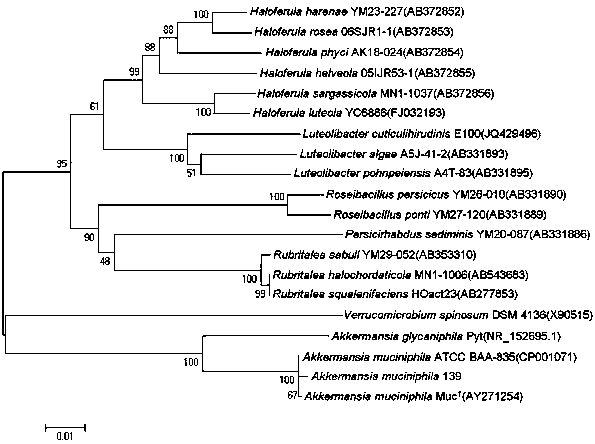
Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain and purpose thereof
A technology of strains and uses, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as inflammation and immunity in mice, and achieve the effects of promoting Treg cell differentiation, regulating permeability and improving health.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain
[0031] Fresh feces of male C57 / BL6 mice of specific pathogen free (SPF) grade were selected and diluted in a gradient from 10-3 to 10-13, and then the bacterial solutions of different dilutions were spread on the surface of the culture medium respectively. To cultivate. A plate with more and clear colonies was selected, and all colonies were identified by PCR using Akkermansia muciniphila species-specific primers. The positive colonies were streaked and purified three times, and finally identified by Sanger sequencing using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE), ERIC fingerprinting and full-length 16S rRNA gene.
[0032] Wherein, the sequence of Akkermansia muciniphila species-specific primer is as follows:
[0033] AM1: 5'-CAGCACGTGAAGGTGGGGAC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0034]AM2: 5'-CCTTGCGGTTGGCTTCAGAT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0035] The 25µL PCR reaction system is: 2.5µL of 10× buffer, 2...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Morphology and growth curve of embodiment 2 Akkermansia muciniphila 139 bacterial strain
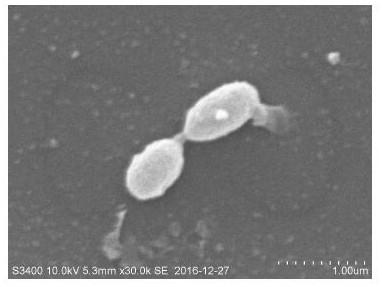
[0044] The morphology of the Akkermansia muciniphila 139 bacterial strain obtained by the separation of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is observed by a scanning electron microscope, and it is observed that the bacterial cell size of the bacterial strain is about 0.9 × 0.5 μm, and the surface is smooth, oval, and without flagella, such as figure 2 shown.
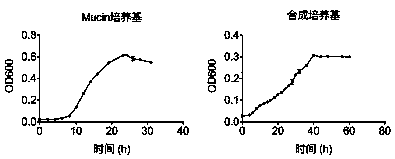
[0045] The growth curves of the Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain were measured in Mucin medium and synthetic medium respectively, the fermentation system was 200ml, and 3 repetitions were set at each time point, and the measurement results were expressed as mean ± standard error. The results of the growth curve measurement were as follows: image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that the strain grows faster in the Mucin medium, reaching the plateau in about 23 hours, and the growth amount in the plateau is about 1.58×109...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain in vitro fermentation
[0047] The pH value of the fermentation supernatant after the above-mentioned Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain reached plateau in Mucin medium and synthetic medium was measured respectively. The results showed that in these two mediums, the fermentation of Akkermansia muciniphila 139 made the fermentation supernatant A significant drop in pH occurred (see Table 2).
[0048] Table 2 Changes in pH value of Akkermansia muciniphila 139 strain reaching plateau
[0049]
[0050] Note: The fermentation system is 200ml, and each group has 3 repetitions, and the measurement results are expressed as mean ± standard error.
[0051] In order to further study the reasons for the drop in pH value, gas chromatography (Agilent, USA) was used to measure the content of short-chain fatty acids in the fermentation supernatant of the Akkermansiamuciniphila 139 strain when it was fermented to the plateau stage in Muci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com