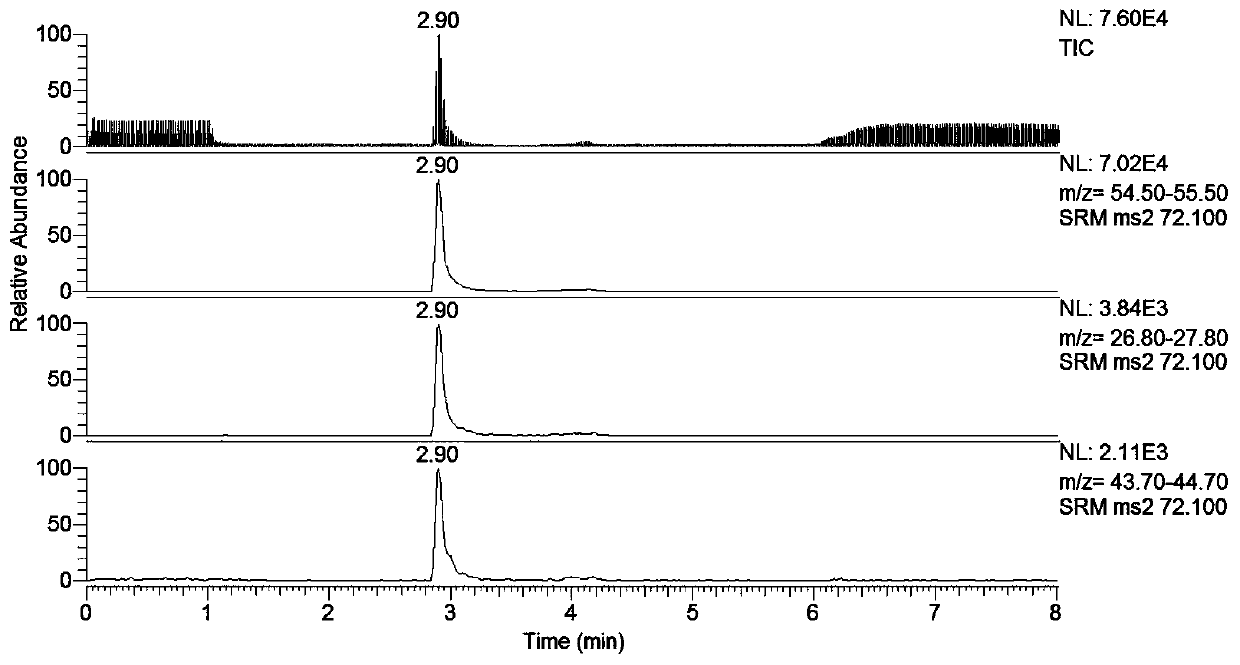
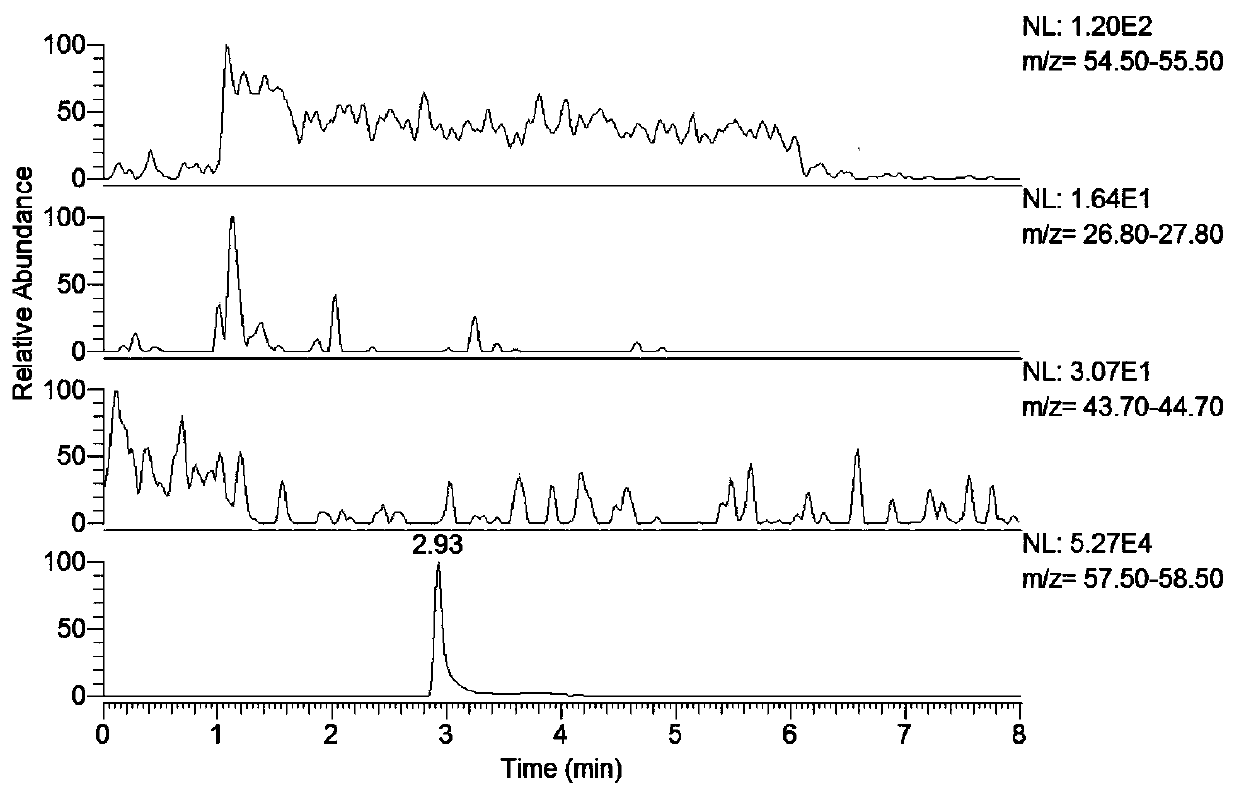
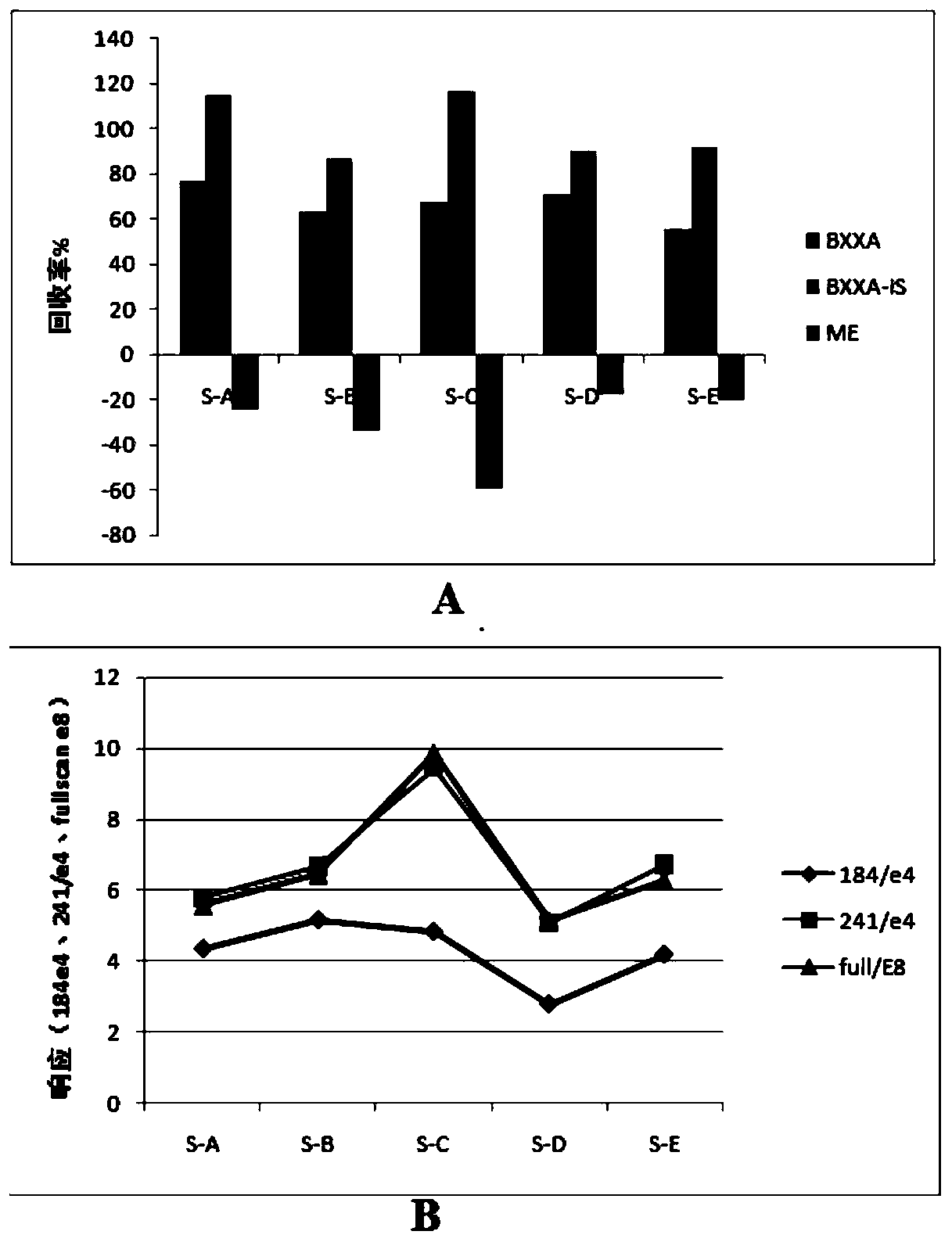
Method for rapidly determining acrylamide in vegetable oil by QuEChERS-LC-MS/MS
A technology for rapid determination of acrylamide, applied in the field of food inspection, can solve the problems of complex derivatization process, cumbersome operation, low recovery rate, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing matrix effect, high detection efficiency, and improving recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1 Instruments and reagents
[0041] TSQ Quantiva liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer, equipped with electrospray ion source, ThermoFisher Company of the United States; Sigma 3-18K high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, Sigma Company of Germany; ultrasonic cleaner, Ningbo Xinzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; MS3 vortex mixer, IKA company, N-EVAP-45 position nitrogen blowing instrument, American Organomation company; SQP-electronic balance, Sartorius Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.; ultrapure water, Mili-Q ultrapure water machine.
[0042] Acrylamide standard substance (purity ≥ 99%), German Dr company, 13C3-acrylamide isotope internal standard (purity ≥ 99%), German WITEGA company; Methanol, acetonitrile, cyclohexane, ethyl acetate (chromatographically pure), the United States Bruker company; Formic acid, ammonium acetate (chromatographically pure), U.S. Sigma-Aldrich company; Water is Milli-Q ultrapure water machine preparation; Nitrogen (>99.999%);...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com