Fluorescent probe targeting CKIP-1 and used for detecting osteoporosis and application of fluorescent probe in in-vivo detection
A technology for CKIP-1, osteoporosis, applied in the direction of analysis, application, diagnostic recording/measurement using fluorescence emission, which can solve the lack of biomarkers or indicators, and the inability to monitor bone density or osteoporosis status in living animals and other problems, to achieve the effect of fast detection speed, high sensitivity and simple operation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
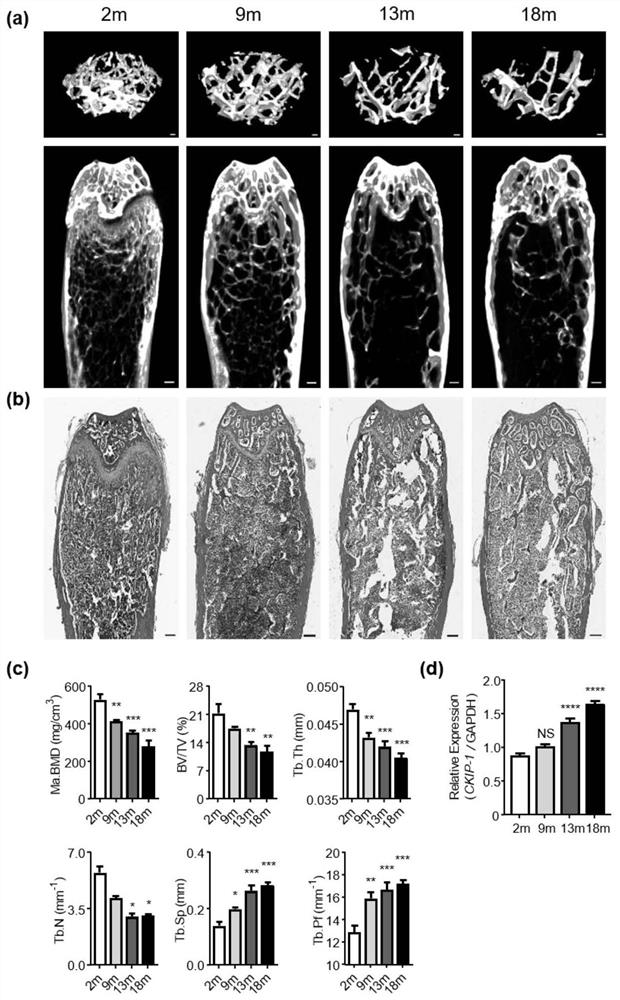
[0051] Example 1, Correlation between CKIP-1mRNA expression and osteoporosis
[0052] 1. To construct an aging osteoporosis model, use C57BL / 6J male mice (n=5 / group) of different ages (9m, 13m and 18m), and use 2m mice as a control group (n=5).
[0053] 2. To construct a postmenopausal osteoporosis model, C57BL / 6J female mice (20) were sham-operated (sham) or ovariectomized (OVX) at the age of 4 months, and raised under the same feeding conditions for 8 weeks, specifically The surgical operation is as follows: After the mice were weighed and anesthetized successfully, the ovaries were removed and placed in a dirt tray. After complete hemostasis was confirmed, the tissue was also brought into the abdominal cavity. Subsequently, the same operation was performed at the corresponding position on the contralateral side, and the right ovary of the mouse was excised, and finally disinfected with iodophor. Sham-operated group: After exposing the bilateral ovaries, no resection was p...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2, preparation and detection of near-infrared fluorescent probes based on CKIP-1
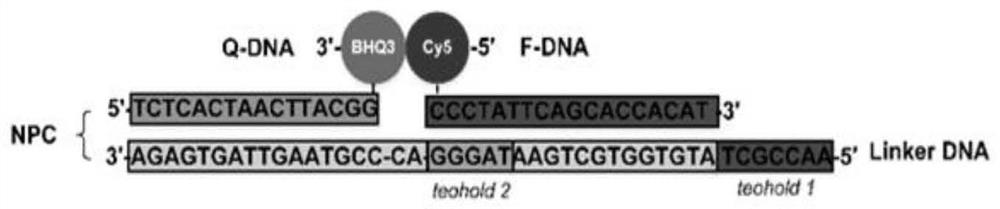
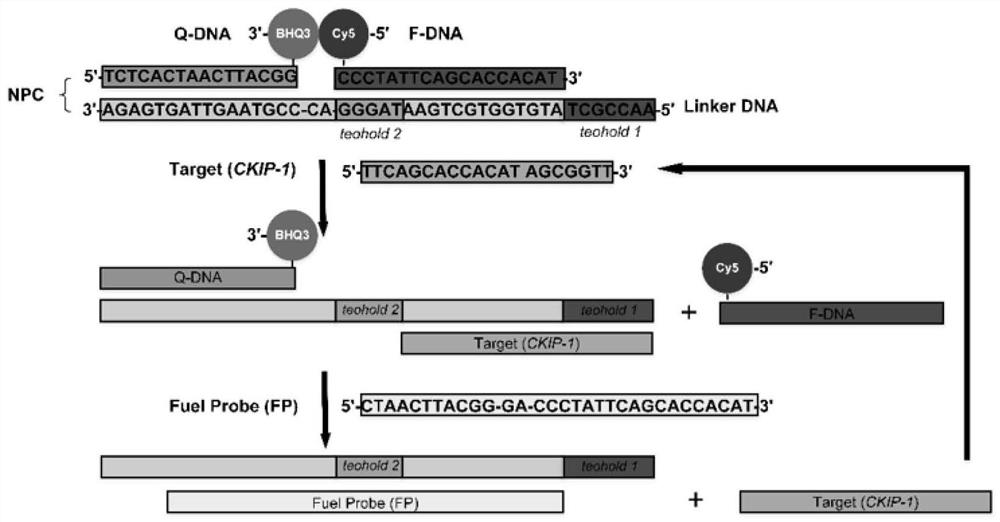
[0075] 1. Mix 50μL Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.4, 10mM MgCl2), 20μL Linker DNA strand (100μM), 20μL Q-DNA strand (100μM) and 10μL F-DNA strand (100μM) in a PCR tube, and incubate at 95°C 10 minutes, and then lower the temperature to 37°C with a gradient of 0.1°C / s. The formed Linker / F / Q double chain structure was determined by UV spectrophotometer. Then the probe is further mixed with the fuel chain, the mixing molar ratio is 1:5, and 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was incubated at room temperature for 30 min to complete the preparation of the probe system.
[0076] When the probe is used for live cell detection, the preparation system and steps are as follows: Lipofectamine TM 3000 Reagent 6μl and Opti-MEM TM Mix 100 μl of culture medium (solution A), probe (5 μg / μl) 8 μl, P3000 TM Reagent 16 μl and Opti-MEM TM Mix 100 μl of medium (solution B), incubate at room temperatur...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3. Fluorescence imaging of CKIP-1-based near-infrared fluorescent probes in living cells and in vivo fluorescence imaging of mice
[0090] 1. Inoculate the mouse macrophage precursor cell line RAW264.7 cells in a confocal culture dish, add 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 μg / mL) and streptomycin (100 μg / mL) in DMEM medium , after culturing at 37°C under 5% carbon dioxide for 24 hours, replace the complete medium with the probe-containing culture solution and immediately place the culture dish in a live cell imaging system to monitor the changes of the probe in the cells for 22 hours. 1.5h after adding the probe, the cells began to show near-infrared fluorescence, reached the peak fluorescence signal at 6h, and then gradually decreased, see Figure 8 (a)-(b). In contrast, there was no activation probe in MC3T3-E1 cells with very low background CKIP-1 expression, see Figure 8 (c), indicating its high selectivity.
[0091] 2. After injecting the near-inf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com