A reducing ion exchange membrane for treating waste water containing precious/heavy metals and recovering high-purity metal elements, and its method and application
A technology of ion exchange membrane and metal element, which is applied in the field of heavy metal treatment, can solve the problems of unrecoverable metal element recovery, difficulty in metal element recovery, limited capacity of adsorption method, etc., and achieve effective removal/recovery of metal, high metal removal/recovery Efficiency, Ease of Scale Production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A reductive ion exchange technology for treating precious / heavy metal wastewater and recovering high-purity metal elements, comprising the following steps:
[0067] (1) With 0.6mol / L CH 3 COONa solution was used as electrolyte, reducing ion exchange membrane was used as working electrode, RuO 2 / IrO 2 The coated Ti mesh electrode was used as the counter electrode, the Ag / AgCl electrode was used as the reference electrode, and -10mA / cm was applied to the working electrode 2 The current is charged with sodium;
[0068] (2) Immerse the reducing ion exchange membrane filled with sodium into 0.1mol / L AgNO 3 Let it stand in the solution for 1 minute, then take it out with tweezers;
[0069] (3) again in CH 3 COONa solution was filled with sodium, then immersed in 0.1mol / L AgNO 3 Stand still in the solution for 1 minute, and circulate like this 10 times, and finally blow dry with nitrogen to obtain a reducing ion exchange membrane with simple Ag attached to the surface. ...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Step is the same as embodiment 1, and difference is the AgNO in step (2) and (3) 3 The solution was changed to Cu(NO 3 ) 2 solution.
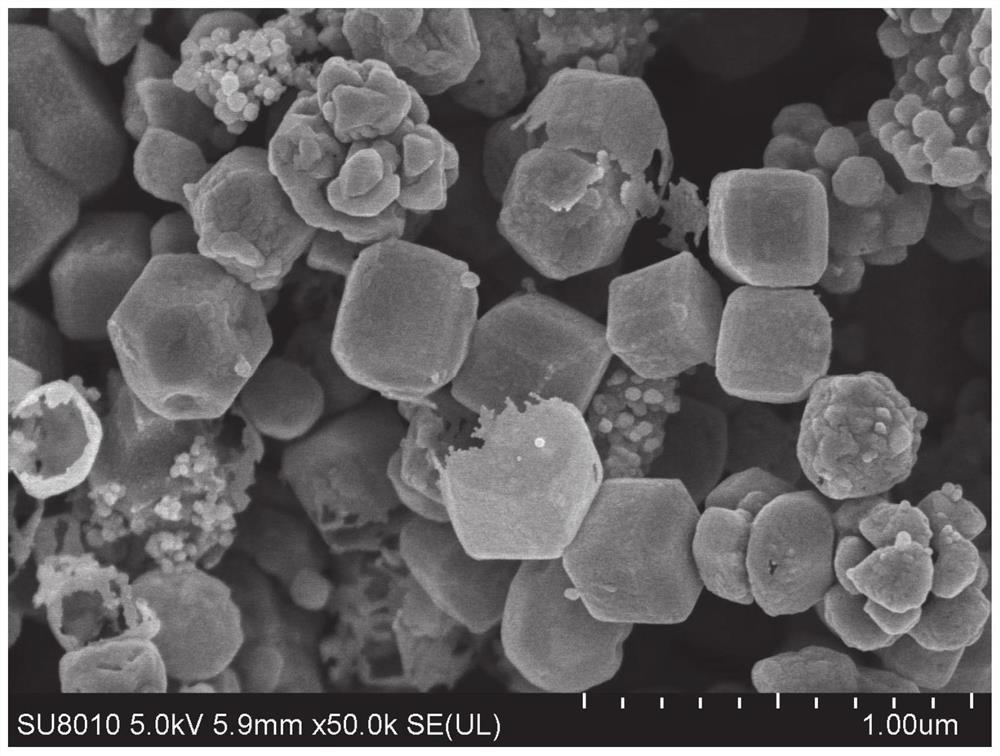
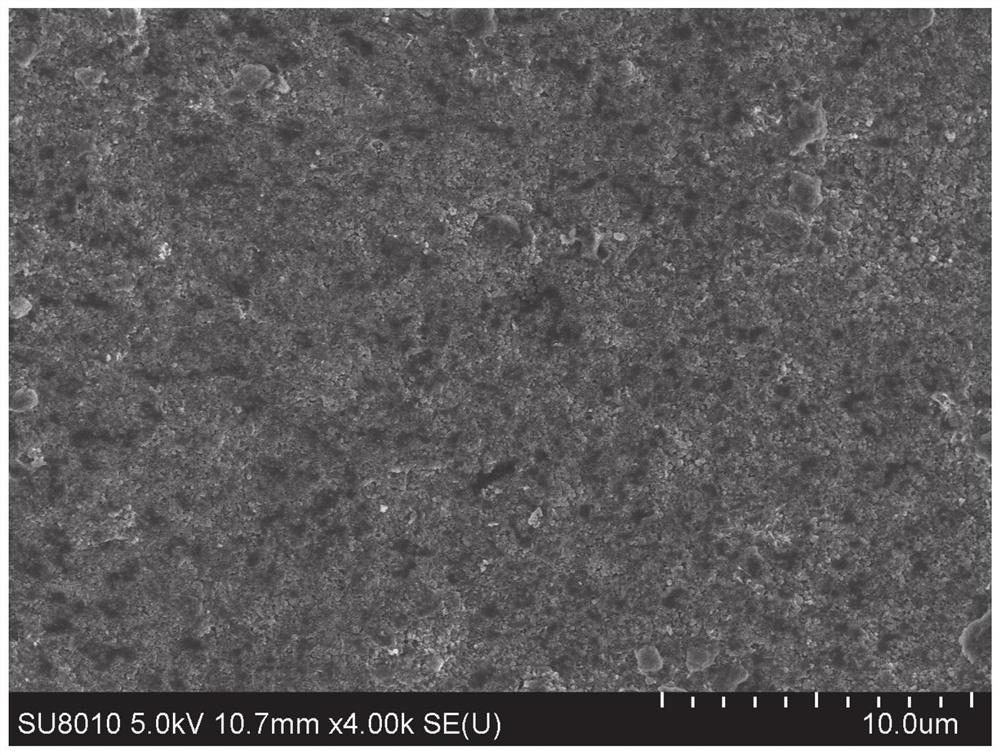
[0084] Figure 6 It is the SEM photo of the surface of the reducing ion exchange membrane after reducing Cu, and the granular Cu element can be observed.
[0085] Figure 7 It is the XRD spectrum of the reducing ion exchange membrane after reducing Cu. The diffraction peak shape is sharp and there are no other impurity peaks. It matches the standard card of Cu, confirming that the surface of the membrane is reduced to Cu simple substance.
[0086] Figure 8 It is the element distribution on the surface of the reducing ion exchange membrane after reducing Cu, and the contrast between the granular Cu element and the membrane background is obvious.
Embodiment 3
[0088] Step is the same as embodiment 1, and difference is the AgNO in step (2) and (3) 3 The solution was changed to Pb(NO 3 ) 2 solution.
[0089] Figure 9 It is the SEM photograph of the surface of the reducing ion exchange membrane after Pb is reduced, and block-shaped Pb element can be observed.
[0090] Figure 10 It is the XRD spectrum of the reducing ion exchange membrane after reducing Pb. The diffraction peak shape is sharp and there are no other miscellaneous peaks, which matches the standard card of Pb, confirming that the surface of the membrane is reduced to Pb elemental substance.
[0091] Figure 11 is the element distribution on the surface of the reducing ion exchange membrane after reducing Pb, and the Pb element is uniformly distributed on the block particles, indicating that the block particles are the reduced Pb element.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com