL PEG8000 precipitant to 250 μL pleural and peritoneal fluid; mix upside down 5 times, and let stand at 4-8°C for 30 minutes; then centrifuge at 13000 rpm for 2 minutes, discard the supernatant to retain the precipitate, Add 100 μL PBS to resuspend and mix well to obtai...
Embodiment 2
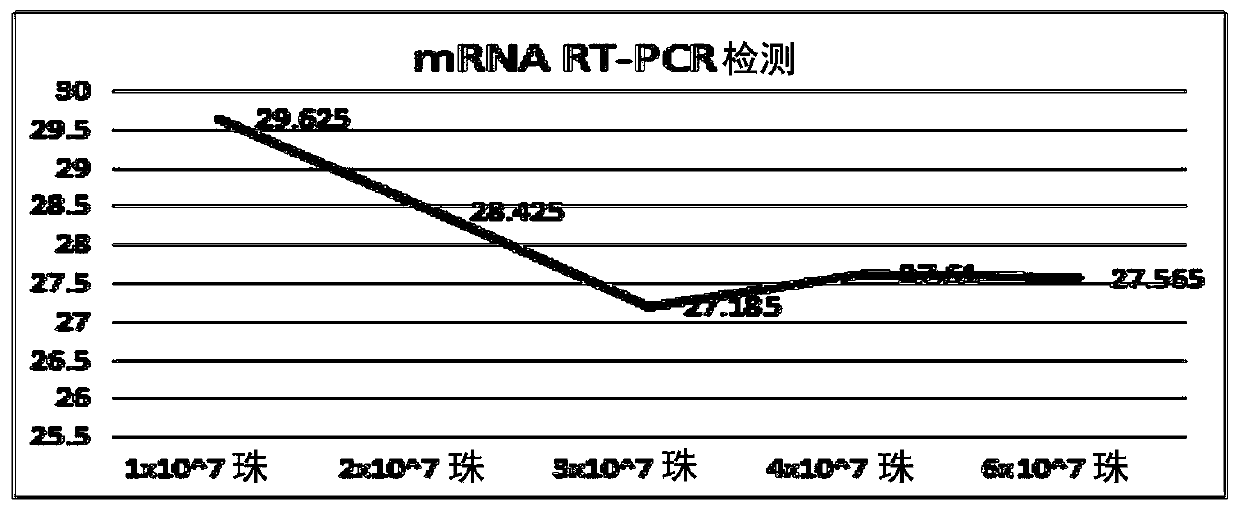
[0143]Example 2 Comparison of Specific Exosome Capture and Separation Method System Optimization
[0144] 2.1 Capture carrier optimization
[0145] 2.1.1 Capture carrier magnetic bead screening
[0146] Considering the principles of magnetic bead dispersion, sedimentation, non-specific adsorption, etc., and considering that the larger the particle size of the magnetic bead (the larger the specific surface area, the more sites that bind to the target), the capture efficiency will be higher. Therefore, two magnetic beads with a particle size of more than 1 μm and mature commercialization were selected for comparison and verification.
[0147] The verification method and steps are as follows:
[0148] 1) Take 10 μL of each of the two types of magnetic beads and incubate with 30 μg of exosomes at room temperature (10 rpm) for 15 minutes, then dilute to 1 mL with PBS and rotate at room temperature for 30 minutes
[0149] 2) Termination reaction: PBS containing 100mM glycine, 2%B...
Embodiment 3
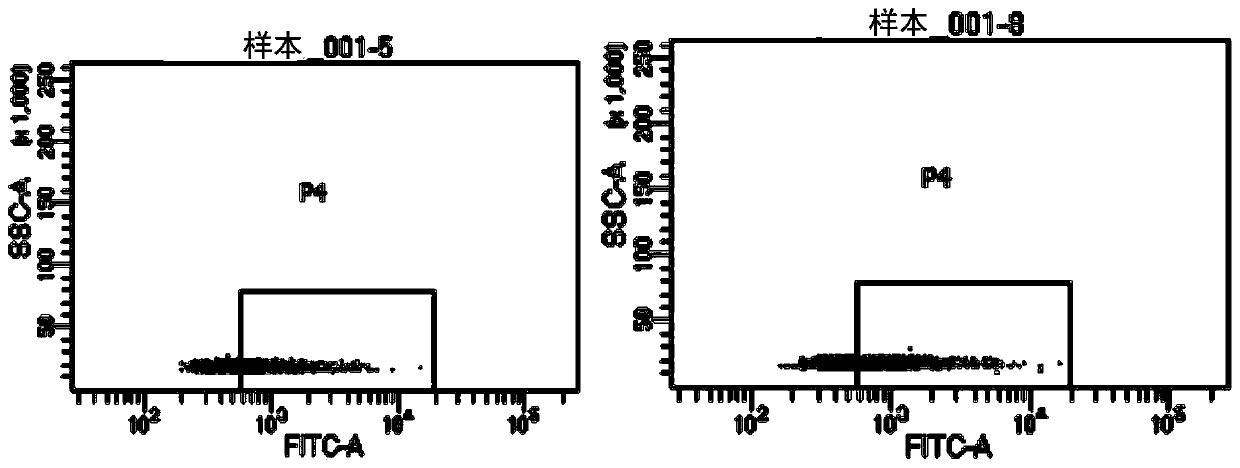
[0227] Example 3: Validation of the capture system effect
[0228] 3.1. Thyroid transcription factor (TTF-1) captures exosomes from lung tissue and thyroid tissue
[0229] The verification method is as follows:
[0230] 1) Lung cancer, intestinal cancer, breast cancer, thyroid cancer, liver cancer and gastric cancer cells (purchased by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Cell Bank) were starved for culture, and supernatant total exosomes were enriched by ultracentrifugation
[0231] 2) TTF-1-positive exosomes from exosome samples secreted by different tumor cell supernatants were captured by the resin method (the method is the same as part 1.3 of Example 1)
[0232] Western Blot (WB) was used to detect the target protein TTF-1 exosome protein to verify whether TTF-1 positive exosomes could be captured in samples from different tissue sources.
[0233] Such as Figure 7 As shown, WB detection after TTF-1 affinity capture of exosomes in tumor cell supernatant, TTF-1 positive exos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com