Method for separating and purifying sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil
A technology for separation and purification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, applied in the direction of material separation, measuring devices, and analysis materials, etc., to achieve the effect of less co-spillage, good effect, and less background interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] After vacuum freeze-drying the soil sample, grind it evenly, pass through a 200-mesh (0.074mm) nylon sieve, obtain the sample and store it at -20°C to obtain the soil to be tested.
[0059] Accurately weigh 4g of the soil to be tested (according to the concentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sample, it can be appropriately increased), add 0.5g of copper powder and 1g of diatomaceous earth, mix well and put them into a 34mL stainless steel extraction pool with a glass fiber filter membrane pre-installed at the bottom, and carry out Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), the filling volume does not exceed 3 / 4 of the cell body. The extraction solvent was a mixed solvent of dichloromethane and acetone with a volume ratio of 1:1. The ASE extraction conditions were static extraction at 100°C for 5 min, 3 cycles, the default pressure was 1500 psi, heating for 5 min, and nitrogen purge for 100 s. If the sample volume is too large and the filling volume exceeds 3...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2: concentration gradient test
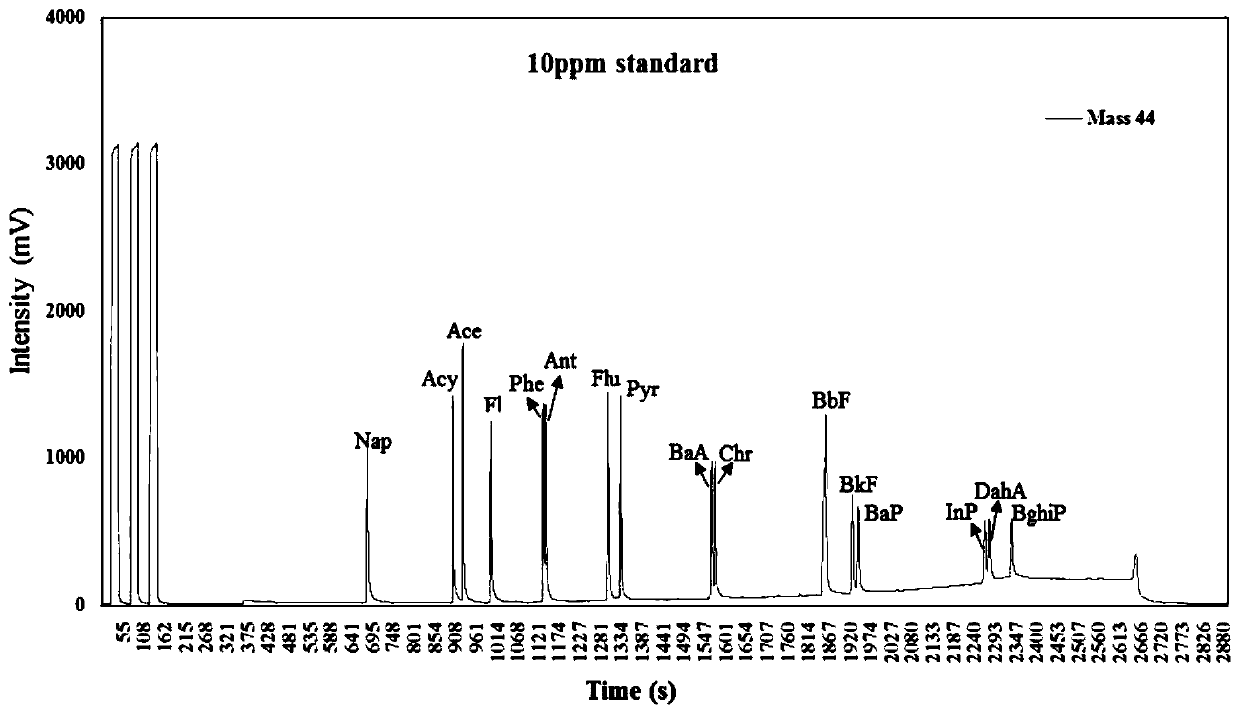
[0071] According to the stable carbon isotope properties, PAH monomer δ at different target concentrations 13 The C value will not change with the concentration, and the mixed standard substances of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with concentrations of 0.1mg / L, 0.5mg / L, 1mg / L, 2.5mg / L, 5mg / L and 10mg / L were prepared respectively, according to the implementation The detection method of gas chromatography-isotope ratio mass spectrometer in Example 1 carried out a concentration gradient experiment to observe the lowest signal value under the condition that all 16 PAHs peaked, and based on this, estimated the minimum sample amount of the actual sample in the follow-up test. The experimental results are shown in Table 1:
[0072] Table 1 Mixed standards of PAHs with different concentrations δ 13 C value
[0073]
[0074]
[0075] Note: nd means that the instrument has not detected
[0076] It can be seen from Table 1 th...
Embodiment 3
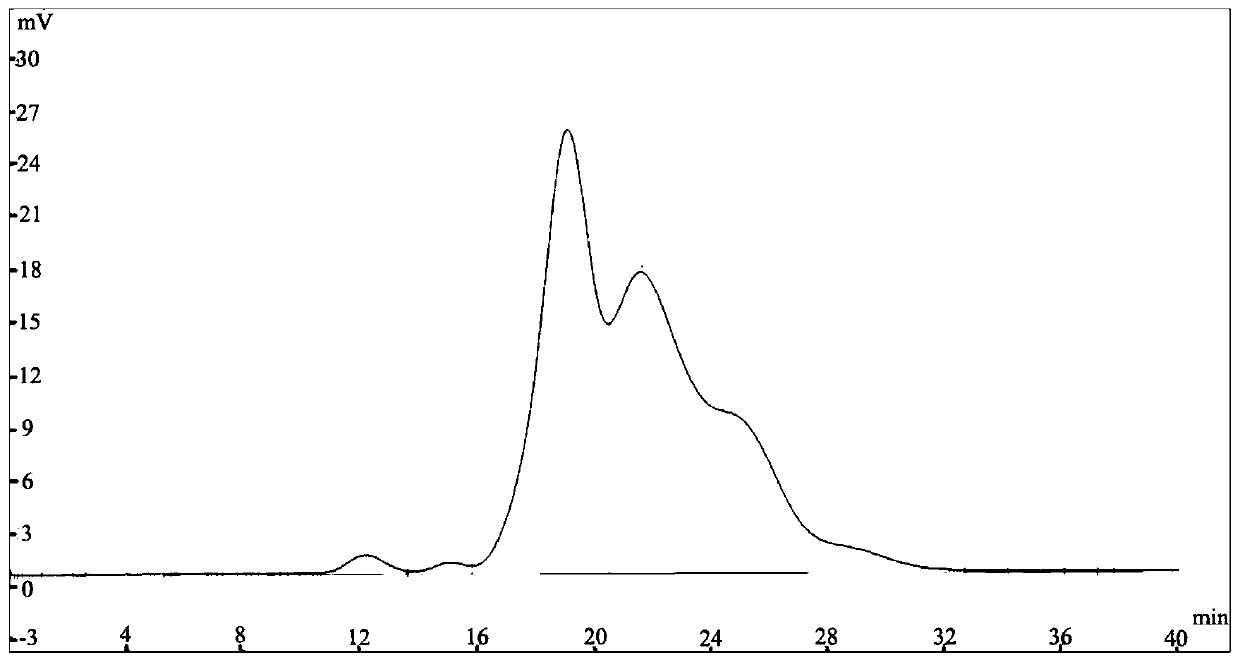
[0077] Embodiment 3: Matrix spike test
[0078] A soil sample of about 5 g was randomly selected, and 5 μL of 2000 mg / L 16 kinds of PAHs mixed standard solutions were added to its ASE extract (extraction conditions were consistent with Example 1), and the matrix addition test was carried out according to the method of Example 1 , the test results are as Figure 4 shown. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen from the test results that the co-elution of samples and the co-distillation of target compounds in the method provided by the present invention have a low degree of interference.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com