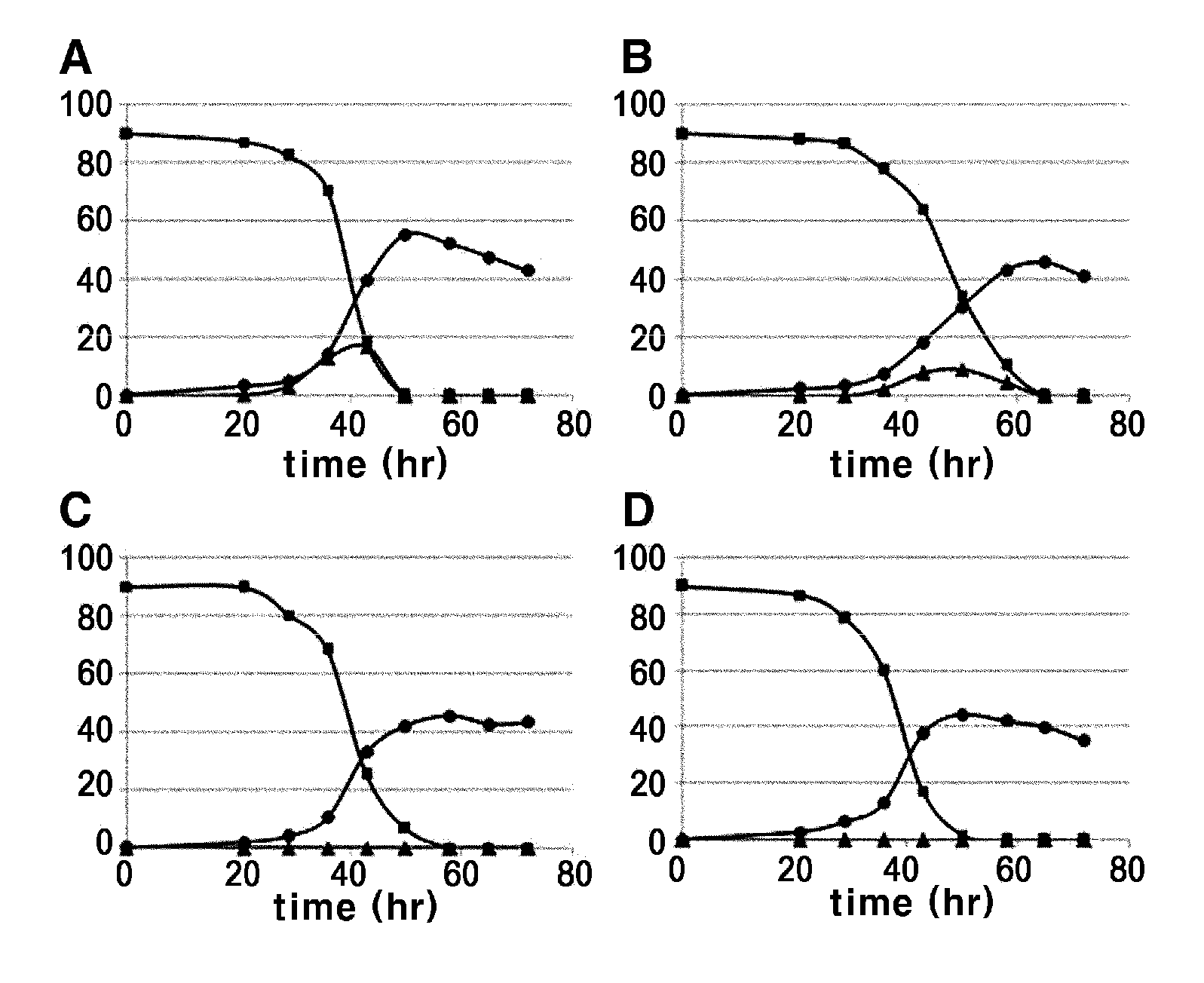
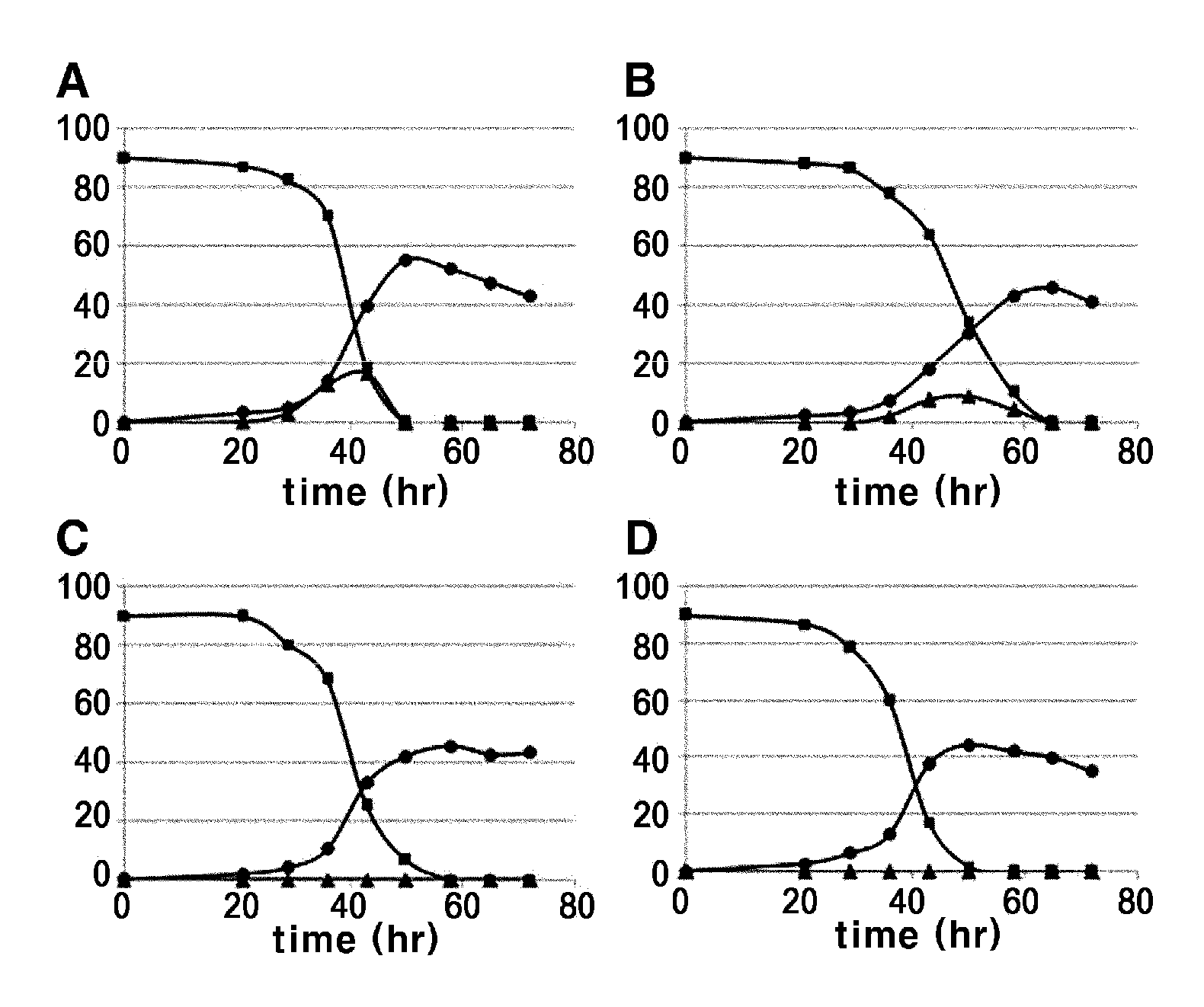
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Fructokinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fructokinase (/fruc•to•ki•nase/ [-ki´nas]), also known as D-fructokinase or D-fructose (D-mannose) kinase, is an enzyme (EC 2.7.1.4) of the liver, intestine, and kidney cortex. Fructokinase is in a family of enzymes called transferases, meaning that this enzyme transfers functional groups; it is also considered a phosphotransferase (or, frequently, a kinase) since it specifically transfers a phosphate group. Fructokinase specifically catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP (the substrate) to fructose as the initial step in its utilization. The main role of fructokinase is in carbohydrate metabolism, more specifically, sucrose and fructose metabolism. The reaction equation is as follows: ATP + D-fructose = ADP + D-fructose 6-phosphate. This is notable because in most tissues this reaction is catalyzed by hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1).
Methods and compositions for the inhibition of fructokinase
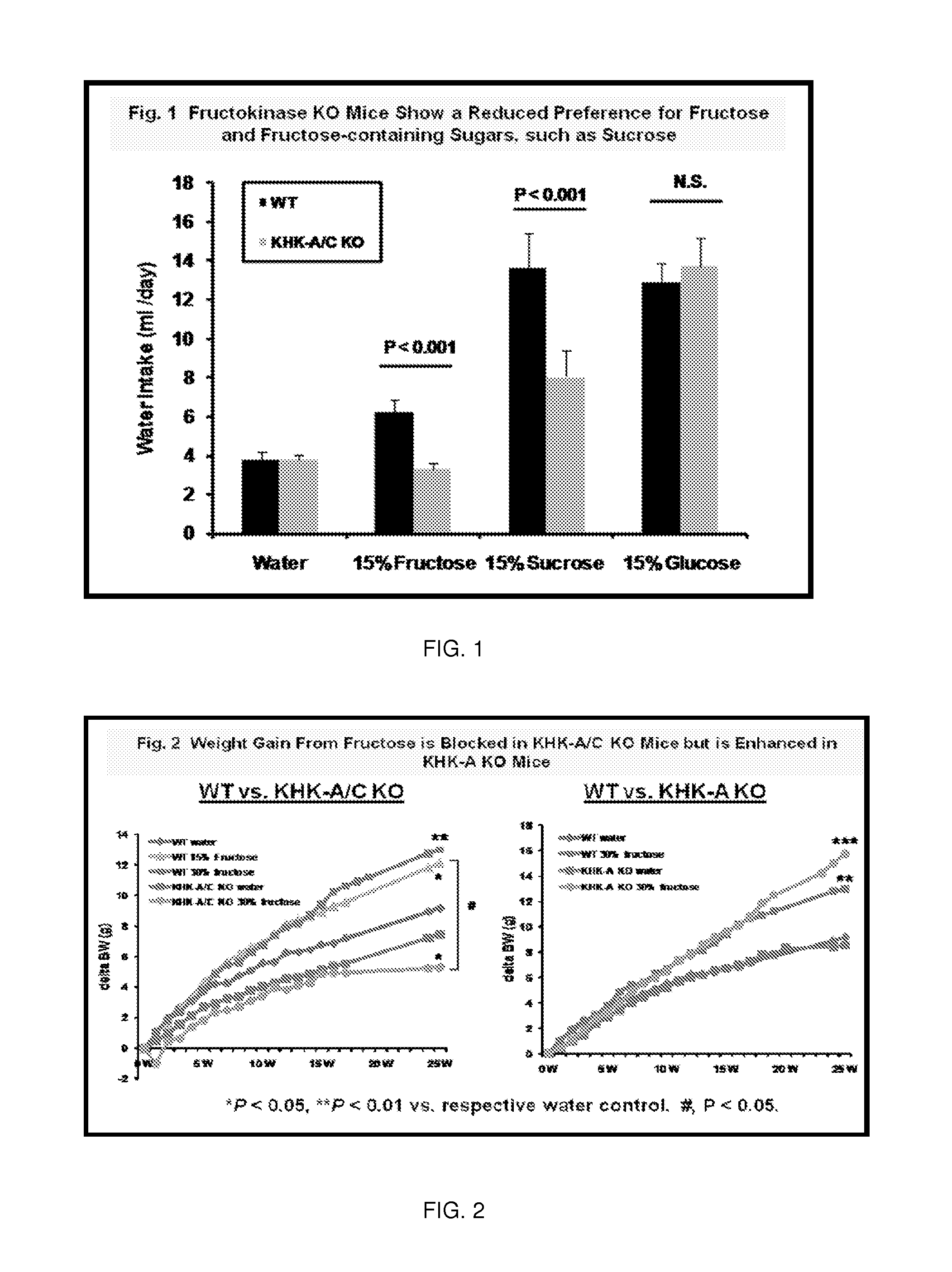
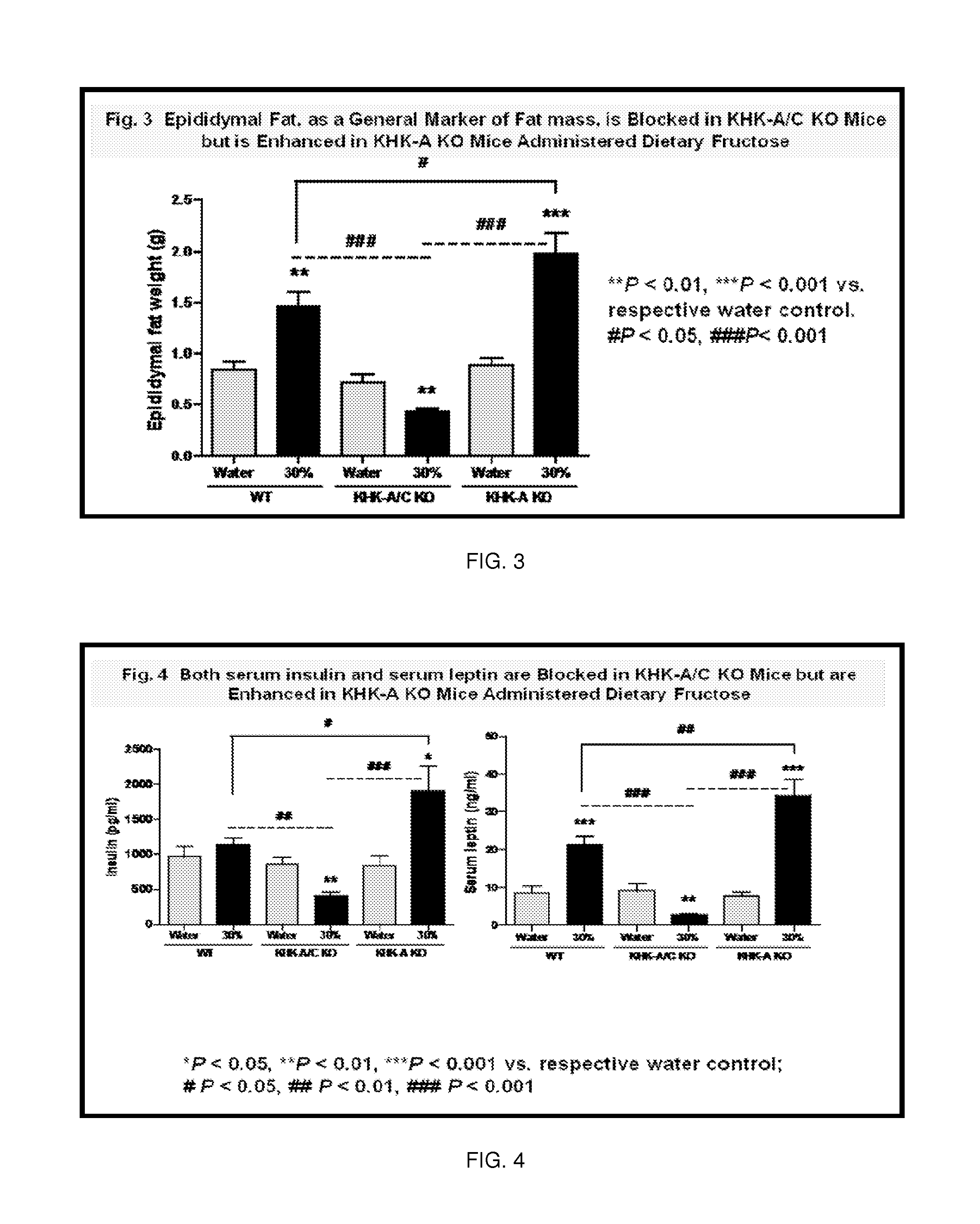
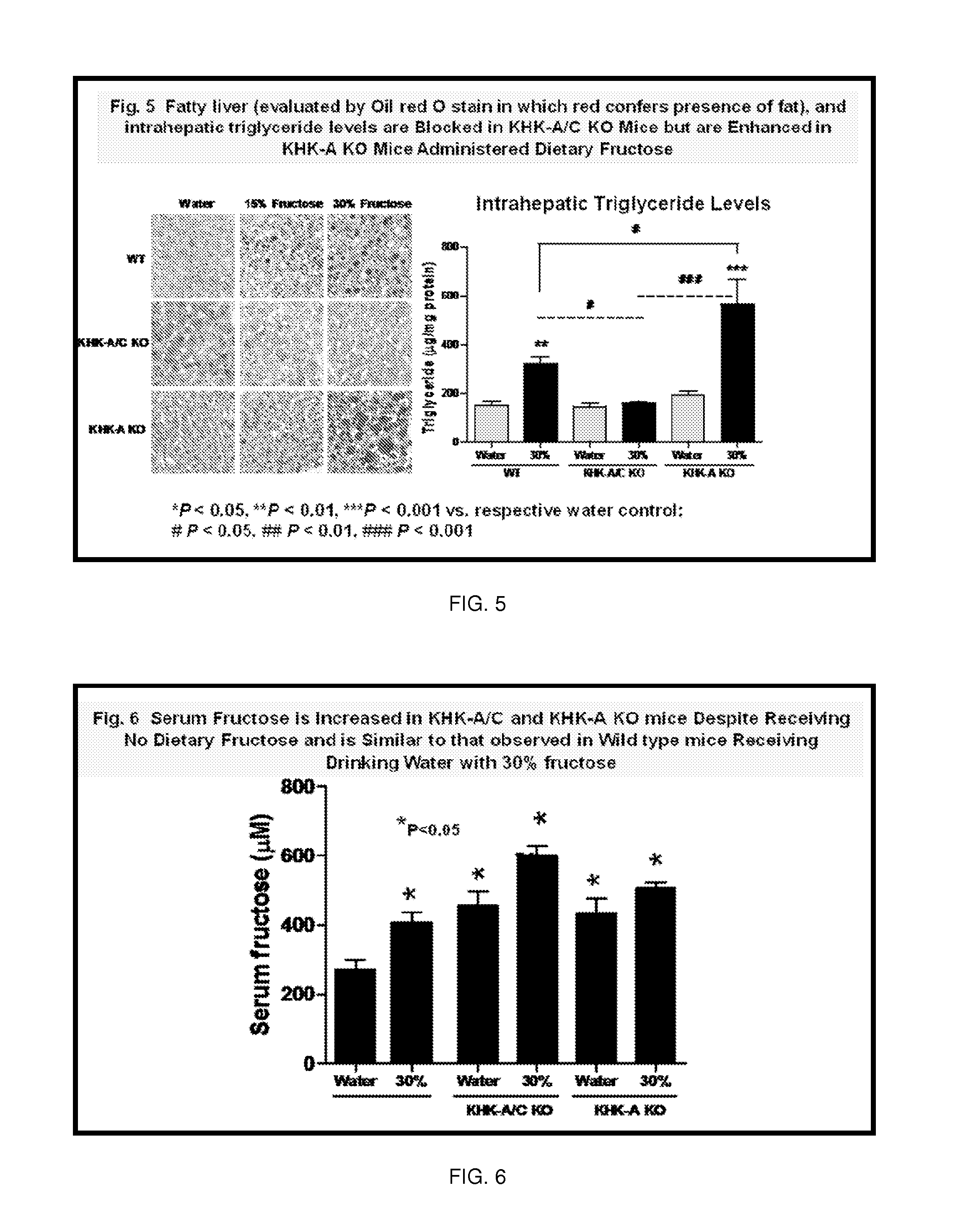
ActiveUS9387245B2Reduce sugar intakeInhibitionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiabetic kidneyFatty liver
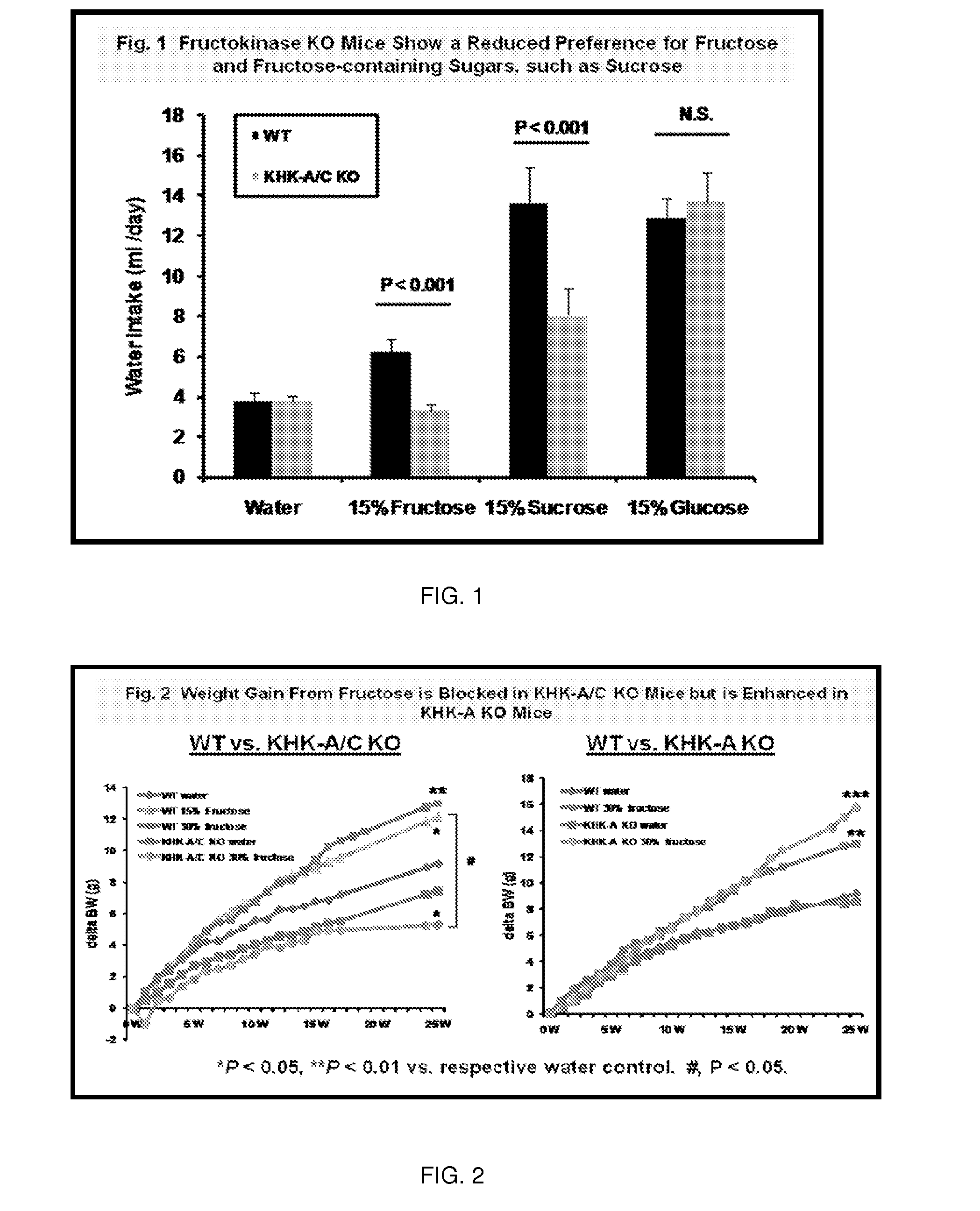
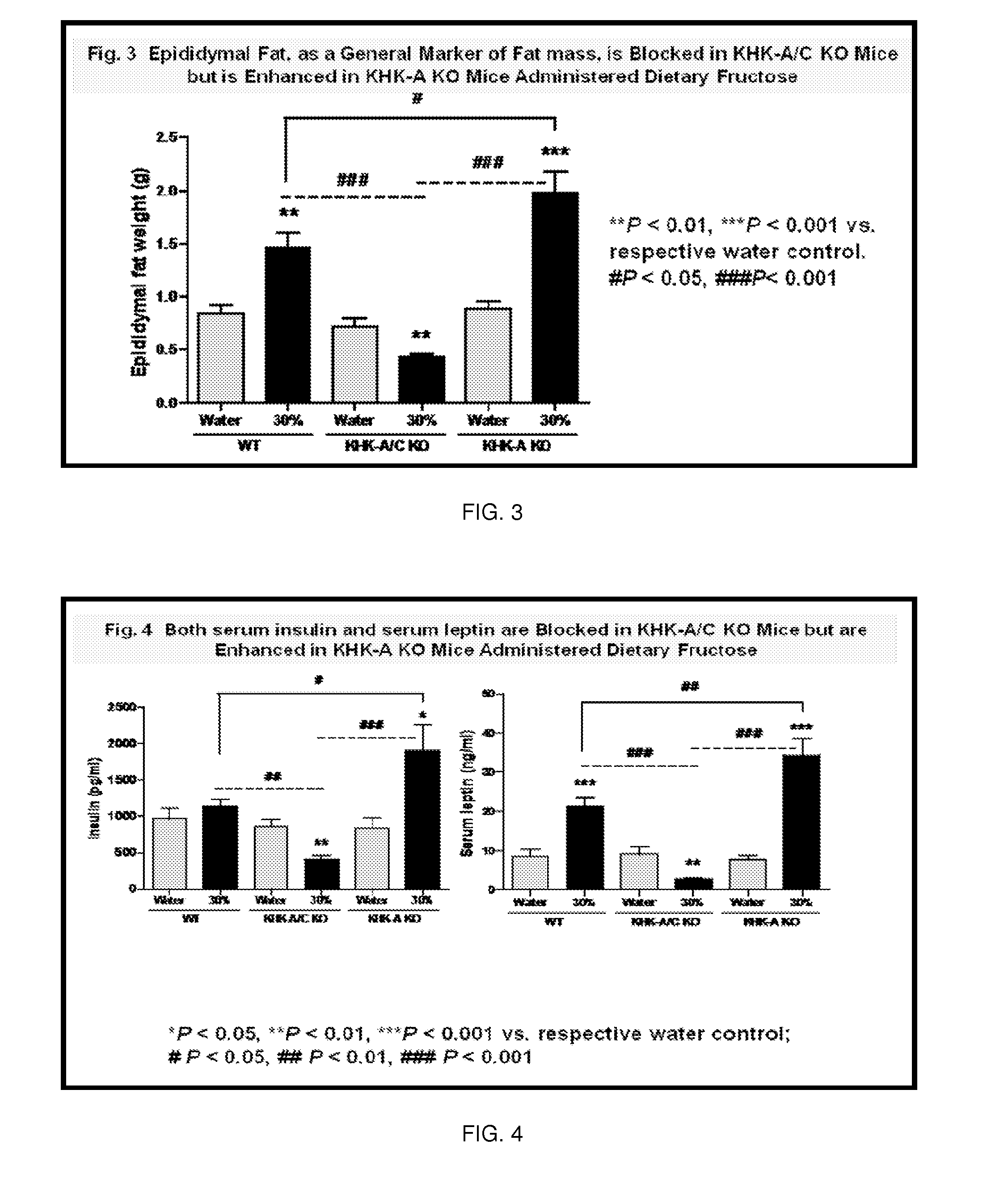
The invention relates to the use of isoform-specific fructokinase (ketohexokinase) (KHK) inhibitors alone or in combination with various agents to both prevent and treat a wide variety of diseases including, but not limited to, sugar craving, obesity, features of metabolic syndrome (including insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension, and fatty liver), polyuria, proximal tubular injury, and diabetic kidney disease.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO A BODY
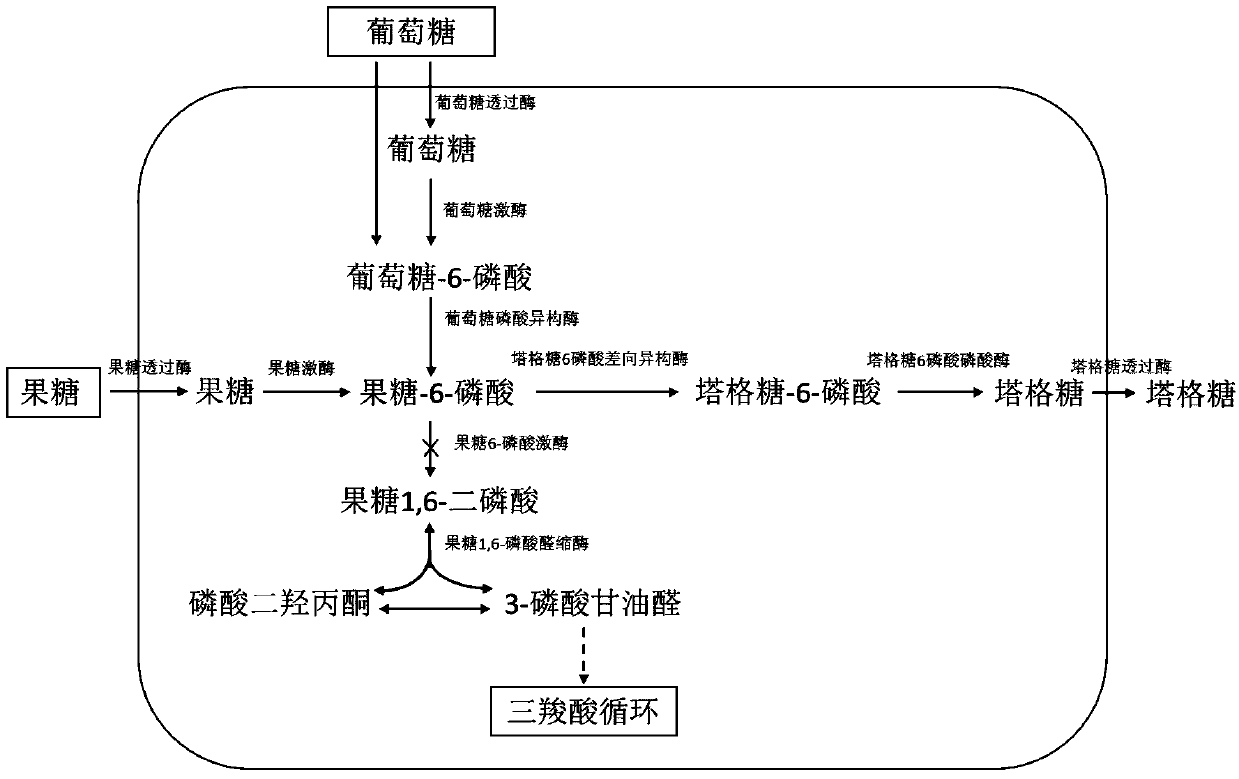
Engineering strain for generating allulose, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN110079488AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionBacteriaHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphate
The invention discloses a construction method of an engineering strain for generating allulose and an application thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: increasing content ofintracellular fructose 6-phosphoric acid by reducing enzymatic activity of fructose 6-phosphokinase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in corynebacterium glutamicum and enhancing enzymatic activityof glucokinase and glucose 6-phophate isomerase by regulating glucose intracellular metabolism; constructing a synthetic route of allulose composed of 6-aloxone phosphate 3-epimerase and 6-aloxone phosphate phosphorylase; constructing a metabolic pathway of fructose composed of fructose transmittase and fructokinase; constructing a metabolic pathway of glycerinum composed of glycerol transmittase, glycerol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone kinase, thereby acquiring a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain. The strain is capable of metabolizing glycerinum, glucose, fructose or saccharose for synthesizing allulose. Compared with the present reported method for compounding allulose through bioconversion of fructose, the construction method provided by the invention has the advantagesof high conversion rate, low production cost, and the like, and is suitable for large-scale production of allulose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
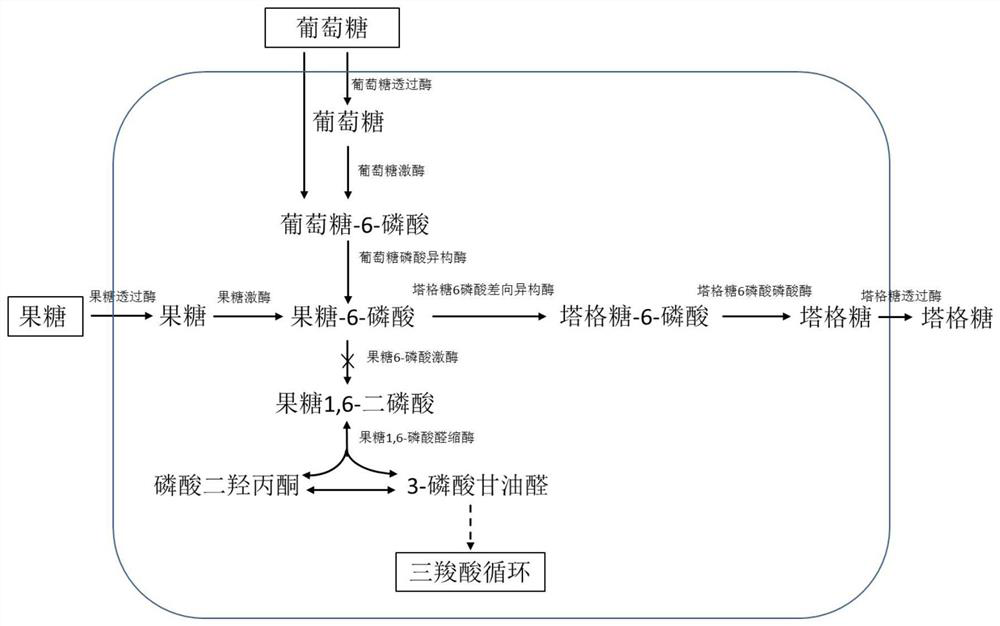
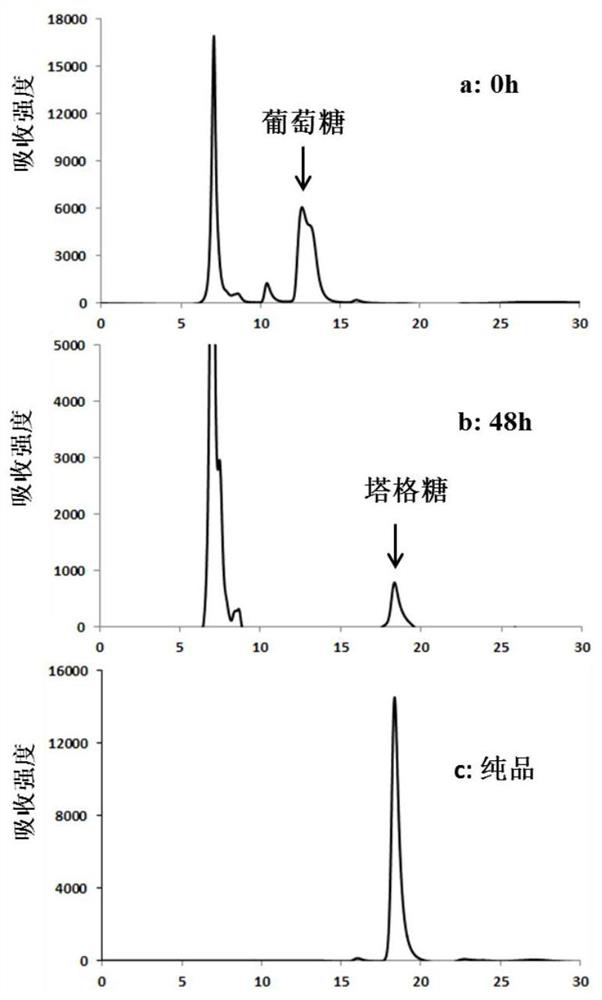
Engineered strain for producing tagatose and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109666620AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologySynthesis methods
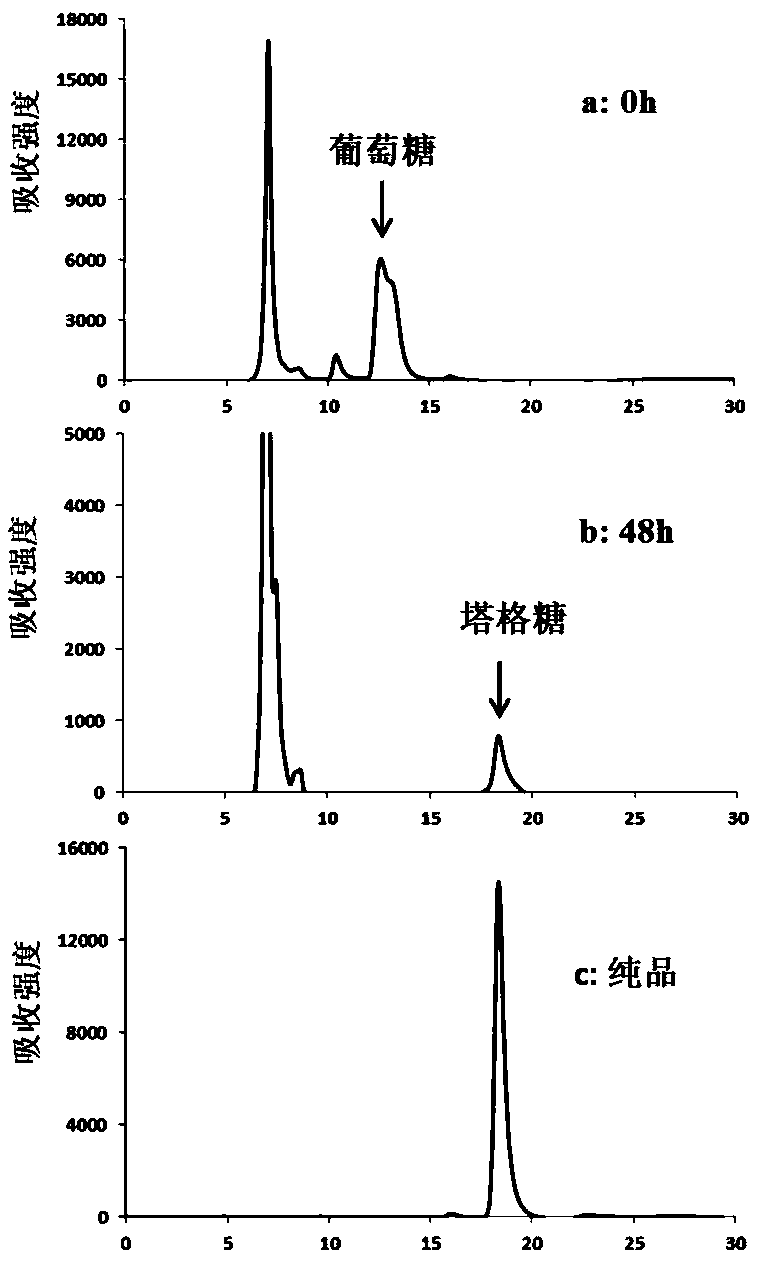
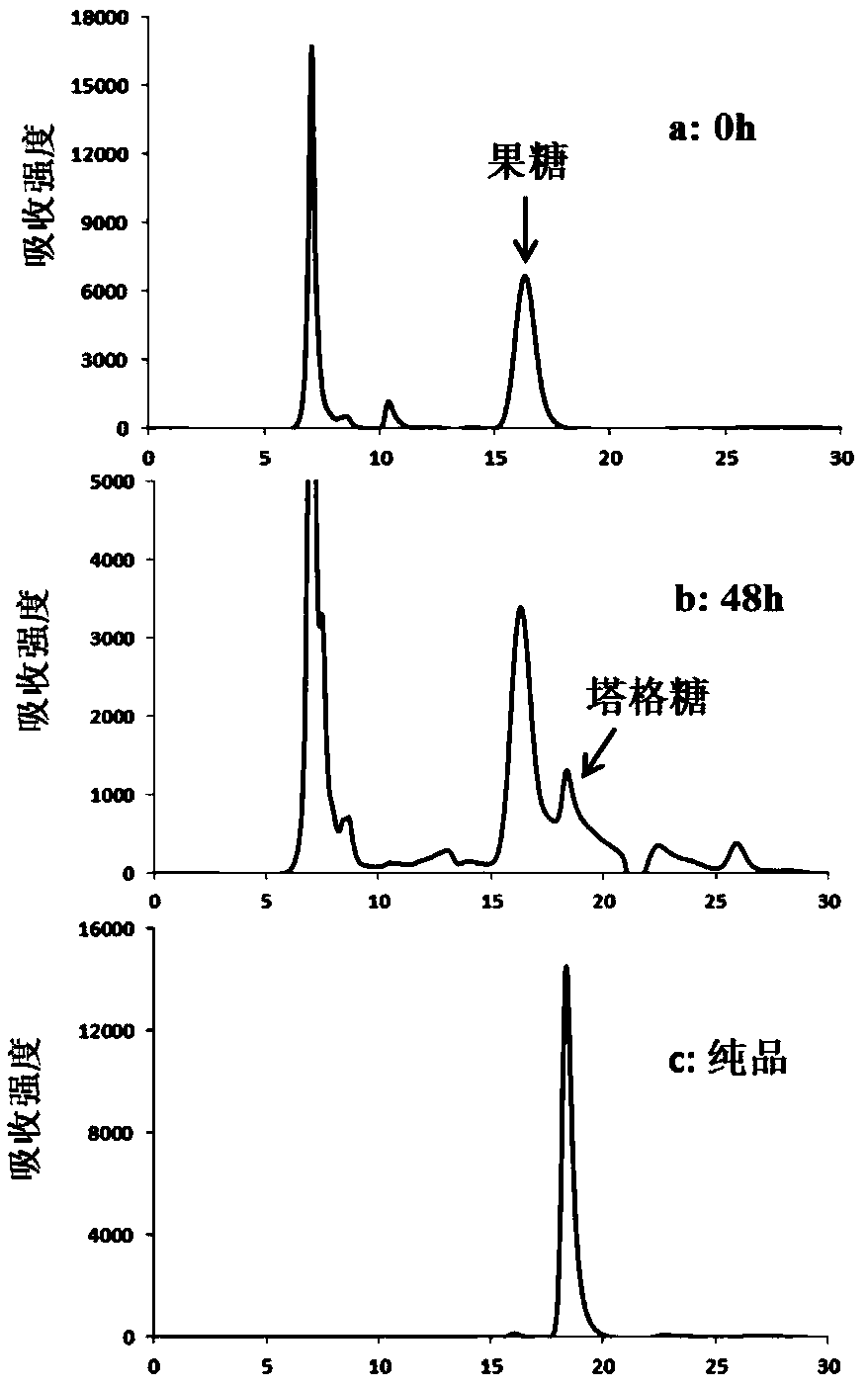
The invention discloses an engineered strain for producing tagatose and a construction method and application thereof. According to the construction method, by regulating intracellular glucose metabolism, the enzymatic activity of 6-phosphofructokinase in cells is reduced, the enzymatic activity of glucokinase and the enzymatic activity of glucose 6-phosphate isomerase are improved, therefore, thecontent of fructose-6-phosphate in the cells is increased, a tagatose synthesis path composed of tagatose-6-phosphate 3-epimeriase and tagatose-6-phosphate phosphorylase is constructed, and a fructose metabolism path composed of fructose permease and fructokinase is constructed. The glutamic acid corynebacterium recombination strain is obtained and can synthesize tagatose by metabolizing glucose,fructose or saccharose. Compared with currently reported fructose biotransformation tagatose synthesis methods, the construction method of the engineered strain has the advantages of being easy to operate and facilitating separation and is suitable for large-scale tagatose production.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Methods and Compositions for the Inhibition of Fructokinase
ActiveUS20130224218A1Reduce sugar intakeInhibitionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiabetic kidneyHypertriglyceridemia
The invention relates to the use of isoform-specific fructokinase (ketohexokinase) (KHK) inhibitors alone or in combination with various agents to both prevent and treat a wide variety of diseases including, but not limited to, sugar craving, obesity, features of metabolic syndrome (including insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension, and fatty liver), polyuria, proximal tubular injury, and diabetic kidney disease.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO A BODY
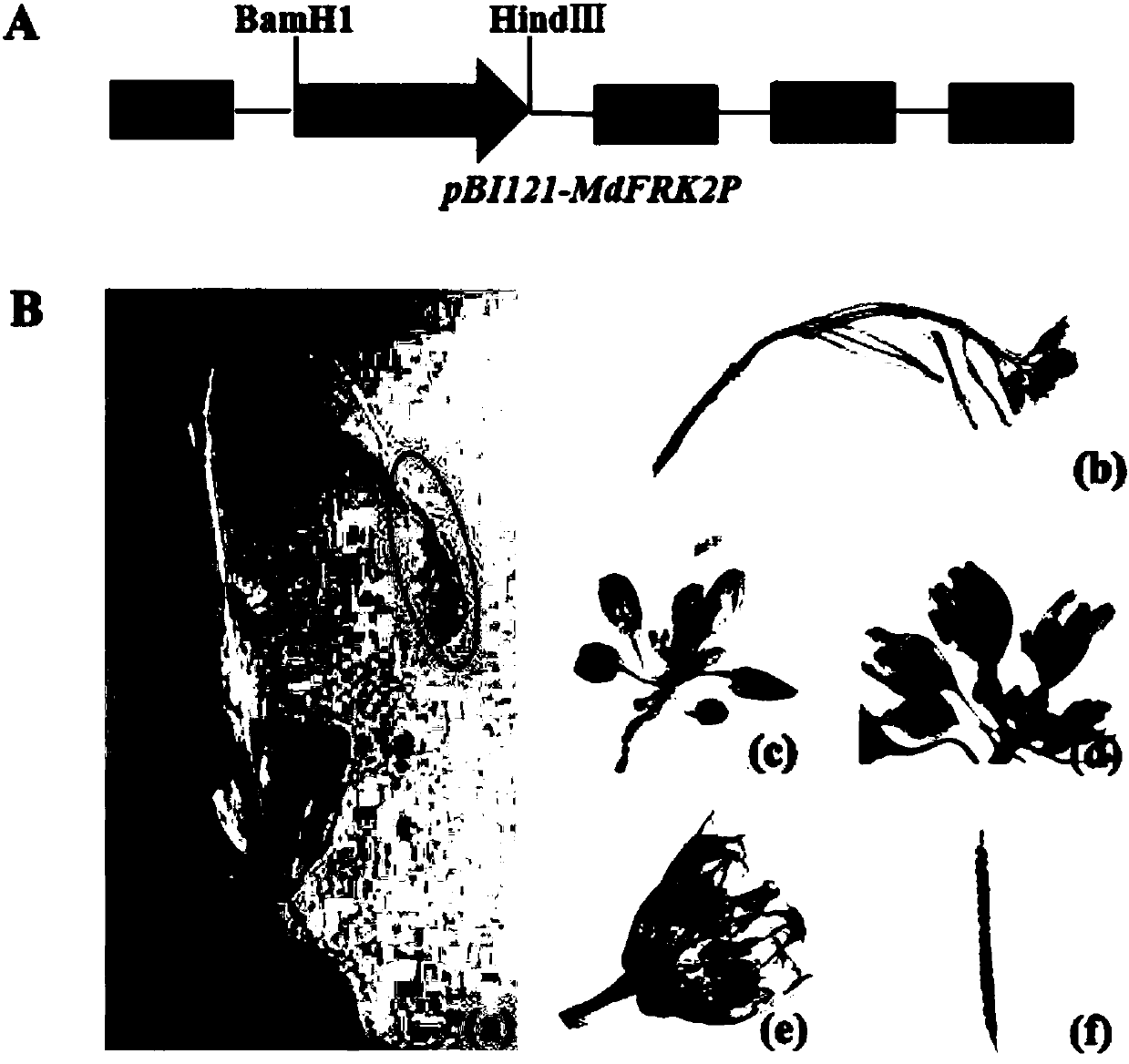
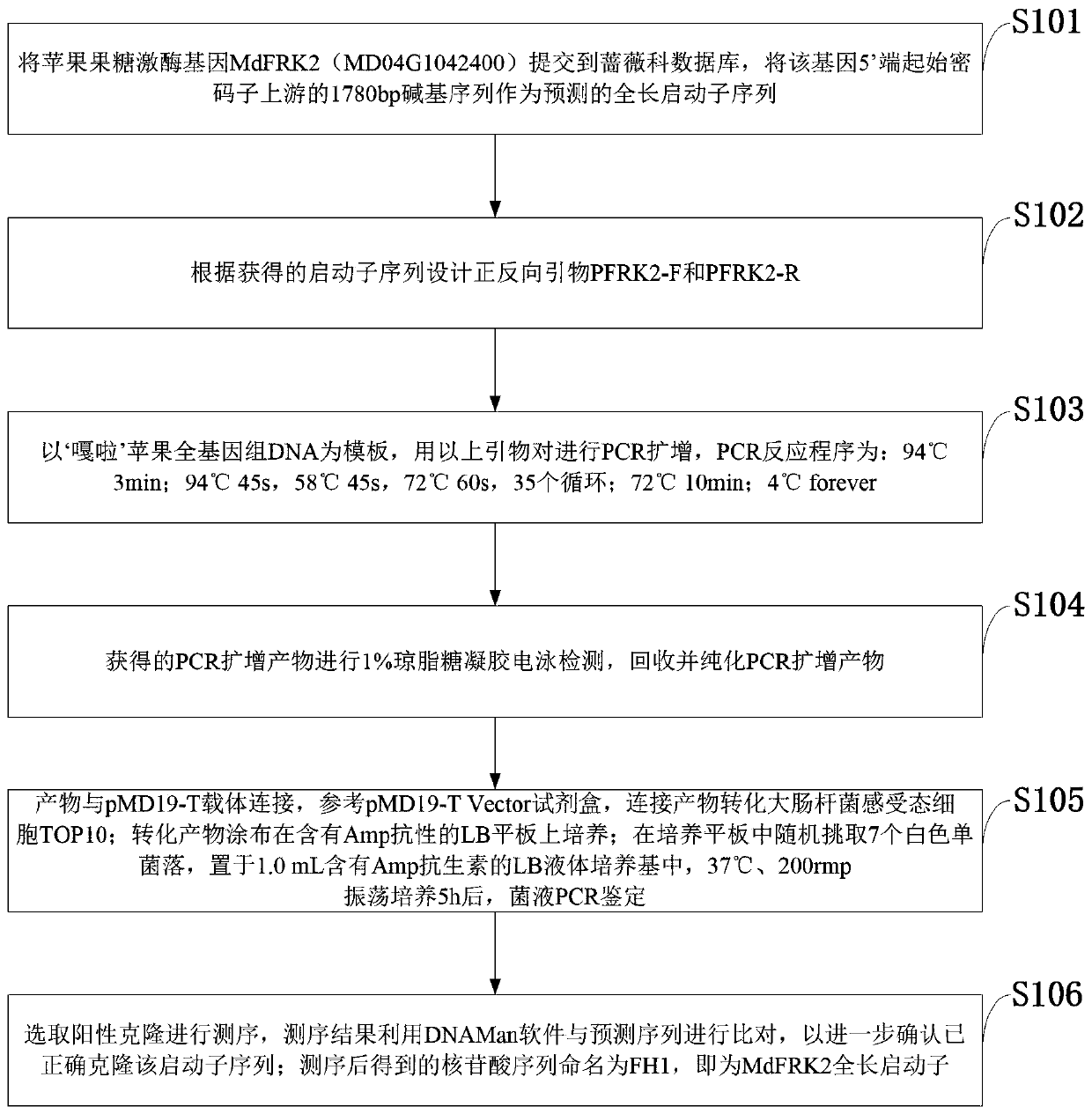
Promoter sequence of fructokinase gene in apple, and deletion mutants and application of
PendingCN111019943AFew research reportsRich researchTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological gene engineering and discloses a promoter sequence of a fructokinase gene in an apple, and deletion mutants and application of. A promoter isnamed as FH1 and is a 1780-bp nucleotide sequence at the upper stream of the 5'-end of an MdFRK2 gene coding frame in an apple; and the mutants are sequences obtained by deleting fragments with different lengths from the 5'-end of the sequence of FH1 and are named as FH2, FH3 and FH4 respectively. The invention further discloses application of the MdFRK2 promoter and the deletion mutants of the MdFRK2 promoter in research on plant functional genes. The MdFRK2 promoter can regulate and control the specific expression of a target gene in cambium of stem tip growth points, old leaves, functionalleaf margins and other library tissues of arabidopsis thaliana and poplar, and a fragment from a transcription starting site to upstream-600 bp is determined to be a core fragment of a promoter region of the MdFRK2 promoter. The full length of the MdFRK2 promoter is induced by exogenous sugar and drought, which indicates that the promoter has important application value in industrial developmentof plant genetic engineering.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing D-allulose, and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112080453ABlock metabolic pathwayEasy to produceBacteriaTransferasesArthrobacter globiformisEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for synthesizing D-allulose, and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The invention provides a bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium capable of synthesizing the D-allulose by D-fructose, and a construction method of the bacillus subtilis genetically engineered bacterium. Particularly,bacillus subtilis WB600 is taken as a host bacterium, a fructokinase gene on the genome of the host bacterium and the genes of PTS system fructose specific translocator components IIABC and IID are knocked out to obtain a bacillus subtilis mutant, and a D-allulose-3-epimerase encoding gene from Arthrobacter globiformis M30 is subjected to free expression in the host bacterium to obtain recombinantbacillus subtilis. By use of the genetically engineered bacterium disclosed by the invention, the substrate D-allulose can be fully utilized, the yield of biosynthesis D-allulose is greatly improvedso as to be favorable for industrial production of the D-allulose, and the genetically engineered bacterium has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
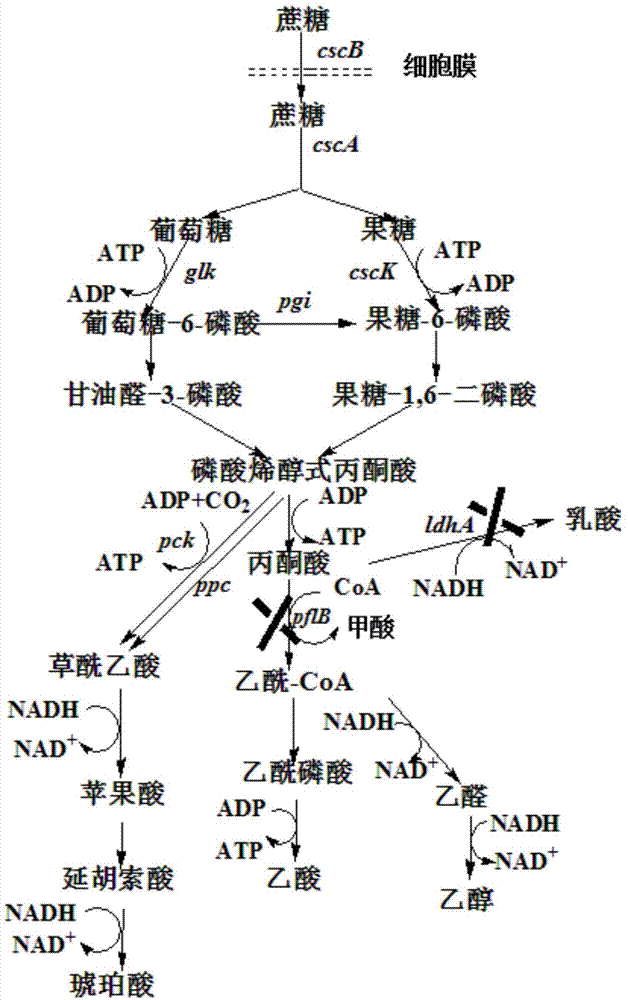
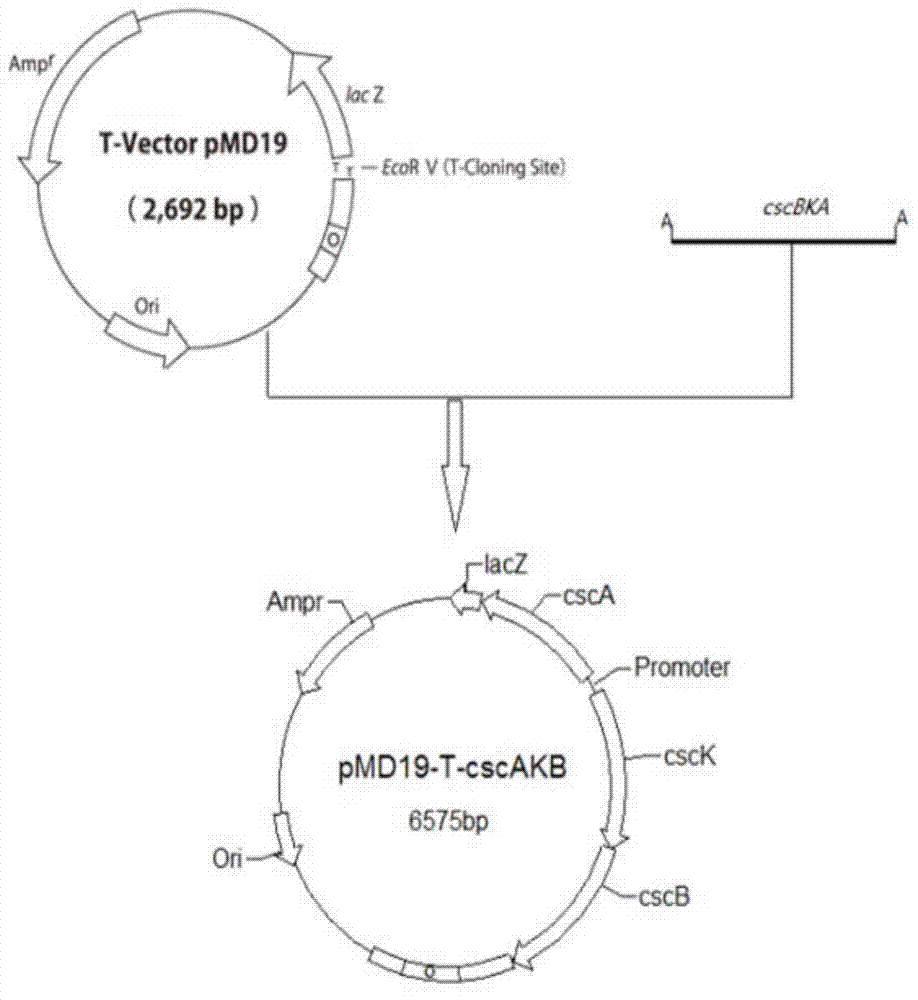
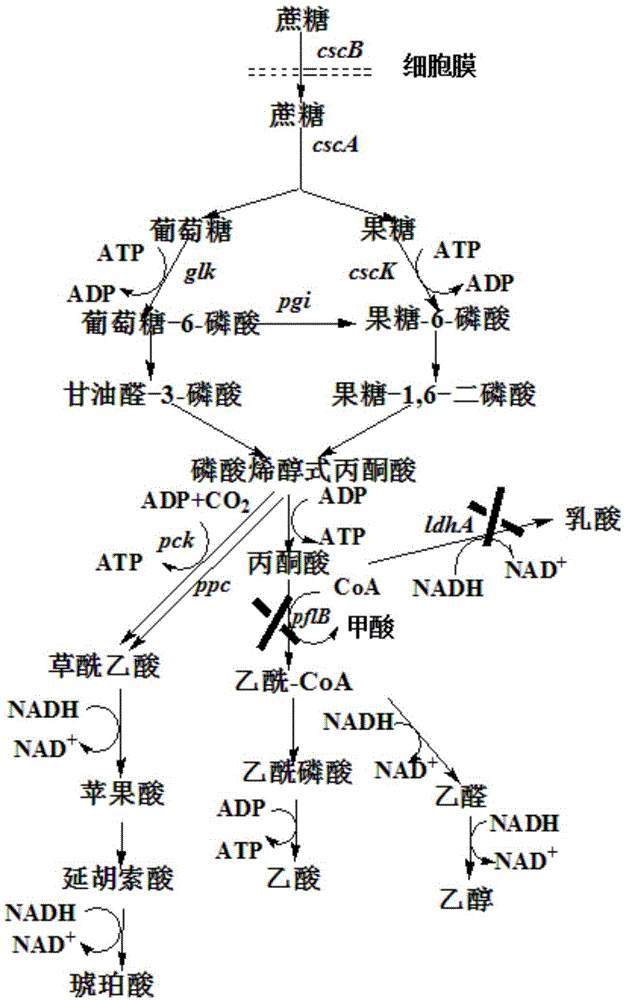
Genetic engineering strain utilize sucrose to produce succinic acid from and method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the same
ActiveCN103937733AImprove fermentation effectIncrease useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactate dehydrogenase
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to a genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid and a method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the strain, particularly a recombinant strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. The genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid is classified and named as Escherichia coli BA501, and has a preservation registration number of CCTCC NO:M2014014. The construction process of the strain mainly includes: taking Escherichia coli AFP111 that lacks lactate dehydrogenase gene and pyruvate formate lyase activity and has the chromosome ptsG gene undergoing spontaneous mutation as the starting strain, expressing exogenous sucrose permease, sucrose hydrolase and fructokinase genes, and then carrying out continuous domestication cultivation to obtain the strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. Thus, the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly improved. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation way, in the aerobic stage the biomass is improved oxygen, and in the anaerobic stage, fermentation and acid production are achieved.
Owner:态创生物科技(广州)有限公司
Phosphofructokinase and application of coding gene thereof
The invention discloses a phosphofructokinase, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein has one of the following amino acid residue sequences: 1) amino acid residue sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table; and 2) protein with phosphofructokinase derived from SEQ ID No.1, subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid residue sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. The transgenic experiment on the protein indicates that the gene has the function of phosphofructokinase; and after the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of the gene is transfected into a phosphofructokinase deficient strain RL257, the obtained transgenic strain can normally grow in an M63 basal culture medium which uses mannitol as the unique carbon source.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
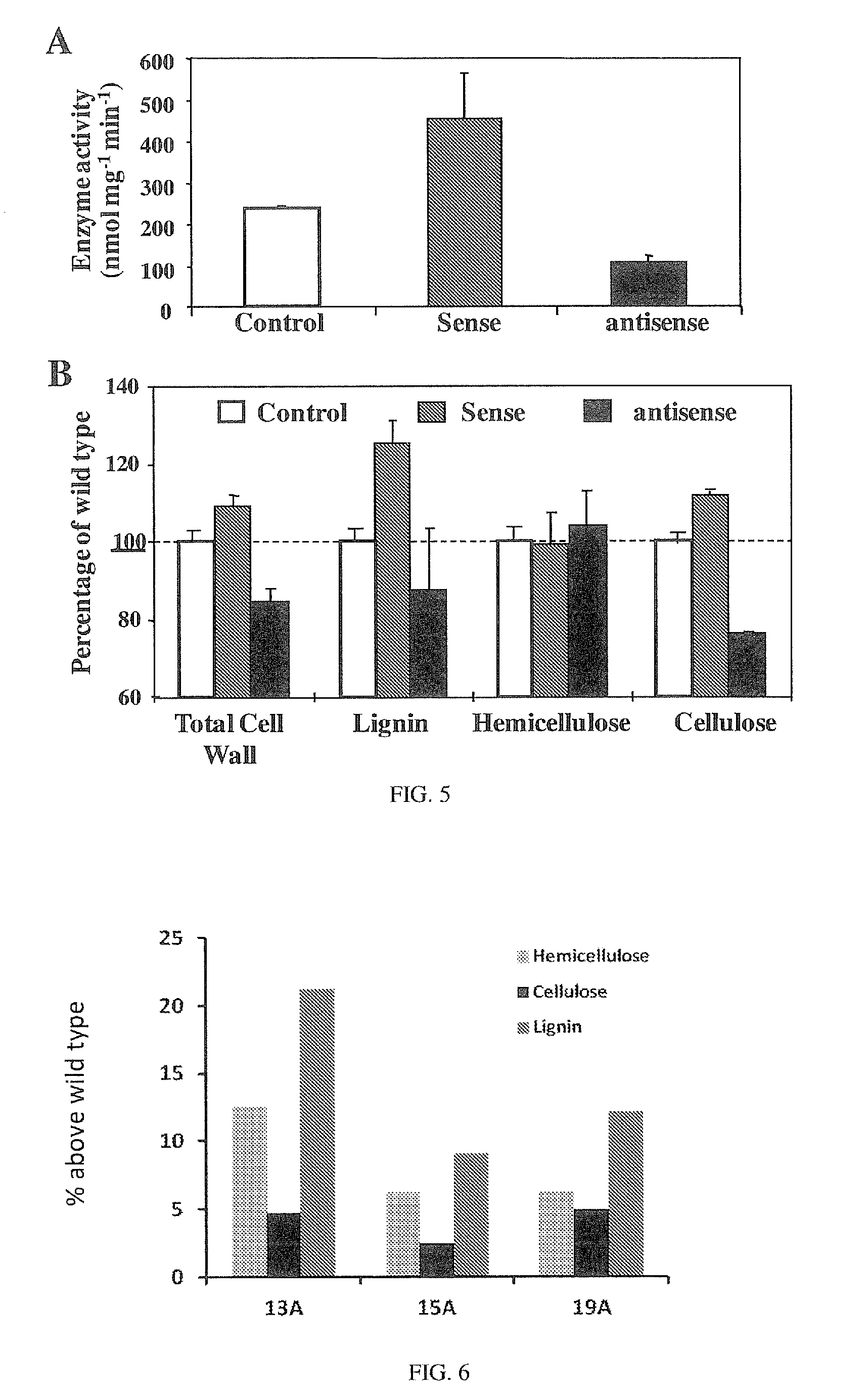
Method for increasing plant cellulose content by utilizing apple fructokinase gene
PendingCN112175972AImprove utilization efficiencyLow costTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a method for increasing the plant cellulose content by utilizing an apple fructokinase gene. An apple fructokinase gene MdFRK2, a recombinant overexpression vector containing the apple fructokinase gene MdFRK2 and recombinant bacteria containing the apple fructokinase gene MdFRK2 are involved in the method. The apple fructokinase gene MdFRK2 in the method can be used for increasing the cellulose content; and the method plays an important role in cell wall transformation and green energy development.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Compound native microorganism domestication enzyme for efficiently improving urban black and odorous water body, and method for treating urban black and odorous water body
ActiveCN111073869ATo promote metabolismEasy to removeMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a compound native microorganism domestication enzyme for efficiently improving an urban black and odorous water body, and a method for treating the urban and odorous water body. The compound native microorganism domestication enzyme comprises acetyl CoA acyltransferase, 1-phosphofructokinase, pyruvate phosphate dikinase, beta-hydroxybutyryl coenzyme dehydrogenase, 3-phosphoglycerate kinase, NAD-dependent beta-hydroxybutyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase, and thiolase. The method for treating the urban black and odorous water body comprises the following steps: preparation andactivation of the compound native microorganism domestication enzyme; putting of the activated compound native microorganism domestication enzyme into the black and odorous water body for a period oftime; and then aquatic plant construction. The compound native microorganism domestication enzyme of the invention has the advantages of efficiently improving the quality of the black and odorous sewage water body. In addition, the treatment method of the invention has the advantages of efficiently purifying the water body, and continuously adjusting and optimizing the water body environment.
Owner:北京京阳环保工程有限公司
Fructokinase from fungal traditional Chinese medicine and coding gene and use thereof
ActiveCN113430186AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaTransferasesBiosynthetic genesNucleotide
The invention discloses fructokinase from a fungal traditional Chinese medicine and a coding gene and use thereof. The fungal traditional Chinese medicine fructokinase has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and a nucleotide sequence of the coding gene as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The fungal traditional Chinese medicine fructokinase participates in synthesis of main precursor monosaccharide D-fructose of cordyceps polysaccharide from D-fructose-6-phosphoric acid. A fungal traditional Chinese medicine hirsutella sinensis polysaccharide biosynthetic metabolism pathway is studied in details in principle. A cloned DNA containing the nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacteria by transduction, transformation and conjugal transfer methods. An expression of a D-fructose biosynthetic gene is regulated, the host is endowed with high expressivity of D-fructose, an effective way is provided for increasing the yield of the D-fructose and a derivative thereof, and the fructokinase has a great application prospect.
Owner:北京中医药大学深圳医院
Use of fructokinases and sucrose synthases for increasing cell wall polymers
InactiveUS9556421B2Promote plant growthHigh expressionTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionSucrose synthetaseCell wall
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
A genetically engineered strain using sucrose to produce succinic acid and its fermentation method for producing succinic acid
ActiveCN103937733BImprove fermentation effectIncrease useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactate dehydrogenase
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to a genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid and a method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the strain, particularly a recombinant strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. The genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid is classified and named as Escherichia coli BA501, and has a preservation registration number of CCTCC NO:M2014014. The construction process of the strain mainly includes: taking Escherichia coli AFP111 that lacks lactate dehydrogenase gene and pyruvate formate lyase activity and has the chromosome ptsG gene undergoing spontaneous mutation as the starting strain, expressing exogenous sucrose permease, sucrose hydrolase and fructokinase genes, and then carrying out continuous domestication cultivation to obtain the strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. Thus, the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly improved. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation way, in the aerobic stage the biomass is improved oxygen, and in the anaerobic stage, fermentation and acid production are achieved.
Owner:态创生物科技(广州)有限公司
Recombinant filamentous fungus for producing ethanol from phosphofructokinase 2 mutant, construction of recombinant filamentous fungus and application of recombinant filamentous fungus in ethanol production
PendingCN114107357AEnhance ethanol production capacityImprove glucose metabolismTransferasesBiofuelsEthanol synthesisKinase activity
The invention discloses a phosphofructokinase 2 mutation and / or knockout recombinant filamentous fungus for ethanol production and construction and ethanol production application thereof, which is characterized in that an endogenous phosphofructokinase 2 gene is knocked out and / or a mutated phosphofructokinase 2 gene is expressed in the filamentous fungus; wherein the mutated phosphofructokinase 2 means that only kinase activity is retained and phosphatase activity is lost or reduced after mutation. Compared with the original strain, the obtained genetic engineering strain has the advantages that the ethanol synthesis capability is improved, and the glucose metabolism rate is accelerated.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
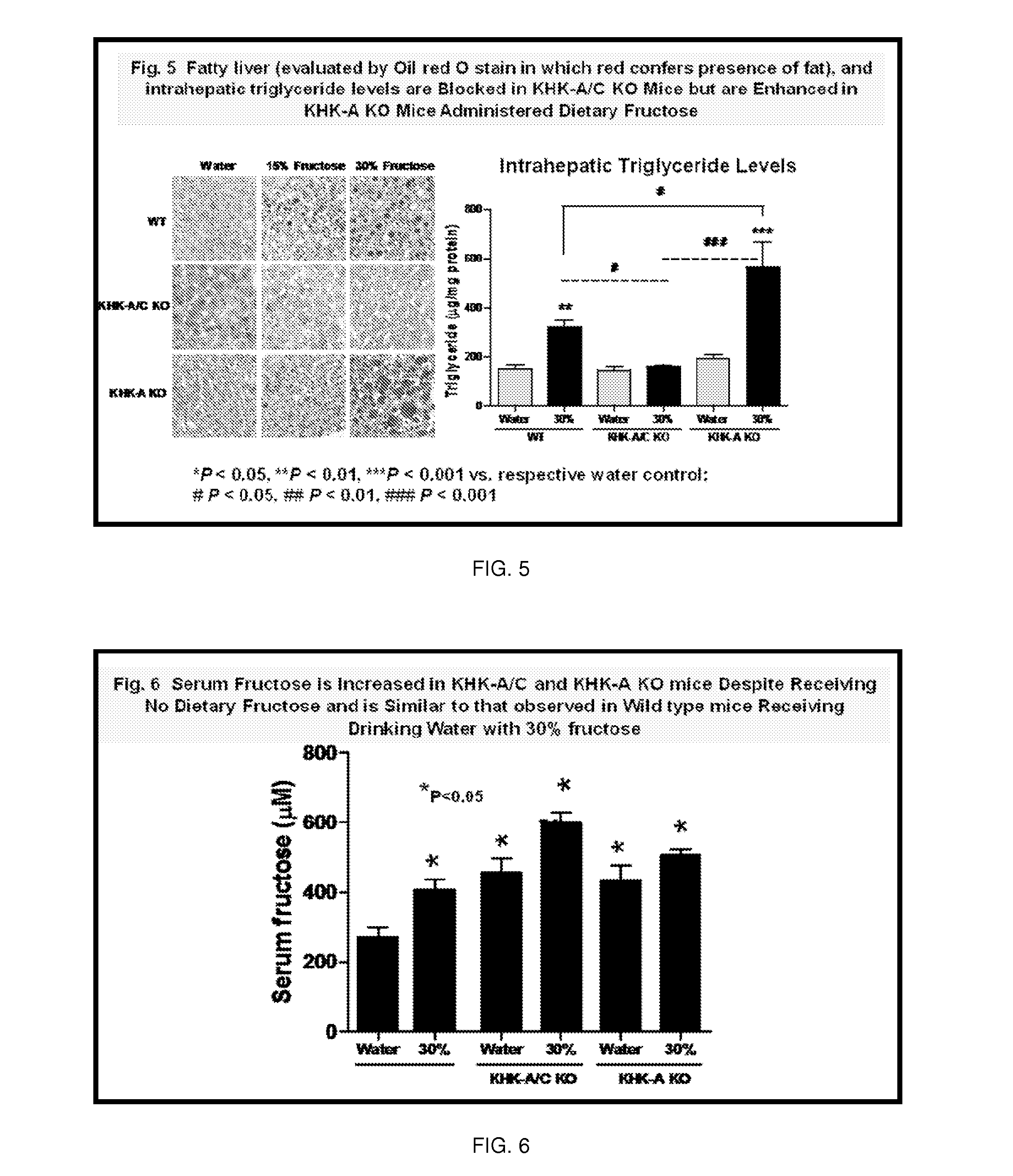
Methods for fructokinase mediation of alcohol craving and alcohol induced liver disease
PendingUS20210275494A1Induce toxicityStimulate dopamineNervous disorderDigestive systemFatty liverAlcohol
The invention relates to the use of one or more fructokinase (ketohexokinase) (KHK) inhibitors to both prevent and treat a wide variety of diseases including, but not limited to, alcohol craving, alcohol addiction, alcohol induced liver disease including fatty liver and cirrhosis.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
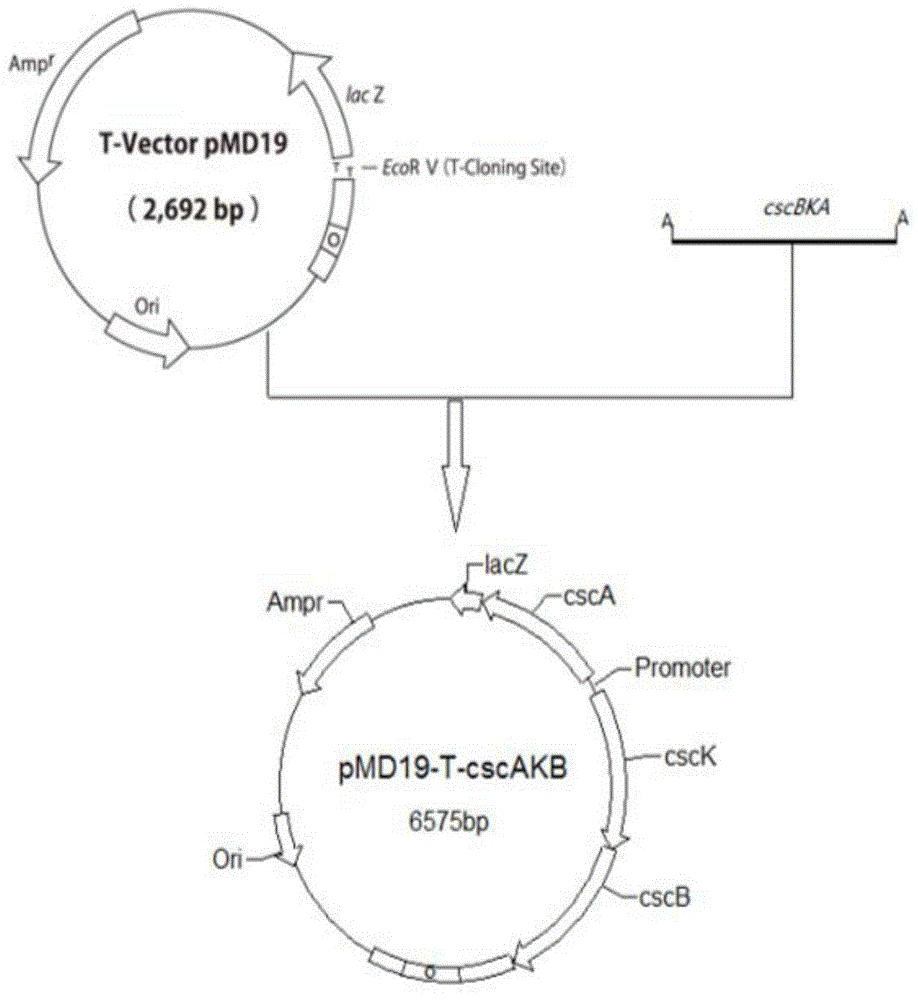
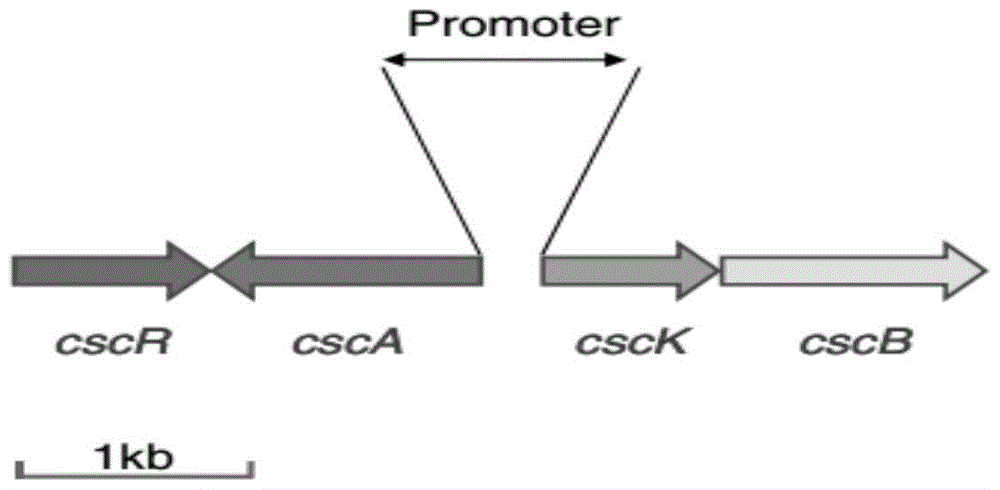
Method for producing lactic acid from plant-derived raw material, and lactic-acid-producing bacterium
ActiveUS8679800B2Short timeImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliSucrose hydrolysis
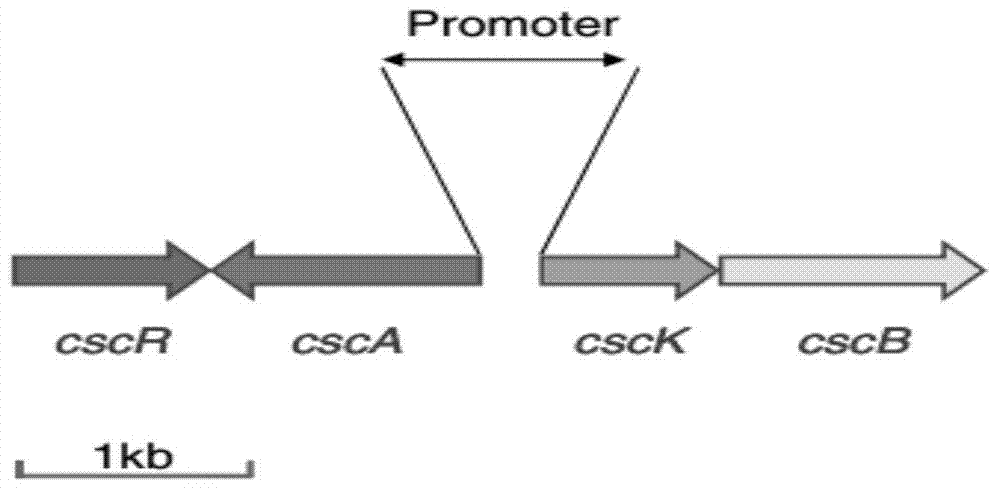
The present invention provides: a lactic acid-producing Escherichia coli comprising at least one gene of a sucrose non-PTS gene group, including at least a sucrose hydrolase gene, provided that a combination of a repressor protein (cscR), a sucrose hydrolase (cscA), a fructokinase (cscK) and a sucrose permease (cscB) and a combination of a sucrose hydrolase (cscA), a fructokinase (cscK) and a sucrose permease (cscB) are excluded, wherein the lactic acid-producing Escherichia coli comprises a lactic acid production enhancing system provided by genetic recombination; and a lactic acid production method including producing lactic acid from a plant-derived sucrose-containing raw material by using the lactic acid-producing Escherichia coli.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Process for producing D-mannitol
InactiveUS8338147B2100% yield of mannitol from fructoseEfficient, robust production processBacteriaFermentationHigh concentrationProduction rate
High concentration of free cells of heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in a resting or slowly growing state are used to convert fructose into mannitol. Efficient volumetric mannitol productivities and mannitol yields from fructose are achieved in a process applying cell-recycle, continuous stirred tank reactor and / or circulation techniques with native LAB cells or with LAB cells with inactivated fructokinase gene(s). Mannitol is recovered in high yield and purity with the aid of evaporation and cooling crystallization.
Owner:ZUCHEM
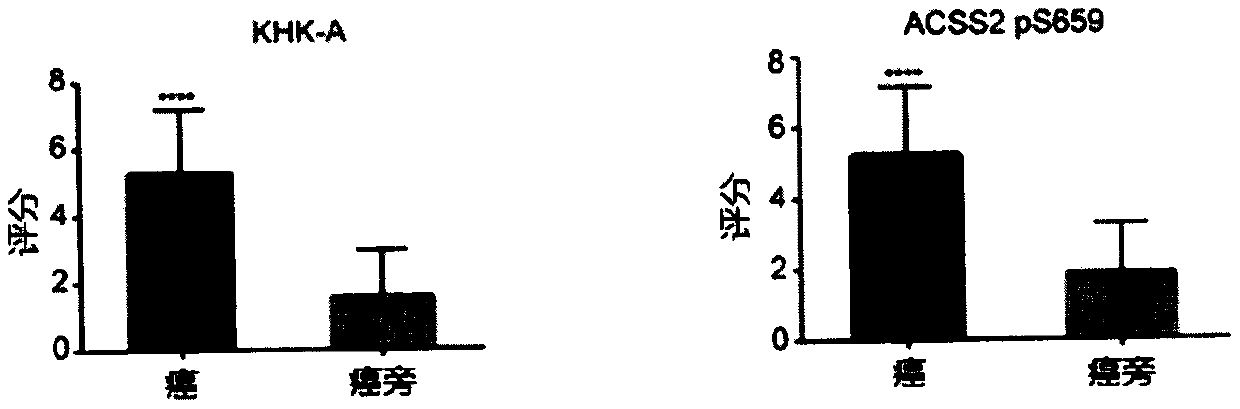
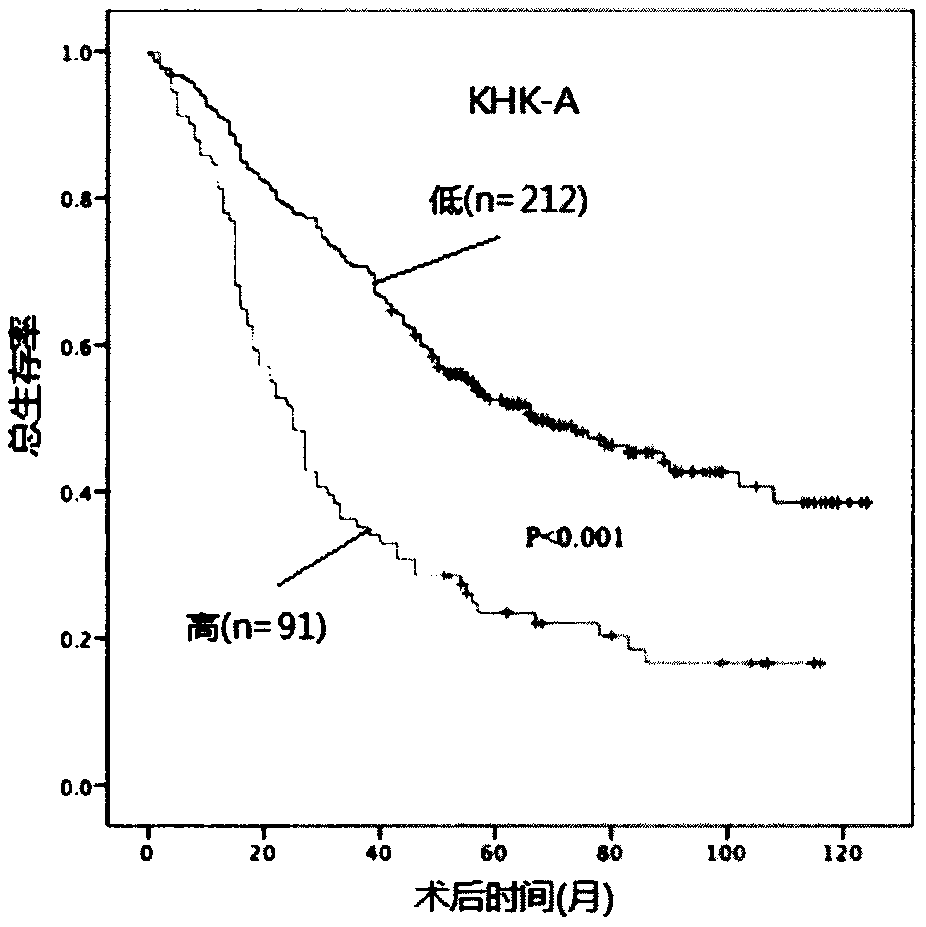
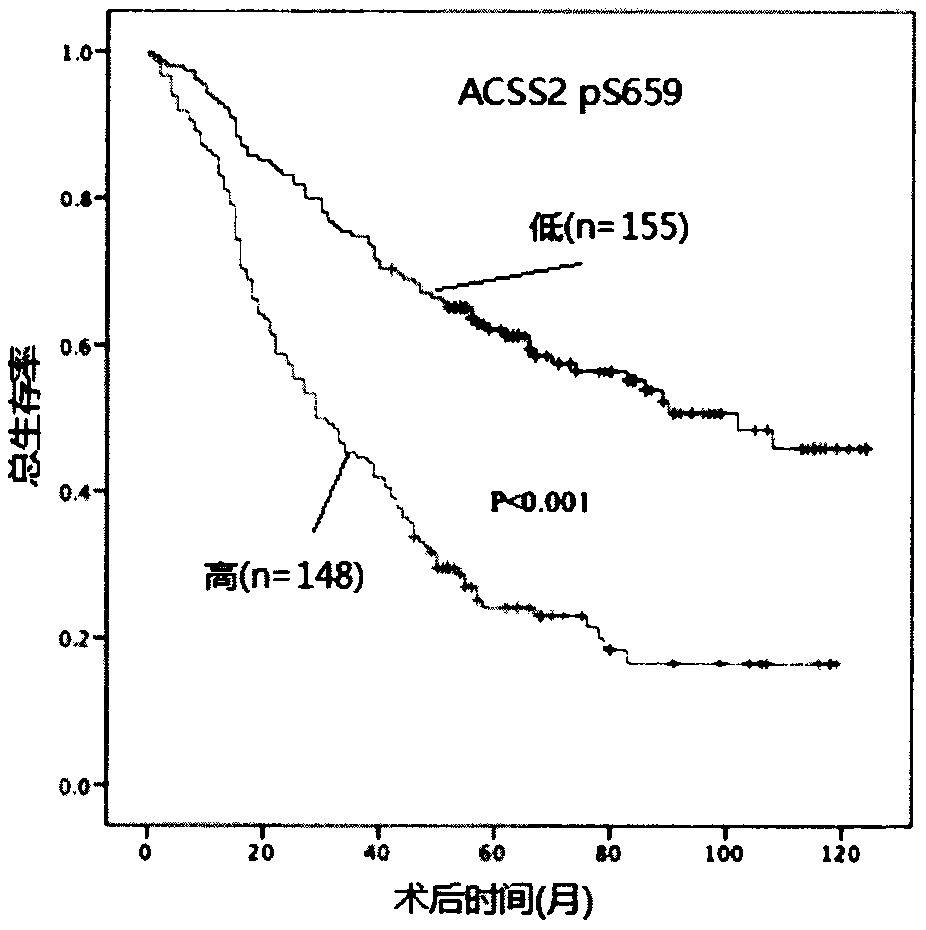
Prognostic prediction method for non-small cell lung cancer
The invention provides a prognostic prediction method for a non-small cell lung cancer. The prognostic prediction method comprises the step of detecting phosphorylation levels of fructokinase A and anS659 site of acetyl-coenzyme A synthase kinase 2 of a cancer cell. According to the prognostic prediction method, the phosphorylation expression levels of the fructokinase A and / or the S659 site of the acetyl-coenzyme A synthase kinase 2 are detected through an immunohistochemical technique on the basis of phosphorylation of the fructokinase A and / or the S659 site of the acetyl-coenzyme A synthase kinase 2, and the survival time of the non-small cell lung cancer is independently predicted.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
A composite native microbial domestication enzyme for efficiently improving urban black and odorous water bodies and a method for treating urban black and odorous water bodies
ActiveCN111073869BTo promote metabolismEasy to removeMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyGlycerate kinase
The invention discloses a composite native microorganism domestication enzyme for efficiently improving urban black and odorous water bodies and a method for treating urban black and odorous water bodies. The composite native microorganism domestication enzyme includes acetyl CoA acyltransferase, 1-phosphofructokinase and pyruvate phospho-dikinase. , β-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, 3-phosphoglycerate kinase, NAD-dependent β-hydroxybutyl-CoA dehydrogenase and thiolase. A method for treating urban black and odorous water bodies includes the following steps: preparing and activating compound native microorganism domestication enzymes; putting the activated compound native microorganism domestication enzymes in black and smelly water bodies for a period of time; and then constructing aquatic plants. The composite indigenous microbial domestication enzyme of the present invention has the advantages of efficiently improving the quality of black and odorous sewage; in addition, the treatment method of the present invention has the advantages of efficiently purifying the water body, and sustainably adjusting and optimizing the water body environment.
Owner:北京京阳环保工程有限公司
Fructokinase-disabled cyanobacteria and application thereof in secretion and production of fructose
The invention relates to application of a cyanobacteria fructokinase inactivating agent in preparation of cyanobacteria with fructose secretion capability and high fructose yield, and further relates to a reagent for knocking out a fructokinase gene corresponding to fructokinase in the cyanobacteria or a fructokinase function antagonist. The invention also relates to the fructokinase-disabled cyanobacteria and application of the fructokinase-disabled cyanobacteria in fructose production. According to the invention, fructokinase in a carbon circulation path of cyanobacteria is knocked out, a mutant strain accidentally obtains the capacity of mass production of fructose and secretion of fructose out of cells, the fructose yield is increased by hundreds of times, and the possibility is provided for subsequent industrial production of fructose by using cyanobacteria; and a foundation is provided for further metabolic engineering modification by taking cyanobacteria as a chassis algal strain.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
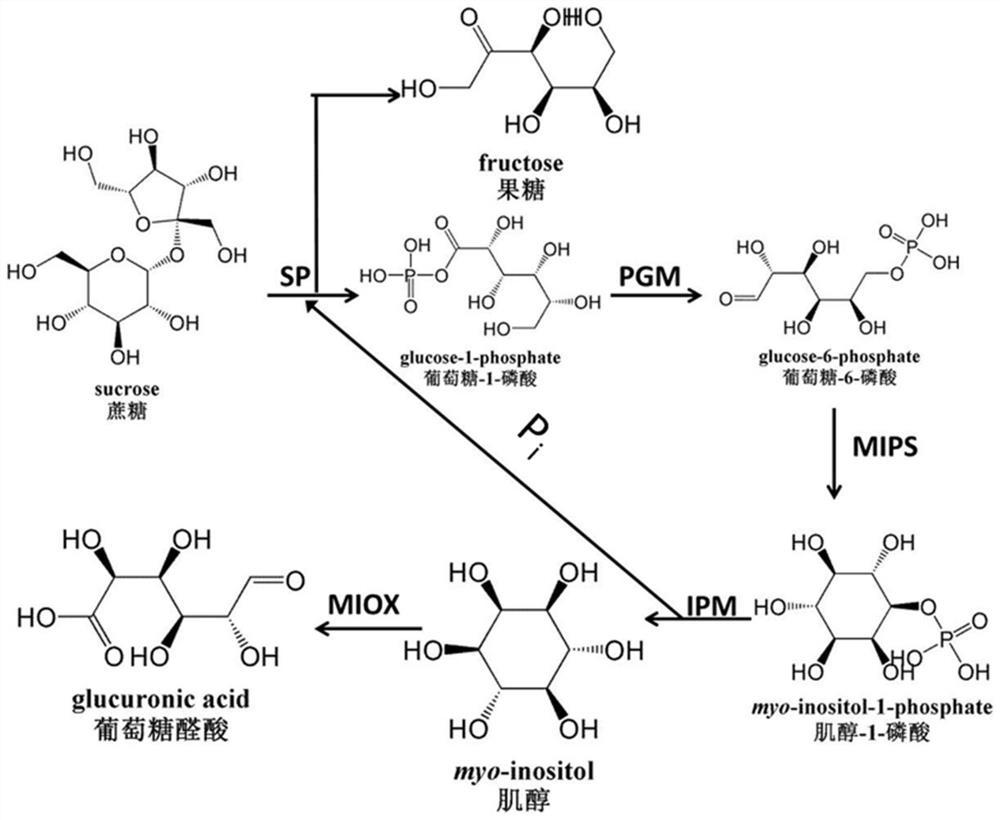
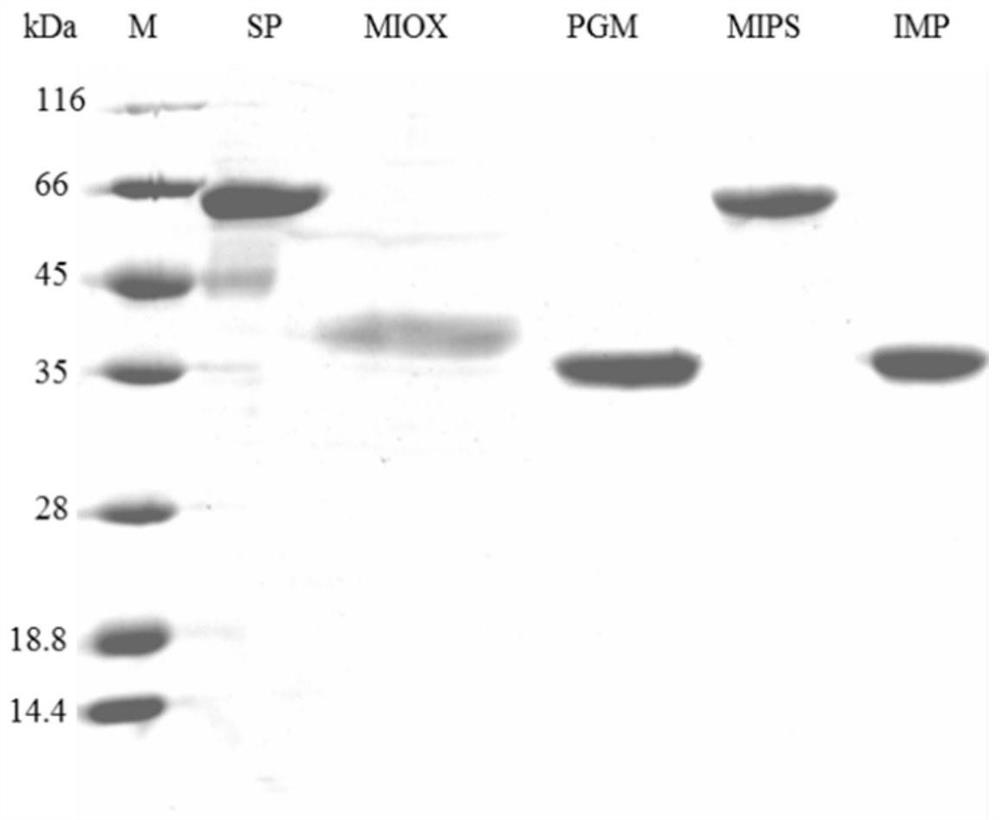
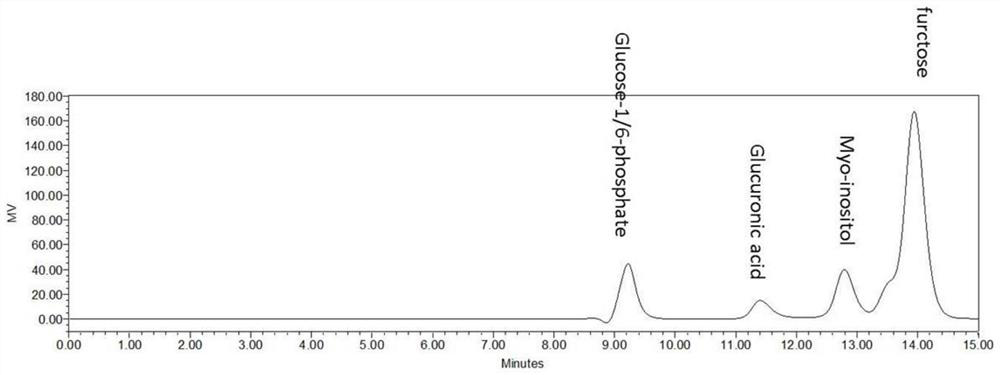
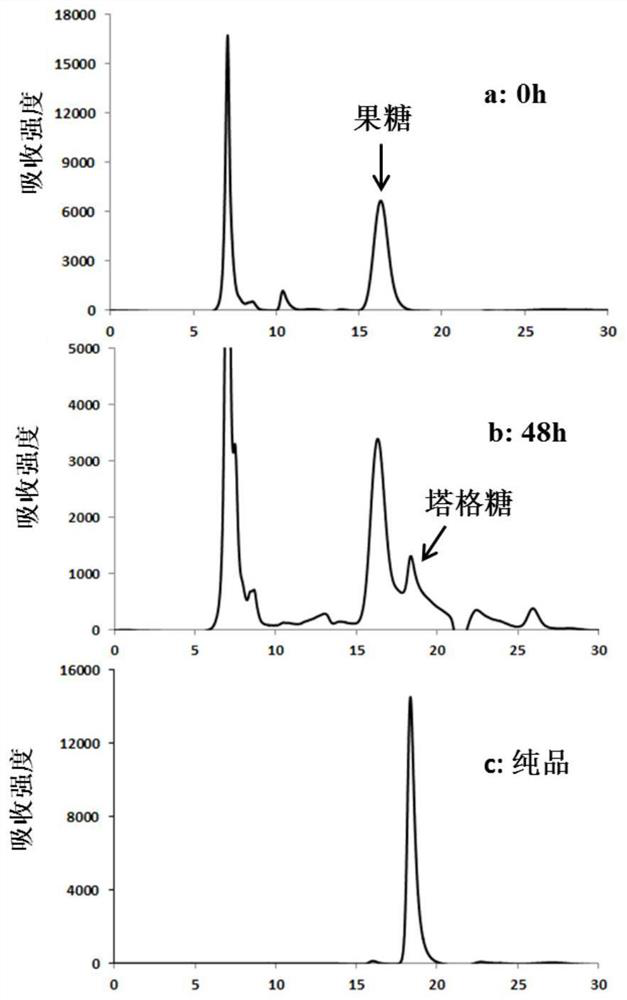
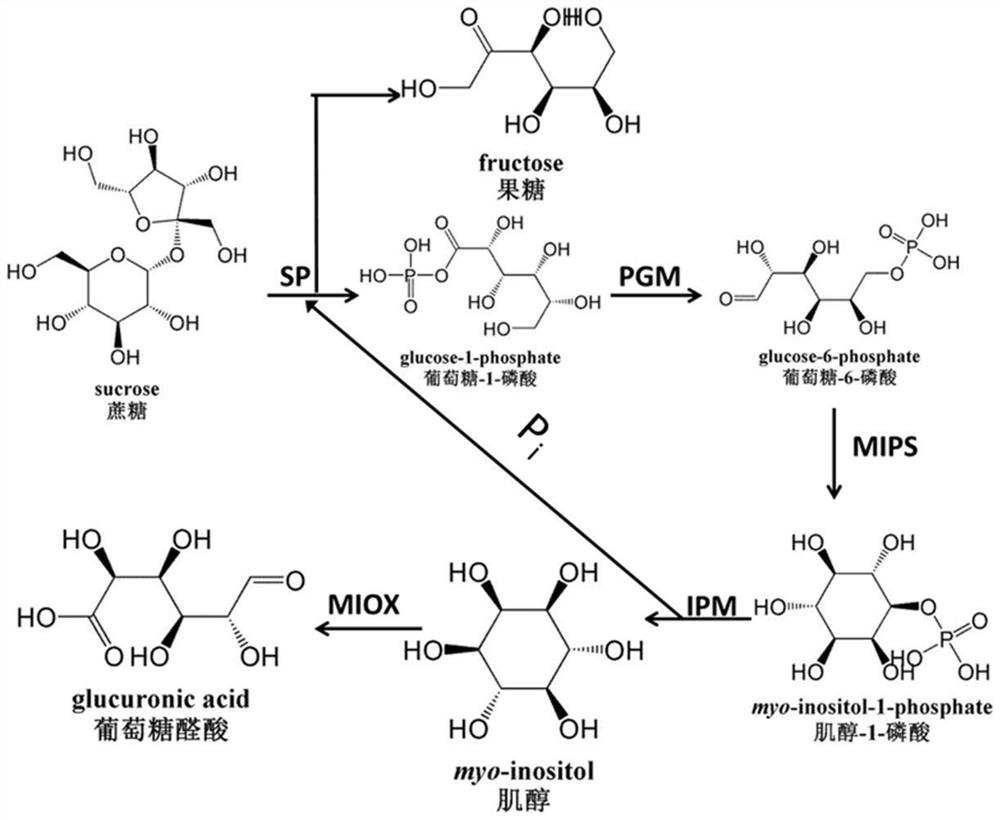
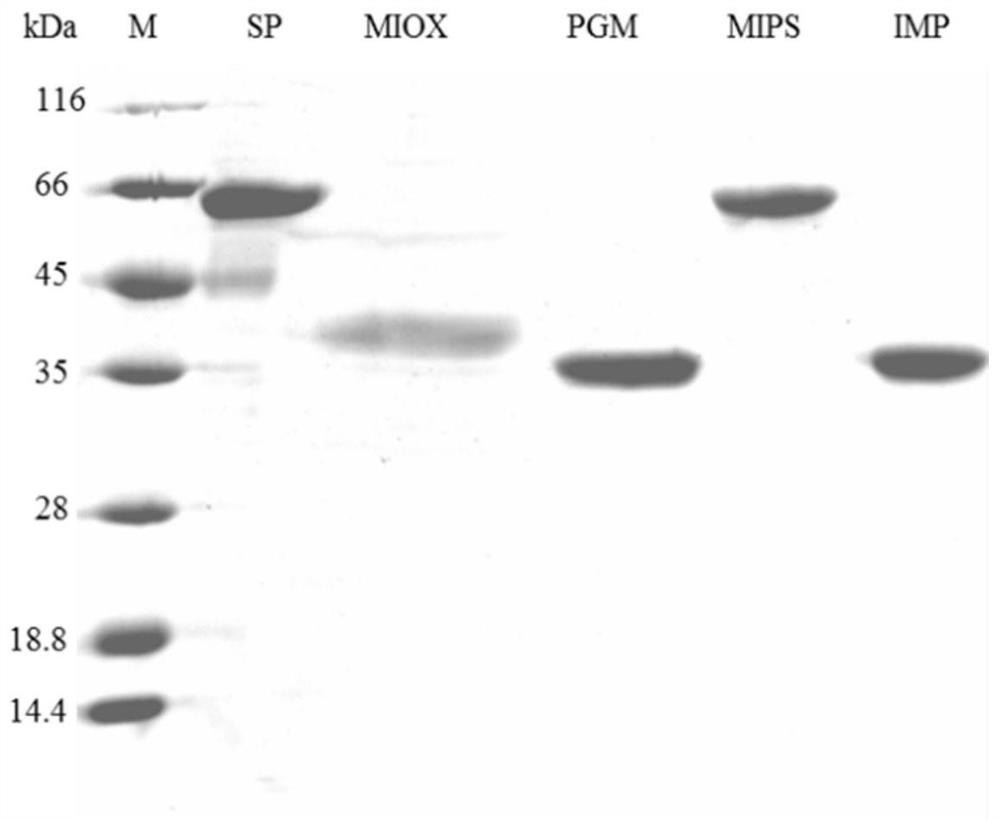
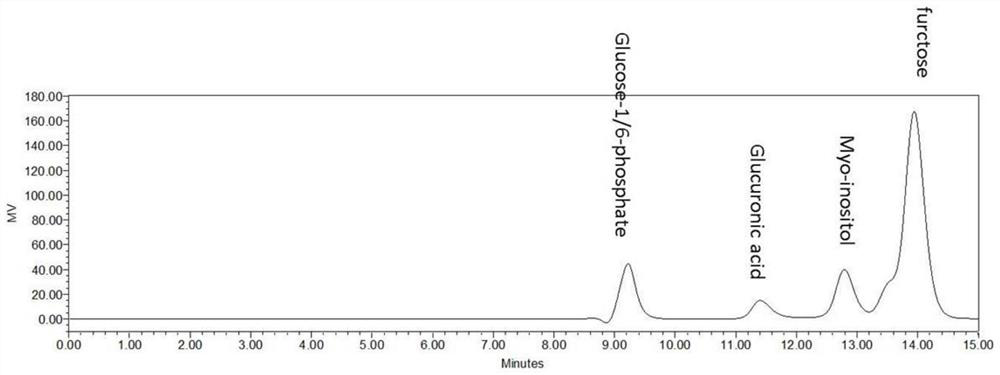
A method for biocatalytic synthesis of d-(+)-glucuronic acid and its application
ActiveCN111909973BHigh yieldReduce separation costsFermentationSucrose phosphorylaseInositol monophosphatase
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining ammonia (ammonia ion) and ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis/determination kit
InactiveCN102539712AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAssayKinase
The invention relates to a method for determining ammonia (ammonia ion) content by utilizing an enzymatic colorimetric method and enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay and composition and components of a reagent for determining ammonia (ammonia ion) content. The technical principle of the method is as follow: determination is completed based on serial catalytic reactions of ammonia kinase, fructokinase and fructose dehydrogenase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / determination kit. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity and few errors; therefore the method and the kit can be widely applied to clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Use of fructokinases and sucrose synthases for increasing cell wall polymers
InactiveUS20150322450A1High expressionIncrease synthesisTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesCell wallTransgene
The invention relates to transgenic plants exhibiting increased cell wall content. In one embodiment, transgenic plants engineered to over-express fructokinase (FRK) or both FRK and sucrose synthase (SuSy) are provided. The FRK+SuSy double-transgenic plants of the invention consistently exhibit enhanced cell wall polymer deposition.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Recombinant microorganism capable of efficiently utilizing methanol and application thereof
PendingCN114134092AIncrease biomassReduce accumulationBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and biological fermentation, and particularly discloses a recombinant microorganism capable of efficiently utilizing methanol and application of the recombinant microorganism. The invention provides a recombinant microorganism which has increased expression and / or enzymatic activity of methanol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone synthetase and reduced expression quantity of a formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB and expression and / or enzymatic activity of 6-phosphofructokinase compared with an original strain, and the recombinant microorganism has the advantages that the expression quantity of the methanol dehydrogenase and the dihydroxyacetone synthetase is increased, and the expression quantity of the formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB and the expression quantity of 6-phosphofructokinase are reduced; the starting strain is escherichia coli. Specifically, after a formaldehyde dissimilatory gene frmAB, a 6-phosphofructokinase gene pfkAB and an alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene sucA are knocked out at the same time, and a 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase gene gapA is inhibited, the utilization rate of methanol can be further improved, and accumulation of intermediate formaldehyde is reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Corynebacterium sp. transformed with a fructokinase gene derived from escherichia sp. and process for preparing l-amino acid using the same
ActiveUS20140099680A1Prevent unnecessary energy consumptionCost effective productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliCorynebacterium efficiens
The present invention relates to Corynebacterium sp. that is transformed with an Escherichia sp.-derived fructokinase gene to express fructokinase showing a sufficient activity of converting fructose into fructose-6-phosphate, thereby preventing unnecessary energy consumption, and a method for producing L-amino acids using the strain. The transformed Corynebacterium sp. of the present invention is able to express fructokinase from the Escherichia-derived fructokinase gene to prevent unnecessary energy consumption during fructose metabolism, leading to more cost-effective production of L-amino acids. Therefore, it can be widely used for the effective production of L-amino acids.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
An engineering strain producing tagatose, its construction method and application
ActiveCN109666620BHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionBacteriaTransferasesTagatosePhosphorylation
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Ammonia (ammonia ion) determination method and ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis/determination kit
InactiveCN102466701AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAmmoniaMannitol 2-Dehydrogenase
The invention relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) content determination method employing an enzymatic colorimetric method and an enzyme-linked technology. The invention also relates to the composition and components of a reagent. The technological principle of the determination is that: the determination is achieved with a series of catalytic reactions of ammonia kinase, ketohexokinase fructokinase and mannitol 2-dehydrogenase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / determination kit. The determination method provided by the invention is advantaged in high sensitivity and low error. Therefore, the determination method and the kit provided by the invention can be widely applied in clinical medicine / food examination.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for biocatalytically synthesizing D-(+)-glucuronic acid and application of method
The invention discloses a method for biocatalytically synthesizing D-(+)-glucuronic acid and an application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: by taking cane sugar as a substrate, adding enzyme to perform a catalytic reaction to obtain D-(+)-glucuronic acid, wherein the enzyme comprises sucrose phosphorylase, phosphoglucose mutase, inositol-1-phosphate synthase, inositol monophosphate esterase and inositol oxidase. The enzyme catalysis system can obtain a very high conversion rate. In addition, phosphate, phosphofructokinase and phosphoglucose isomerase are added into thereaction system, the conversion rate of the D-(+)-glucuronic acid can be further improved. The method is high in raw material utilization rate, high in D-(+)-glucuronic acid conversion rate, simple in step, low in production cost, small in pollution, small in environmental influence and capable of achieving large-scale production of D-(+)-glucuronic acid.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Corynebacterium sp. transformed with a fructokinase gene derived from Escherichia sp. and process for preparing L-amino acid using the same
ActiveUS9267161B2Prevent unnecessary energy consumptionCost effective productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliFructose metabolism
The present invention relates to Corynebacterium sp. that is transformed with an Escherichia sp.-derived fructokinase gene to express fructokinase showing a sufficient activity of converting fructose into fructose-6-phosphate, thereby preventing unnecessary energy consumption, and a method for producing L-amino acids using the strain. The transformed Corynebacterium sp. of the present invention is able to express fructokinase from the Escherichia-derived fructokinase gene to prevent unnecessary energy consumption during fructose metabolism, leading to more cost-effective production of L-amino acids. Therefore, it can be widely used for the effective production of L-amino acids.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for producing lactic acid from plant-derived raw material, and lactic-acid-producing bacterium
ActiveCN102333859AEfficient productionBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliSaccharophagus degradans
Disclosed is a lactic-acid-producing Escherichia coli which has at least one gene including at least a sucrose hydrolase gene and selected from sucrose non-PTS genes (provided that a combination of a repressor protein (cscR), a sucrose hydrolase (cscA), a fructokinase (cscK) and a sucrose permease (cscB) and a combination of a sucrose hydrolase (cscA), a fructokinase (cscK) and a sucrose permease (cscB) are excluded) and is genetically so modified as to have a system for enhancing the production of lactic acid. Also disclosed is a method for producing lactic acid from a plant-derived sucrose-containing raw material by using the lactic-acid-producing Escherichia coli.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com