Plastic crystal-ceramic composite solid electrolyte and low-temperature hot-pressing preparation method thereof
A solid electrolyte and ceramic composite technology, which is applied in the manufacture of electrolyte batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of consumption of solid electrolyte powder, interdiffusion of elements, increase of interface impedance, etc., to avoid elements Effects of interdiffusion and side reactions, high ionic conductivity, and reduced grain boundary resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] The invention provides a method for preparing a plastic crystal-ceramic composite solid electrolyte at low temperature by hot pressing, comprising the following steps:
[0032] Step 1, weighing oxide ceramic powder and plastic crystal solid electrolyte, and mixing them uniformly to obtain a mixed powder; the plastic crystal solid electrolyte includes: plastic crystal and lithium salt;
[0033] Step 2, placing the mixed powder in a mold and paving;
[0034] Step 3, compressing the mixed powder, and at the same time, heat-treating the mixed powder, the heating temperature is lower than 600°C, so that the plastic crystal solid electrolyte absorbs heat and melts; then lower the temperature, the plastic crystal The solid electrolyte is solidified and formed to obtain the plastic crystal-ceramic composite solid electrolyte.
[0035] The mass fraction of the oxide ceramic powder of the present invention in the mixed powder is 30-100%, preferably 60-94%. The mass fraction of ...
Embodiment 1
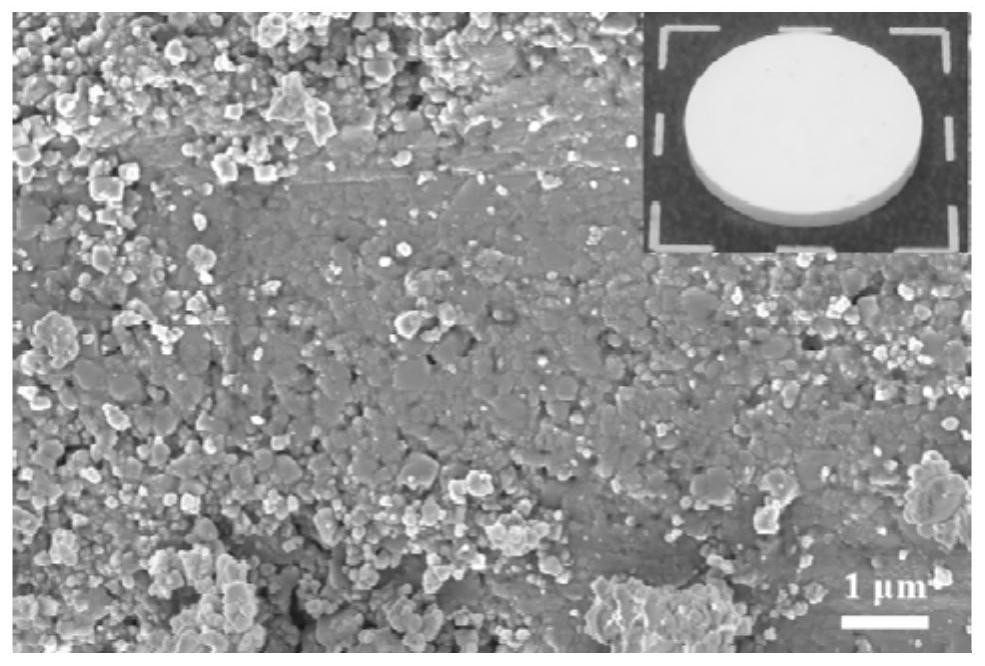
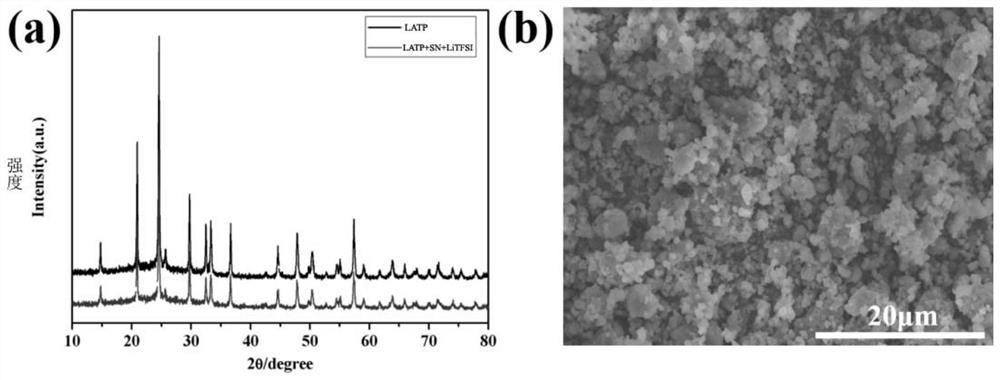
[0042] Weigh CH by stoichiometric ratio 3 COOLi, Al(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O, (C 4 h 9 O) 4 Ti and 85wt%H 3 PO 4(inwater), CH 3 COOLi excess 5mol%. (C 4 h 9 O) 4 Ti was dropped into deionized water for hydrolysis, and then centrifuged to obtain a white precipitate, which was dissolved in 2M oxalic acid solution at 60°C to obtain a colorless and transparent solution. The rest of the raw materials were added to the above colorless transparent solution, and after being fully dissolved, the water was evaporated to dryness at 80°C, and the obtained white precipitate was dried overnight in a blast oven at 80°C. The white precipitate was properly ground in an agate mortar, using absolute ethanol as a dispersant, ball-milled with a planetary ball mill at 450r / min for 12h, and then the dried powder was pre-calcined at 400°C for 2h. Subsequently, the calcined powder was ball-milled for 12 hours with a planetary ball mill at 400 r / min, also using absolute ethanol as a dispersant. Fi...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that during the low-temperature hot pressing process, the temperature of the press molding is changed to 140° C., and other conditions remain unchanged.
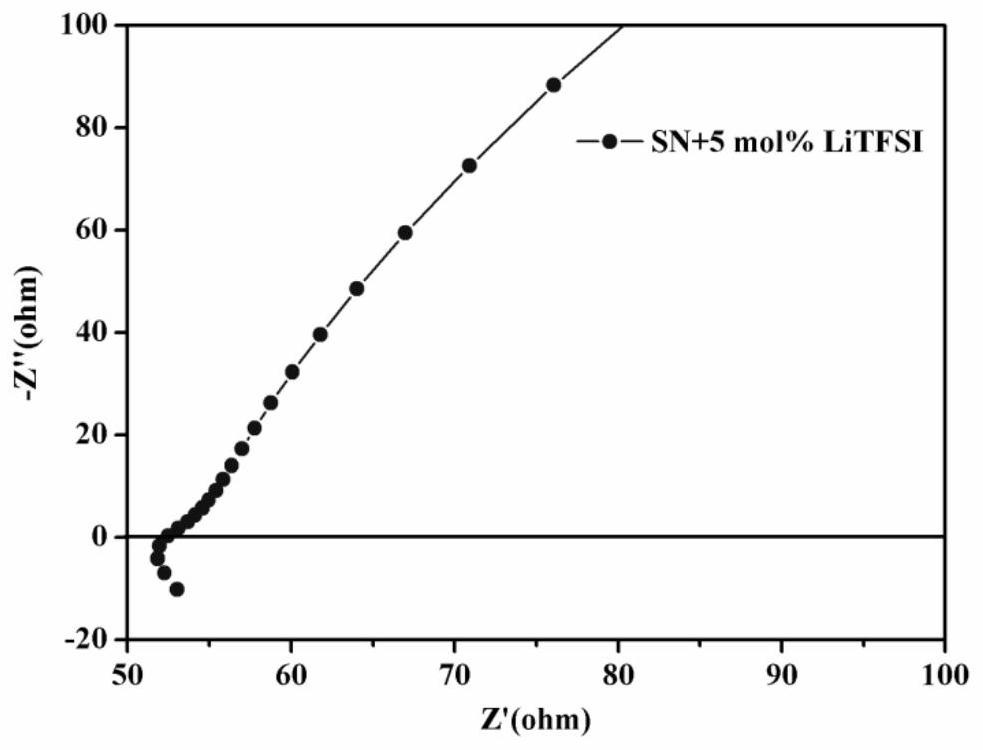
[0049] In Example 2 of the present invention, a plastic crystal-ceramic composite solid electrolyte 2 was prepared. Depend on Figure 4 with Figure 5 It can be seen that the ionic conductivity of plastic crystal-ceramic composite solid electrolyte 2 is 1.67×10 -4 S / cm, its relative density is 92.44%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com