Method for biocatalytically synthesizing D-(+)-glucuronic acid and application of method
A technology of glucuronic acid and biocatalysis, applied in the field of biocatalytic synthesis of D-glucuronic acid, can solve the problems of difficult separation and purification, long production cycle of microbial fermentation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
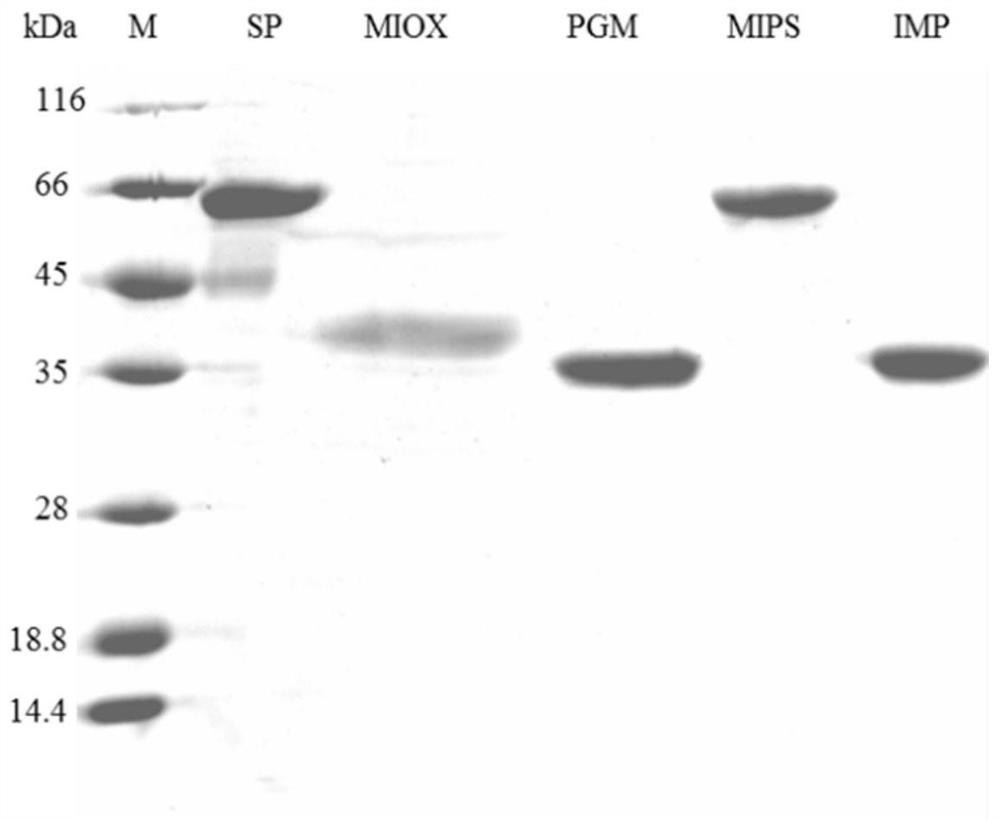
[0066] The preparation of embodiment 1 enzyme
[0067] 1. Preparation of sucrose phosphorylase, glucose phosphate mutase, inositol-1-phosphate synthase, inositol monophosphatase and inositol oxidase:
[0068]In the present invention, sucrose phosphorylase (Sucrose phosphorylase, SP, EC: 2.4.1.7) is derived from E.coli BL21 (DE3), and its NCBI accession number is NC_012892.2; Phosphoglucomutase (Phosphoglucomutase, PGM, EC :5.4.2.2) derived from B.methnoillus PB1 (Bacillusmethanolicus PB1), its NCBI accession number is NZ_AFEU01000003.1:850496-851473; inositol-1-phosphate synthase (Inositol-1-phosphate synthase, MIPS, EC:5.5 .1.4) derived from S.cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C), its NCBI accession number is Chromosome: X; NC_001142.9 (134332..135933); inositol monophosphatase (Inositol monophosphatase, IMP, EC :3.1.3.25) derived from B.methnoillus PB1, its NCBI accession number is NZ_AFEU01000003.1:122318-123091; inositol oxidase (myo...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2 In vitro multi-enzyme catalysis converts sucrose into D-(+)-glucuronic acid
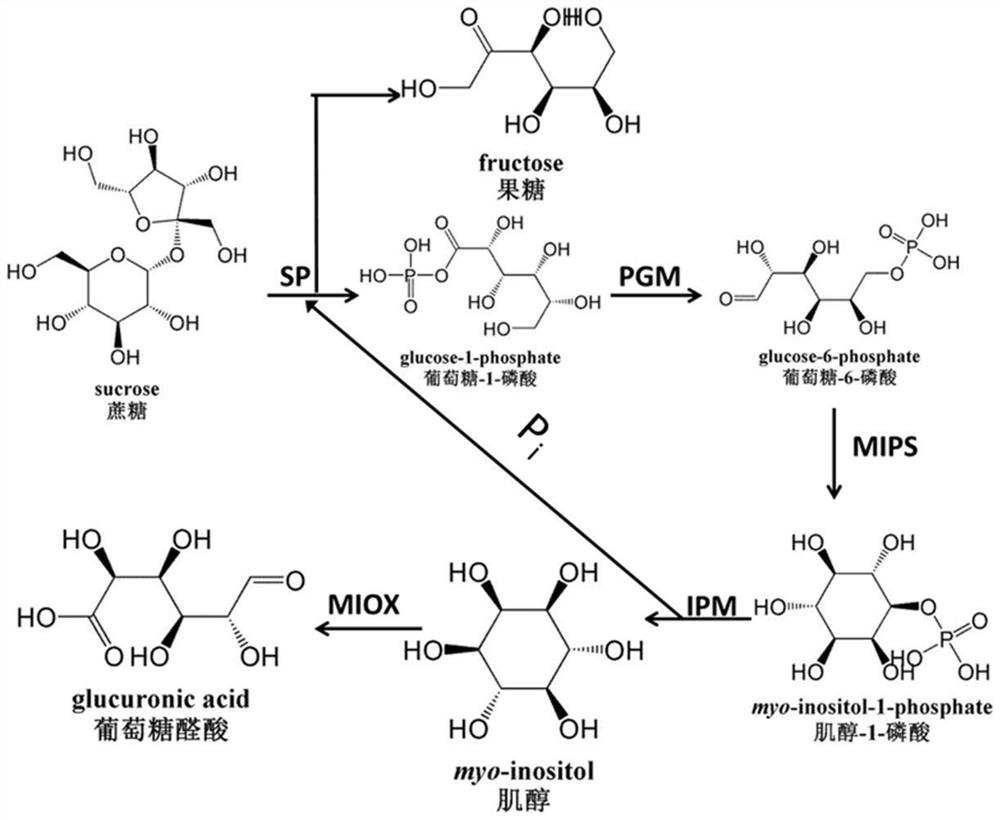
[0086] The present invention converts sucrose into D-(+)-glucuronic acid ( figure 1 ). These key enzymes include:
[0087] 1) Sucrose phosphorylase (SP), which catalyzes the decomposition of sucrose into glucose-1-phosphate and fructose;
[0088] 2) Phosphoglucomutase (PGM), which catalyzes glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate;
[0089] 3) Inositol-1-phosphate synthase (MIPS), which catalyzes glucose-6-phosphate to inositol-1-phosphate;
[0090] 4) Inositol monophosphatase (IMP), which catalyzes the dephosphorylation of inositol-1-phosphate to inositol;
[0091] 5) Inositol oxidase (MIOX), which catalyzes inositol to D-(+)-glucuronic acid.
[0092] Among them, the first step and the second step reaction are reversible, and the subsequent reactions are all irreversible reactions, so the enzyme catalytic system can obtain a high conversion rate.
[0093] The specific experi...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Example 3 In vitro multi-enzyme catalysis converts sucrose into glucuronic acid
[0098] (1) The preparation of sucrose phosphorylase, glucose phosphomutase, inositol-1-phosphate synthase, inositol monophosphatase and inositol oxidase is the same as in Example 1.
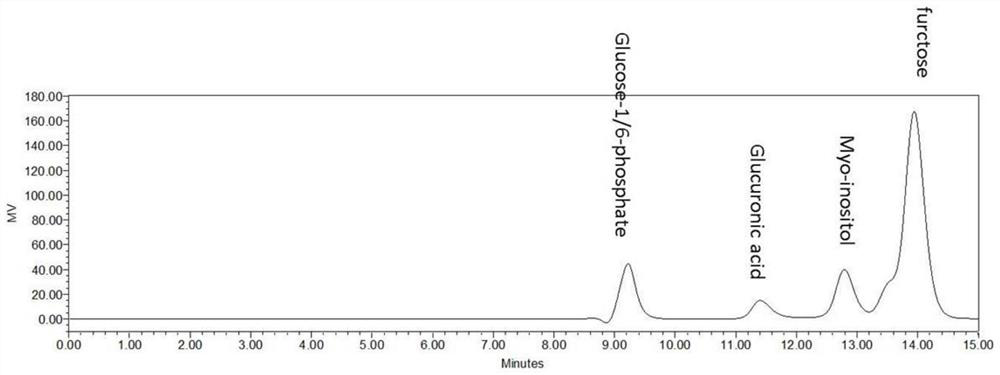
[0099] (2) Contain 150mM Tris-HCl buffer solution, 20mM NaH in a 2.0ml reaction system 2 PO 4 , 5mmol / L MgCl 2 , 2mmol / L L-cysteine, 1U / mL SP, 1U / mL PGM, 2U / mL MIPS, 1U / mL IMP and 5U / mL MIOX, 50mmol / L sucrose, the pH of the catalytic reaction system is 7.5, in The catalytic reaction was carried out at 35°C for 60 hours.
[0100] (3) After the reaction, the final concentration of D-(+)-glucuronic acid was 19.5 mM (the quantitative method was the same as in Example 2), and the conversion rate of sucrose atoms reached 39%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com